|
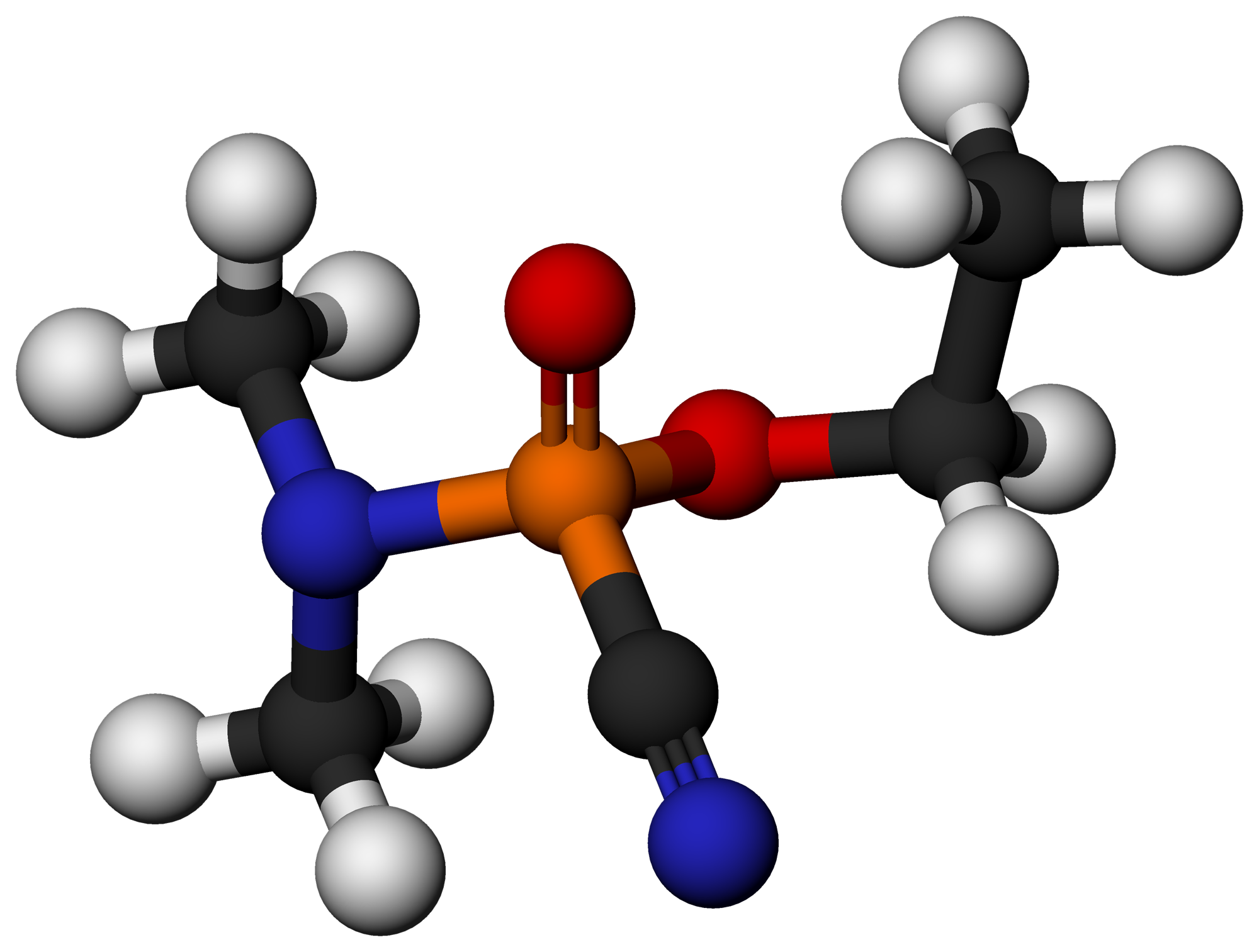
Thiosarin
Thiosarin, sulfursarin or GBS, is the organophosphorus compound analogous to sarin.U.S. Chemical Warfare Policy: Hearings, Ninety-third Congress, Second Session. May 1, 2, 7, 9 and 14, 1974. pg 341-344 It differs structurally in that sulfur replaces the oxygen of the P=O bond. It is an extremely toxic substance related to Nerve agent, G-agents.Ledgard, J. A Laboratory History of Chemical Warfare Agents. 171-174 Characteristics For thiosarin, unlike sarin, the literature contains little information. It is reported as a colorless liquid with a characteristic organosulfur odor when pure. It is estimated to have a boiling point of 144-167 °C. It is a more nonpolar compound, with a solubility in water of 7 g/L. Thiosarin probably belongs to the IVA compound series, leaving it much less volatile than sarin. It has a greater persistence in the environment than sarin. Absorption frequencies of sarin derivatives showed that the frequency of stretching of the P-F and P=S bond of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarin
Sarin (NATO designation GB G-series, "B"">Nerve_agent#G-series.html" ;"title="hort for Nerve agent#G-series">G-series, "B" is an extremely toxic synthetic organophosphorus compound.Sarin (GB) Emergency Response Safety and Health Database. National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health. Accessed April 20, 2009. A colourless, odourless , it is used as a due to its extreme potency as a . Exposure is lethal even at very low ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organophosphorus Compound
Organophosphorus compounds are organic compounds containing phosphorus. They are used primarily in pest control as an alternative to chlorinated hydrocarbons that persist in the environment. Some organophosphorus compounds are highly effective insecticides, although some are extremely toxic to humans, including sarin and VX nerve agents. Organophosphorus chemistry is the corresponding science of the properties and reactivity of organophosphorus compounds. Phosphorus, like nitrogen, is in group 15 of the periodic table, and thus phosphorus compounds and nitrogen compounds have many similar properties. The definition of organophosphorus compounds is variable, which can lead to confusion. In industrial and environmental chemistry, an organophosphorus compound need contain only an organic substituent, but need not have a direct phosphorus-carbon (P-C) bond. Thus a large proportion of pesticides (e.g., malathion), are often included in this class of compounds. Phosphorus can adopt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nerve Agent
Nerve agents, sometimes also called nerve gases, are a class of organic chemicals that disrupt the mechanisms by which nerves transfer messages to organs. The disruption is caused by the blocking of acetylcholinesterase (AChE), an enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter. Nerve agents are acetylcholinesterase inhibitors used as poison. Poisoning by a nerve agent leads to constriction of pupils, profuse salivation, convulsions, and involuntary urination and defecation, with the first symptoms appearing in seconds after exposure. Death by asphyxiation or cardiac arrest may follow in minutes due to the loss of the body's control over respiratory and other muscles. Some nerve agents are readily vaporized or aerosolized, and the primary portal of entry into the body is the respiratory system. Nerve agents can also be absorbed through the skin, requiring that those likely to be subjected to such agents wear a full body suit in addition to a respirator. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Warfare
Chemical warfare (CW) involves using the toxic properties of chemical substances as weapons. This type of warfare is distinct from nuclear warfare, biological warfare and radiological warfare, which together make up CBRN, the military acronym for chemical, biological, radiological, and nuclear (warfare or weapons), all of which are considered " weapons of mass destruction" (WMDs), a term that contrasts with conventional weapons. The use of chemical weapons is prohibited under customary international humanitarian law. Definition Chemical warfare is different from the use of conventional weapons or nuclear weapons because the destructive effects of chemical weapons are not primarily due to any explosive force. The offensive use of living organisms (such as anthrax) is considered biological warfare rather than chemical warfare; however, the use of nonliving toxic products produced by living organisms (e.g. toxins such as botulinum toxin, ricin, and saxitoxin) ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluorides
Fluoride (). According to this source, is a possible pronunciation in British English. is an inorganic, monatomic anion of fluorine, with the chemical formula (also written ), whose salts are typically white or colorless. Fluoride salts typically have distinctive bitter tastes, and are odorless. Its salts and minerals are important chemical reagents and industrial chemicals, mainly used in the production of hydrogen fluoride for fluorocarbons. Fluoride is classified as a weak base since it only partially associates in solution, but concentrated fluoride is corrosive and can attack the skin. Fluoride is the simplest fluorine anion. In terms of charge and size, the fluoride ion resembles the hydroxide ion. Fluoride ions occur on Earth in several minerals, particularly fluorite, but are present only in trace quantities in bodies of water in nature. Nomenclature Fluorides include compounds that contain ionic fluoride and those in which fluoride does not dissociate. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Degradation Of GBS
Degradation may refer to: Science * Degradation (geology), lowering of a fluvial surface by erosion * Degradation (telecommunications), of an electronic signal * Biodegradation of organic substances by living organisms * Environmental degradation in ecology * Land degradation, a process in which the value of the biophysical environment is affected by a combination of human-induced processes acting upon the land * Polymer degradation, as plastics age Other * Elegant degradation, gradual rather than sudden * Graceful degradation, in a fault-tolerant system * Degradation (knighthood), revocation of knighthood * Cashiering, whereby a military officer is dismissed for misconduct * Reduction in rank, whereby a military officer is reduced to a lower rank for misconduct * Degradation, the former ceremony of defrocking a disgraced priest * ''Degradation'', a song by the Violent Femmes, from '' Add It Up (1981–1993)'' See also * ''Dégradé ''Dégradé'' ( ar, ديچراد� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Sulfide
Hydrogen sulfide is a chemical compound with the formula . It is a colorless chalcogen-hydride gas, and is poisonous, corrosive, and flammable, with trace amounts in ambient atmosphere having a characteristic foul odor of rotten eggs. The underground mine gas term for foul-smelling hydrogen sulfide-rich gas mixtures is ''stinkdamp''. Swedish chemist Carl Wilhelm Scheele is credited with having discovered the chemical composition of purified hydrogen sulfide in 1777. The British English spelling of this compound is hydrogen sulphide, a spelling no longer recommended by the Royal Society of Chemistry or the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry. Hydrogen sulfide is toxic to humans and most other animals by inhibiting cellular respiration in a manner similar to hydrogen cyanide. When it is inhaled or it or its salts are ingested in high amounts, damage to organs occurs rapidly with symptoms ranging from breathing difficulties to convulsions and death. Despite this, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GBS Hydrolysis
GBS may refer to: People * Guillermo Barros Schelotto, Argentine footballer and coach * George Bernard Shaw, Irish playwright Education * Gandaki Boarding School, in Pokhara, Nepal * Glenbrook South High School, in Glenview, Illinois, US * Globsyn Business School, in Kolkata, India * Goethe Business School, Frankfurt, Germany * Gyeonggibuk Science High School, in Uijeongbu, South Korea Medicine * Glasgow-Blatchford score, a screening tool * Group B streptococcus * Guillain–Barré syndrome, a muscle weakness Technology * Game Boy Sound System, a file format * Geostationary balloon satellite * Global Broadcast Service, a United States military communications network * Gravity-based structure, a support structure * IBM Global Business Services Politics * ''Gabungan Bersatu Sabah'', a Sabah-based political parties coalition in Malaysia Other uses * Gbesi language * Genotyping by sequencing * Gifu Broadcasting System, in Japan * Goals breakdown structure, a hierarchic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nerve Agents
Nerve agents, sometimes also called nerve gases, are a class of organic chemistry, organic chemicals that disrupt the mechanisms by which nerves transfer messages to organs. The disruption is caused by the blocking of acetylcholinesterase (AChE), an enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter. Nerve agents are acetylcholinesterase inhibitors used as poison. Poisoning by a nerve agent leads to constriction of pupils, profuse salivation, convulsions, and involuntary urination and defecation, with the first symptoms appearing in seconds after exposure. Death by asphyxiation or cardiac arrest may follow in minutes due to the loss of the body's control over Respiration (physiology), respiratory and other muscles. Some nerve agents are readily vaporized or aerosolized, and the primary portal of entry into the body is the respiratory system. Nerve agents can also be absorbed through the skin, requiring that those likely to be subjected to such agents wear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
G-series Nerve Agents
G series may refer to: Transportation *G series (Toronto subway), a line of subway cars * Chevrolet G-series vans *G-series trains, the designation for the fastest long-distance trains in China *Infiniti G-series (Q40/Q60), a line of luxury sports cars *Nissan G engine, a series of engines produced in the 1960s *Series G, a series of Porsche 911 Other uses *G-Series (record label), a music label *ITU-T G Series, telecommunications systems recommendations for transmission systems and media, digital systems and networks *LG G series, a line of Android devices produced by LG Electronics * ''QI'' (G series), the seventh series of the TV quiz show ''QI'' *Sony Vaio G series, laptop computers *Sony Ericsson G series, a series of cell phones *The G series variety of Gatorade *Lumix G-series, cameras built by Panasonic; see Panasonic Lumix DMC-GF5 *G-series, a class of nerve agent See also *F series (other) *H series (other) H series may refer to: *H series (Toronto subwa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors
Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (AChEIs) also often called cholinesterase inhibitors, inhibit the enzyme acetylcholinesterase from breaking down the neurotransmitter acetylcholine into choline and acetate, thereby increasing both the level and duration of action of acetylcholine in the central nervous system, autonomic ganglia and neuromuscular junctions, which are rich in acetylcholine receptors. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors are one of two types of cholinesterase inhibitors; the other being butyryl-cholinesterase inhibitors. Acetylcholinesterase is the primary member of the cholinesterase enzyme family. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors are classified as reversible, irreversible, or quasi-irreversible (also called pseudo-irreversible). Mechanism of action Organophosphates Organophosphates like TEPP and sarin inhibit cholinesterases, enzymes that hydrolyze the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. The active centre of cholinesterases feature two important sites, namely the an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isopropyl Esters
In organic chemistry, propyl is a three- carbon alkyl substituent with chemical formula for the linear form. This substituent form is obtained by removing one hydrogen atom attached to the terminal carbon of propane. A propyl substituent is often represented in organic chemistry with the symbol Pr (not to be confused with the element praseodymium). An isomeric form of propyl is obtained by moving the point of attachment from a terminal carbon atom to the central carbon atom, named 1-methylethyl or isopropyl. To maintain four substituents on each carbon atom, one hydrogen atom has to be moved from the middle carbon atom to the carbon atom which served as attachment point in the ''n''-propyl variant, written as . Linear propyl is sometimes termed normal and hence written with a prefix ''n''- (i.e., ''n-''propyl), as the absence of the prefix ''n''- does not indicate which attachment point is chosen, i.e. absence of prefix does not automatically exclude the possibility of it b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_-_Gassed_-_Google_Art_Project.jpg)
