|
Thermoplastic Polyurethane
Thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) is any of the polyurethane polymers that are thermoplastic; that is, they become pliable when heated and harden when cooled. This is in contrast to most polyurethanes, which are thermosets, hardening irreversibly. Thermoplastic polyurethanes (TPUs) reveal vast combinations of both physical properties and processing applications. Usually, they are flexible and elastic with good resistance to impact, abrasion and weather. With TPUs, there is the possibility for colouring as well as fabrication using a wide range of techniques. The incorporation of TPUs could therefore improve the overall durability of many products. Thermoplastic polyurethanes have many desirable properties, including elasticity, transparency, and resistance to oil, grease, and abrasion. Technically, they are thermoplastic elastomers, consisting of linear segmented block copolymers composed of hard and soft segments. Chemistry TPU is a block copolymer consisting of alternating se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyurethane
Polyurethane (; often abbreviated PUR and PU) is a class of polymers composed of organic chemistry, organic units joined by carbamate (urethane) links. In contrast to other common polymers such as polyethylene and polystyrene, polyurethane term does not refer to the single type of polymer but a group of polymers. Unlike polyethylene and polystyrene, polyurethanes can be produced from a wide range of starting materials resulting in various polymers within the same group. This chemical variety produces polyurethanes with different chemical structures leading to many List of polyurethane applications, different applications. These include rigid and flexible foams, and coatings, adhesives, Potting (electronics), electrical potting compounds, and fibers such as spandex and polyurethane laminate (PUL). Foams are the largest application accounting for 67% of all polyurethane produced in 2016. A polyurethane is typically produced by reacting a polymeric isocyanate with a polyol. Since a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laminated Glass
Laminated glass is a type of safety glass consisting of two or more layers of glass with one or more thin polymer interlayers between them which prevent the glass from breaking into large sharp pieces. Breaking produces a characteristic "spider web" cracking pattern (radial and concentric cracks) when the impact is not enough to completely pierce the glass. Laminated glass is used for architecture, glazing, automobile safety, photovoltaic, UV protection, and artistic expression. The most common use of laminated glass is automobile windshields and skylight glazing. In geographical areas requiring hurricane-resistant construction, laminated glass is often used in exterior storefronts, curtain walls, and windows. Laminated glass is also used to increase the sound insulation rating of a window, because it significantly improves sound attenuation compared to monolithic glass panes of the same thickness. The interlayer is typically of polyvinyl butyral (PVB), ethylene-vinyl ace ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Masterbatch
A masterbatch is a concentrated mixture of pigments and / or additives blended and extruded together in a carrier matrix, such as resin or wax, that is used to add these mixed additives to a final plastic product. The additives may be used for colouring (a "colour masterbatch") or for imparting other properties (an "additive masterbatch"). The typical alternative to using a masterbatch is to compound the plastic from raw undiluted additives. Manufacturing plastics from masterbatches The general process for the manufacture of masterbatches involves first identifying and weighing the needed pigments and/or additives, then mixing the pigments or additives with a carrier resin or polymer. Finally, the concentrated mixture is extruded, cooled and formed into granules, powders, or other masterbatch vehicles and the final product is bagged. The carrier material of the masterbatch can be based on wax (a universal carrier) or a specific polymer that is identical to or compatible with th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BASF
BASF SE (), an initialism of its original name , is a European Multinational corporation, multinational company and the List of largest chemical producers, largest chemical producer in the world. Its headquarters are located in Ludwigshafen, Germany. BASF comprises subsidiary, subsidiaries and joint ventures in more than 80 countries, operating six integrated production sites and 390 other production sites across Europe, Asia, Australia, the Americas and Africa. BASF has customers in over 190 countries and supplies products to a wide variety of industries. Despite its size and global presence, BASF has received relatively little public attention since it abandoned the manufacture and sale of BASF-branded consumer electronics products in the 1990s. The company began as a dye manufacturer in 1865. Fritz Haber worked with Carl Bosch, one of its employees, to invent the Haber-Bosch, Haber-Bosch process by 1912, after which the company grew rapidly. In 1925, the company merged with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isocyanate
In organic chemistry, isocyanate is the functional group with the formula . Organic compounds that contain an isocyanate group are referred to as isocyanates. An organic compound with two isocyanate groups is known as a diisocyanate. Diisocyanates are manufactured for the production of polyurethanes, a class of polymers. Isocyanates should not be confused with cyanate esters and isocyanides, very different families of compounds. The cyanate (cyanate ester) functional group () is arranged differently from the isocyanate group (). Isocyanides have the connectivity , lacking the oxygen of the cyanate groups. Structure and bonding In terms of bonding, isocyanates are closely related to carbon dioxide (CO2) and carbodiimides (C(NR)2). The C−N=C=O unit that defines isocyanates is planar, and the N=C=O linkage is nearly linear. In phenyl isocyanate, the C=N and C=O distances are respectively 1.195 and 1.173 Å. The C−N=C angle is 134.9° and the N=C=O angle is 173.1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aliphatic Compound
In organic chemistry, hydrocarbons ( compounds composed solely of carbon and hydrogen) are divided into two classes: aromatic compounds and aliphatic compounds (; G. ''aleiphar'', fat, oil). Aliphatic compounds can be saturated (in which all the C-C bonds are single, requiring the structure to be completed, or 'saturated', by hydrogen) like hexane, or unsaturated, like hexene and hexyne. Open-chain compounds, whether straight or branched, and which contain no rings of any type, are always aliphatic. Cyclic compounds can be aliphatic if they are not aromatic. Structure Aliphatics compounds can be saturated, joined by single bonds ( alkanes), or unsaturated, with double bonds ( alkenes) or triple bonds ( alkynes). If other elements ( heteroatoms) are bound to the carbon chain, the most common being oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, and chlorine, it is no longer a hydrocarbon, and therefore no longer an aliphatic compound. However, such compounds may still be referred to as al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrolysis
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution reaction, substitution, elimination reaction, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water is the nucleophile. Biological hydrolysis is the cleavage of Biomolecule, biomolecules where a water molecule is consumed to effect the separation of a larger molecule into component parts. When a carbohydrate is broken into its component sugar molecules by hydrolysis (e.g., sucrose being broken down into glucose and fructose), this is recognized as saccharification. Hydrolysis reactions can be the reverse of a condensation reaction in which two molecules join into a larger one and eject a water molecule. Thus hydrolysis adds water to break down, whereas condensation builds up by removing water. Types Usually hydrolysis is a chemical process in which a molecule of water is added to a substance. Sometimes this addition causes both the su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ether
In organic chemistry, ethers are a class of compounds that contain an ether group, a single oxygen atom bonded to two separate carbon atoms, each part of an organyl group (e.g., alkyl or aryl). They have the general formula , where R and R′ represent the organyl groups. Ethers can again be classified into two varieties: if the organyl groups are the same on both sides of the oxygen atom, then it is a simple or symmetrical ether, whereas if they are different, the ethers are called mixed or unsymmetrical ethers. A typical example of the first group is the solvent and anaesthetic diethyl ether, commonly referred to simply as "ether" (). Ethers are common in organic chemistry and even more prevalent in biochemistry, as they are common linkages in carbohydrates and lignin. Structure and bonding Ethers feature bent linkages. In dimethyl ether, the bond angle is 111° and C–O distances are 141 pm. The barrier to rotation about the C–O bonds is low. The bonding of ox ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrahydrofuran
Tetrahydrofuran (THF), or oxolane, is an organic compound with the formula (CH2)4O. The compound is classified as heterocyclic compound, specifically a cyclic ether. It is a colorless, water- miscible organic liquid with low viscosity. It is mainly used as a precursor to polymers. Being polar and having a wide liquid range, THF is a versatile solvent. It is an isomer of another solvent, butanone. Production About 200,000 tonnes of tetrahydrofuran are produced annually. The most widely used industrial process involves the acid-catalyzed dehydration of 1,4-Butanediol, 1,4-butanediol. Ashland Inc., Ashland/ISP is one of the biggest producers of this chemical route. The method is similar to the production of diethyl ether from ethanol. The butanediol is derived from Condensation reaction, condensation of acetylene with formaldehyde followed by hydrogenation. DuPont developed a process for producing THF by oxidizing Butane#Isomers, ''n''-butane to crude maleic anhydride, follow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ester
In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an acid (either organic or inorganic) in which the hydrogen atom (H) of at least one acidic hydroxyl group () of that acid is replaced by an organyl group (R). These compounds contain a distinctive functional group. Analogues derived from oxygen replaced by other chalcogens belong to the ester category as well. According to some authors, organyl derivatives of acidic hydrogen of other acids are esters as well (e.g. amides), but not according to the IUPAC. Glycerides are fatty acid esters of glycerol; they are important in biology, being one of the main classes of lipids and comprising the bulk of animal fats and vegetable oils. Lactones are cyclic carboxylic esters; naturally occurring lactones are mainly 5- and 6-membered ring lactones. Lactones contribute to the aroma of fruits, butter, cheese, vegetables like celery and other foods. Esters can be formed from oxoacids (e.g. esters of acetic acid, carbonic acid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adipic Acid
Adipic acid or hexanedioic acid is the organic compound with the formula C6H10O4. It a white crystalline powder at standard temperature and pressure. From an industrial perspective, it is the most important dicarboxylic acid at about 2.5 billion kilograms produced annually, mainly as a precursor for the production of nylon. Adipic acid otherwise rarely occurs in nature, but it is known as manufactured E number food additive E355. Salts and esters of adipic acid are known as adipates. Preparation and reactivity Adipic acid is produced by oxidation of a mixture of cyclohexanone and cyclohexanol, which is called KA oil, an abbreviation of ketone-alcohol oil. Nitric acid is the oxidant. The pathway is multistep. Early in the reaction, the cyclohexanol is converted to the ketone, releasing nitrous acid: : The cyclohexanone is then nitrosated, setting the stage for the scission of the C-C bond: : : Side products of the method include glutaric and succinic acids. Nitrous oxide is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
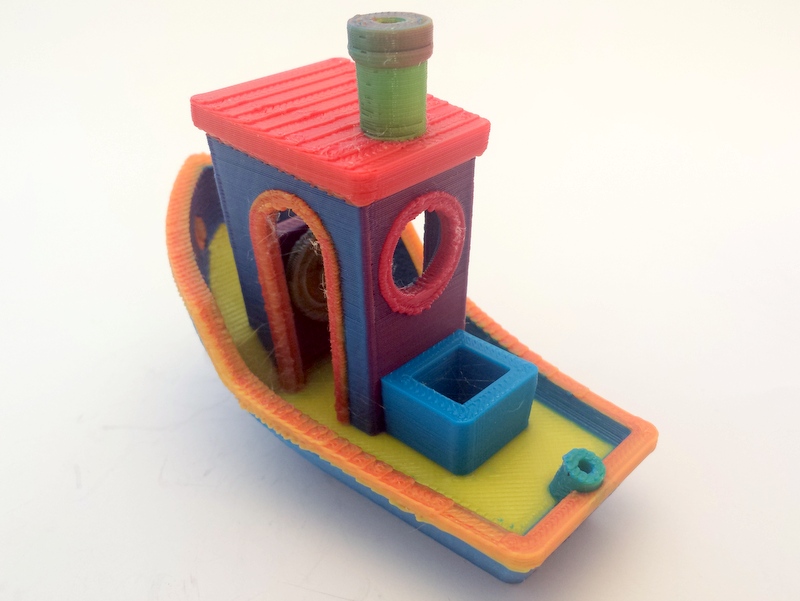
3D Printing
3D printing, or additive manufacturing, is the construction of a three-dimensional object from a CAD model or a digital 3D model. It can be done in a variety of processes in which material is deposited, joined or solidified under computer control, with the material being added together (such as plastics, liquids or powder grains being fused), typically layer by layer. In the 1980s, 3D printing techniques were considered suitable only for the production of functional or aesthetic prototypes, and a more appropriate term for it at the time was rapid prototyping. , the precision, repeatability, and material range of 3D printing have increased to the point that some 3D printing processes are considered viable as an industrial-production technology; in this context, the term ''additive manufacturing'' can be used synonymously with ''3D printing''. One of the key advantages of 3D printing is the ability to produce very complex shapes or geometries that would be otherwise infeasi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |