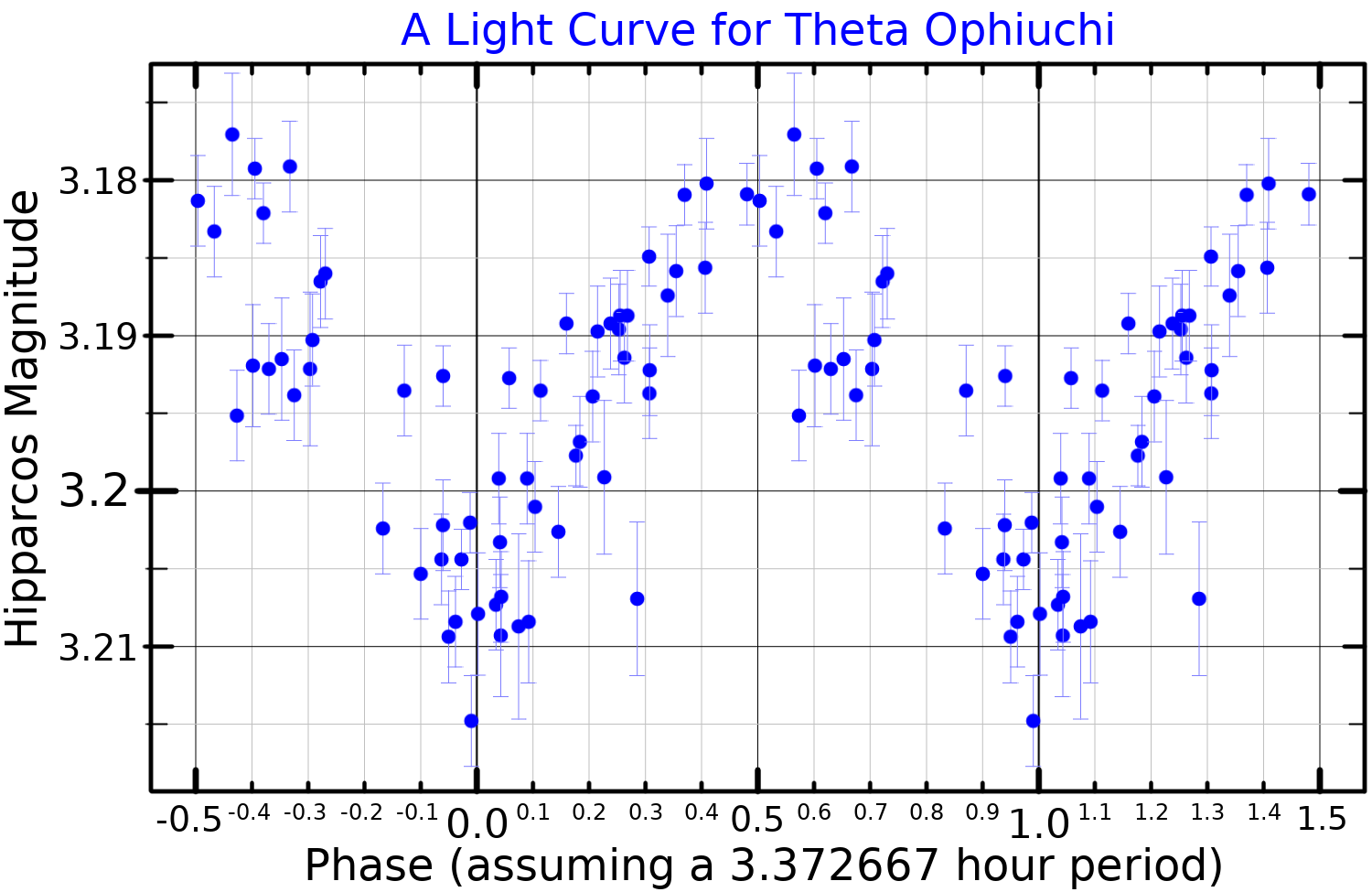
 |
Theta Ophiuchi
Theta Ophiuchi, Latinized from θ Ophiuchi, is a multiple star system in the equatorial constellation of Ophiuchus. It lies on the "right foot" of the serpent-bearer, just southwest of Kepler's Star, the nova of 1604. This star has an apparent visual magnitude of +3.3, making it readily visible to the naked eye. Based upon parallax measurements from the Hipparcos mission, it is roughly from Earth. It is 1.8 degrees south of the ecliptic and therefore subject to lunar occultations and (very rarely) occulted by a planet. The next occultation by a planet will be by Mars on 3 October 2078. Theta Ophiuchi appears to be a triple star system. The brightest component is a spectroscopic binary with an orbital period of 56.71 days and an eccentricity of 0.17. The third component is 5.5 magnitude star with a stellar classification of B5. Its angular separation from the binary pair is 0.15 arcseconds. This system is a proper motion member of the Upper Scorpius sub-gro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Ophiuchus (constellation)
Ophiuchus () is a large constellation straddling the celestial equator. Its name comes from the Ancient Greek (), meaning "serpent-bearer", and it is commonly represented as a man grasping a snake. The serpent is represented by the constellation Serpens. Ophiuchus was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. An old alternative name for the constellation was Serpentarius. Location Ophiuchus lies between Aquila, Serpens, Scorpius, Sagittarius, and Hercules, northwest of the center of the Milky Way. The southern part lies between Scorpius to the west and Sagittarius to the east. In the northern hemisphere, it is best visible in summer. It is opposite of Orion. Ophiuchus is depicted as a man grasping a serpent; the interposition of his body divides the snake constellation Serpens into two parts, Serpens Caput and Serpens Cauda. Ophiuchus straddles the equator with the majority ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
B-type Star
In astronomy, stellar classification is the classification of stars based on their spectral characteristics. Electromagnetic radiation from the star is analyzed by splitting it with a prism or diffraction grating into a spectrum exhibiting the rainbow of colors interspersed with spectral lines. Each line indicates a particular chemical element or molecule, with the line strength indicating the abundance of that element. The strengths of the different spectral lines vary mainly due to the temperature of the photosphere, although in some cases there are true abundance differences. The ''spectral class'' of a star is a short code primarily summarizing the ionization state, giving an objective measure of the photosphere's temperature. Most stars are currently classified under the Morgan–Keenan (MK) system using the letters ''O'', ''B'', ''A'', ''F'', ''G'', ''K'', and ''M'', a sequence from the hottest (''O'' type) to the coolest (''M'' type). Each letter class is then subdivided ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Photosphere
The photosphere is a star's outer shell from which light is radiated. It extends into a star's surface until the plasma becomes opaque, equivalent to an optical depth of approximately , or equivalently, a depth from which 50% of light will escape without being scattered. A photosphere is the region of a luminous object, usually a star, that is transparent to photons of certain wavelengths. Stars, except neutron stars, have no solid or liquid surface. Therefore, the photosphere is typically used to describe the Sun's or another star's visual surface. Etymology The term ''photosphere'' is derived from Ancient Greek roots, φῶς, φωτός/''phos'', ''photos'' meaning "light" and σφαῖρα/''sphaira'' meaning "sphere", in reference to it being a spherical surface that is perceived to emit light. Temperature The surface of a star is defined to have a temperature given by the effective temperature in the Stefan–Boltzmann law. Various stars have photospheres of vari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Luminosity Of The Sun
The solar luminosity () is a unit of radiant flux ( power emitted in the form of photons) conventionally used by astronomers to measure the luminosity of stars, galaxies and other celestial objects in terms of the output of the Sun. One nominal solar luminosity is defined by the International Astronomical Union to be . This corresponds almost exactly to a bolometric absolute magnitude of +4.74. The Sun is a weakly variable star, and its actual luminosity therefore fluctuates. The major fluctuation is the eleven-year solar cycle (sunspot cycle) that causes a quasi-periodic variation of about ±0.1%. Other variations over the last 200–300 years are thought to be much smaller than this. Determination Solar luminosity is related to solar irradiance (the solar constant). Slow changes in the axial tilt of the planet and the shape of its orbit cause cyclical changes to the solar irradiance. The result is orbital forcing that causes the Milankovitch cycles, which determine Earthl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Subgiant Star
A subgiant is a star that is brighter than a normal main-sequence star of the same spectral class, but not as bright as giant stars. The term subgiant is applied both to a particular spectral luminosity class and to a stage in the evolution of a star. Yerkes luminosity class IV The term subgiant was first used in 1930 for class G and early K stars with absolute magnitudes between +2.5 and +4. These were noted as being part of a continuum of stars between obvious main-sequence stars such as the Sun and obvious giant stars such as Aldebaran, although less numerous than either the main sequence or the giant stars. The Yerkes spectral classification system is a two-dimensional scheme that uses a letter and number combination to denote the temperature of a star (e.g. A5 or M1) and a Roman numeral to indicate the luminosity relative to other stars of the same temperature. Luminosity class IV stars are the subgiants, located between main-sequence stars (luminosity class V) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Main Sequence
In astronomy, the main sequence is a classification of stars which appear on plots of stellar color index, color versus absolute magnitude, brightness as a continuous and distinctive band. Stars on this band are known as main-sequence stars or dwarf stars, and positions of stars on and off the band are believed to indicate their physical properties, as well as their progress through several types of star life-cycles. These are the most numerous true stars in the universe and include the Sun. Color-magnitude plots are known as Hertzsprung–Russell diagrams after Ejnar Hertzsprung and Henry Norris Russell. After condensation and ignition of a star, it generates thermal energy in its dense stellar core, core region through nuclear fusion of hydrogen into helium. During this stage of the star's lifetime, it is located on the main sequence at a position determined primarily by its mass but also based on its chemical composition and age. The cores of main-sequence stars are in hydros ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Stellar Evolution
Stellar evolution is the process by which a star changes over the course of time. Depending on the mass of the star, its lifetime can range from a few million years for the most massive to trillions of years for the least massive, which is considerably longer than the current age of the universe. The table shows the lifetimes of stars as a function of their masses. All stars are formed from Gravitational collapse, collapsing clouds of gas and dust, often called nebulae or molecular clouds. Over the course of millions of years, these protostars settle down into a state of equilibrium, becoming what is known as a main sequence star. Nuclear fusion powers a star for most of its existence. Initially the energy is generated by the fusion of hydrogen atoms at the stellar core, core of the main-sequence star. Later, as the preponderance of atoms at the core becomes helium, stars like the Sun begin to fuse hydrogen along a spherical shell surrounding the core. This process causes the st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Mass Of The Sun
The solar mass () is a frequently used unit of mass in astronomy, equal to approximately . It is approximately equal to the mass of the Sun. It is often used to indicate the masses of other stars, as well as stellar clusters, nebulae, galaxies and black holes. More precisely, the mass of the Sun is The solar mass is about times the mass of Earth (), or times the mass of Jupiter (). History of measurement The value of the gravitational constant was first derived from measurements that were made by Henry Cavendish in 1798 with a torsion balance. The value he obtained differs by only 1% from the modern value, but was not as precise. The diurnal parallax of the Sun was accurately measured during the transits of Venus in 1761 and 1769, yielding a value of (9 arcseconds, compared to the present value of ). From the value of the diurnal parallax, one can determine the distance to the Sun from the geometry of Earth. The first known estimate of the solar mass was by Isaac N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Variable Star
A variable star is a star whose brightness as seen from Earth (its apparent magnitude) changes systematically with time. This variation may be caused by a change in emitted light or by something partly blocking the light, so variable stars are classified as either: * ''Intrinsic variables'', whose luminosity actually changes periodically; for example, because the star swells and shrinks. * ''Extrinsic variables'', whose apparent changes in brightness are due to changes in the amount of their light that can reach Earth; for example, because the star has an orbiting companion that sometimes eclipses it. Many, possibly most, stars exhibit at least some oscillation in luminosity: the energy output of the Sun, for example, varies by about 0.1% over an 11-year solar cycle. Discovery An ancient Egyptian calendar of lucky and unlucky days composed some 3,200 years ago may be the oldest preserved historical document of the discovery of a variable star, the eclipsing binary Algol. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Stellar Association
A stellar association is a very loose star cluster, looser than both open clusters and globular clusters. Stellar associations will normally contain from 10 to 100 or more visible stars. An association is primarily identified by commonalities in its member stars' movement vectors, ages, and chemical compositions. These shared features indicate that the members share a common origin. Nevertheless, they have become gravitationally unbound, unlike star clusters, and the member stars will drift apart over millions of years, becoming a moving group as they scatter throughout their neighborhood within the galaxy. Stellar associations were discovered by Victor Ambartsumian in 1947. The conventional name for an association uses the names or abbreviations of the constellation (or constellations) in which they are located; the association type, and, sometimes, a numerical identifier. Types Victor Ambartsumian first categorized stellar associations into two groups, OB and T, based on the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
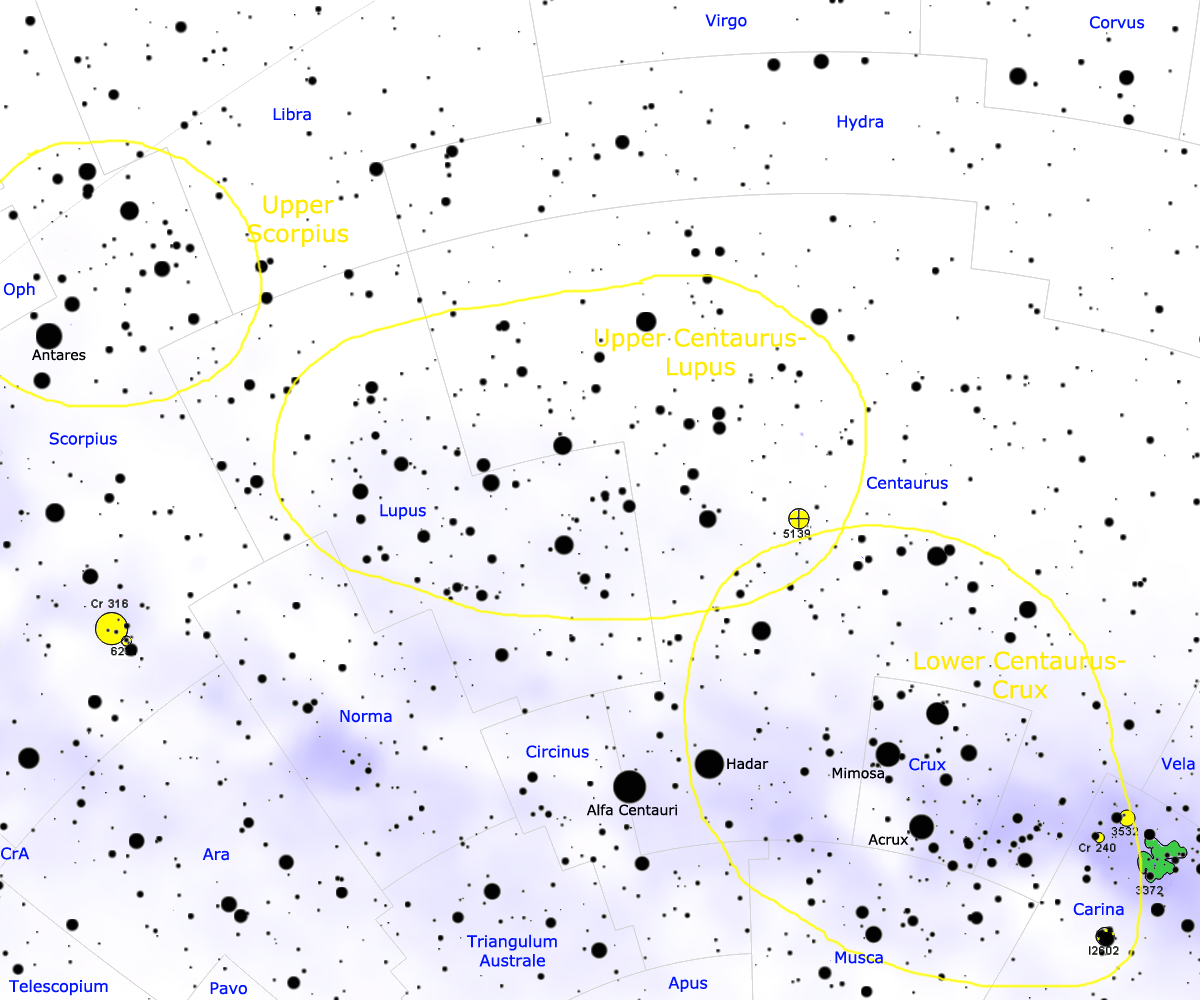 |
Scorpius–Centaurus Association
The Scorpius–Centaurus association (sometimes called Sco–Cen or Sco OB2) is the nearest OB association to the Sun. This stellar association is composed of three subgroups (Upper Scorpius, Upper Centaurus–Lupus, and Lower Centaurus–Crux) and its distance is about 130 parsecs or 420 light-years. Analysis using improved Hipparcos data has brought the number of known members to 436. The cluster shows a continuous spread of stars with no apparent need for subclassification. The Sco–Cen subgroups range in age from 11 million years (Upper Scorpius) to roughly 15 million years (Upper Centaurus–Lupus and Lower Centaurus–Crux). Many of the bright stars in the constellations Scorpius, Lupus, Centaurus, and Crux are members of the Sco–Cen association, including Antares (the most massive member of Upper Scorpius), and most of the stars in the Southern Cross. Hundreds of stars have been identified as members of Sco-Cen, with masses ranging from roughly 15 solar masses (Antares ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |