|
Thermal Management (electronics)
All electronic devices and Electronic circuit, circuitry generate excess heat and thus require thermal management to improve Reliability engineering, reliability and prevent premature failure. The amount of heat output is equal to the Electric power, power input, if there are no other energy interactions. There are several techniques for cooling including various styles of heat sinks, Thermoelectric cooling, thermoelectric coolers, forced air systems and Computer fan, fans, heat pipes, and others. In cases of extreme low environmental temperatures, it may actually be necessary to heat the electronic components to achieve satisfactory operation. Overview Thermal resistance of devices This is usually quoted as the Thermal resistance in electronics, thermal resistance from p–n junction, junction to case of the semiconductor device. The units are °C/W. For example, a heatsink rated at 10 °C/W will get 10 °C hotter than the surrounding air when it dissipat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CFD Forced Convection Heat Sink V4
__NOTOC__ CFD may refer to: Business and economics * Centre for Finance and Development in Geneva, Switzerland * Contract for difference, a type of financial derivative * Contracts for Difference (UK energy), market support mechanism for low carbon electricity generation in the UK * Control-flow diagram, of a process * Cumulative flow diagram, in queueing theory Firefighting services * Calgary Fire Department, Alberta, Canada * Chicago Fire Department, Illinois, U.S. * Cleveland Fire Department, Ohio, U.S. * Columbus Fire Department, Ohio, U.S. Science and technology * Common fill device, in cryptography * Complement factor D, an enzyme * Computational fluid dynamics * Congenital Femoral Deficiency, a birth defect * Constant fraction discriminator, a signal processing device * Counterfactual definiteness, a concept in quantum mechanics Transport * Caulfield railway station, Melbourne * Clarkefield railway station, Melbourne * Coulter Field (IATA: CFD), an airport in Bryan, Texas, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
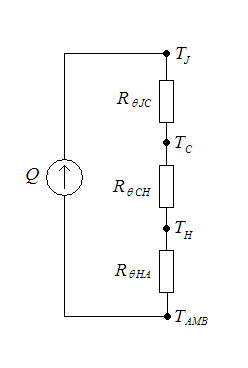
Thermal Resistance In Electronics
In heat transfer, thermal engineering, and thermodynamics, thermal conductance and thermal resistance are fundamental concepts that describe the ability of materials or systems to conduct heat and the opposition they offer to the heat current. The ability to manipulate these properties allows engineers to control temperature gradient, prevent thermal shock, and maximize the efficiency of thermal systems. Furthermore, these principles find applications in a multitude of fields, including materials science, mechanical engineering, electronics, and energy management. Knowledge of these principles is crucial in various scientific, engineering, and everyday applications, from designing efficient temperature control, thermal insulation, and Thermal management (electronics), thermal management in industrial processes to optimizing the performance of electronic devices. Thermal conductance (''G'') measures the ability of a material or system to conduct heat. It provides insights into th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reflow Soldering
Reflow soldering is a process in which a solder paste (a sticky mixture of powdered solder and flux (metallurgy), flux) is used to temporarily attach anywhere from one to thousands of tiny electrical components to their contact pads, after which the entire assembly is subjected to controlled heat. The solder paste reflows in a molten state, creating permanent solder joints. Heating may be accomplished by passing the assembly through a reflow oven, under an Infrared heater, infrared lamp, or (mainly for prototyping) by soldering individual joints with a hot air pencil. Reflow soldering with long industrial convection ovens is the preferred method of soldering surface mount technology (SMT) components to a printed circuit board (PCB). Each segment of the oven has a regulated temperature, according to the specific thermal requirements of each assembly. Reflow ovens meant specifically for the soldering of surface mount components may also be used for Through-hole technology, throu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
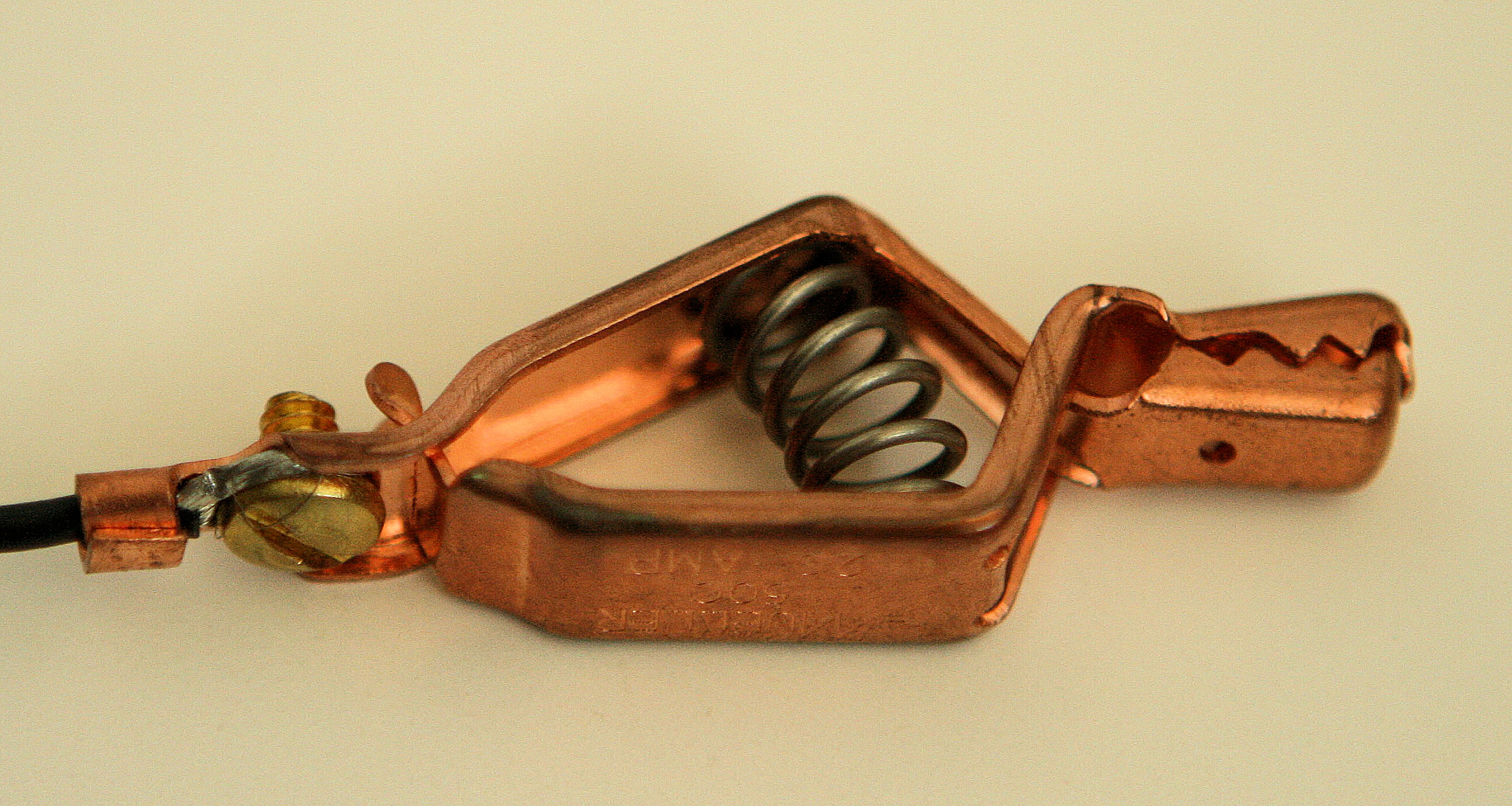
Crocodile Clip
Alligator clip A crocodile clip or alligator clip is a plier-like spring-tensioned metal clip with elongated, serrated jaws that is used for creating a temporary electrical connection. This simple mechanical device gets its name from the resemblance of its serrated jaws to the toothed jaws of a crocodile or alligator. It is used to clamp and grab onto a bare electrical cable to a lead on a battery or some other electrical component. The clip's tapered, serrated jaws are forced together by a spring to grip an object. A Clothespin or Kelvin clip is a special form of crocodile clip whose jaws are insulated from each other, allowing two isolated wires to connect to a single test point. This enables 4-wire measurement of circuits with very low resistances. When manufactured for electronics testing and evaluation, one jaw of the clip is typically permanently crimped or soldered to a wire, or is bent to form the inner tubular contact of a ~ female banana jack, enabling quick n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soldering
Soldering (; ) is a process of joining two metal surfaces together using a filler metal called solder. The soldering process involves heating the surfaces to be joined and melting the solder, which is then allowed to cool and solidify, creating a strong and durable joint. Soldering is commonly used in the electronics industry for the manufacture and repair of Printed circuit board, printed circuit boards (PCBs) and other electronic components. It is also used in plumbing and Metalworking, metalwork, as well as in the manufacture of jewelry and other decorative items. The solder used in the process can vary in composition, with different alloys used for different applications. Common solder alloys include tin-lead, tin-silver, and tin-copper, among others. Lead-free solder has also become more widely used in recent years due to health and environmental concerns associated with the use of lead. In addition to the type of solder used, the temperature and method of heating also p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Personal Computer
A personal computer, commonly referred to as PC or computer, is a computer designed for individual use. It is typically used for tasks such as Word processor, word processing, web browser, internet browsing, email, multimedia playback, and PC game, gaming. Personal computers are intended to be operated directly by an end user, rather than by a computer expert or technician. Unlike large, costly minicomputers and mainframes, time-sharing by many people at the same time is not used with personal computers. The term home computer has also been used, primarily in the late 1970s and 1980s. The advent of personal computers and the concurrent Digital Revolution have significantly affected the lives of people. Institutional or corporate computer owners in the 1960s had to write their own programs to do any useful work with computers. While personal computer users may develop their applications, usually these systems run commercial software, free-of-charge software ("freeware"), which i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overclocking
In computing, overclocking is the practice of increasing the clock rate of a computer to exceed that certified by the manufacturer. Commonly, operating voltage is also increased to maintain a component's operational stability at accelerated speeds. Semiconductor devices operated at higher frequencies and voltages increase power consumption and heat. An overclocked device may be unreliable or fail completely if the additional heat load is not removed or power delivery components cannot meet increased power demands. Many device warranties state that overclocking or over-specification voids any warranty, but some manufacturers allow overclocking as long as it is done (relatively) safely. Overview The purpose of overclocking is to increase the operating speed of a given component. Normally, on modern systems, the target of overclocking is increasing the performance of a major chip or subsystem, such as the main processor or graphics controller, but other components, such as sys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermodynamic Efficiency
In thermodynamics, the thermal efficiency (\eta_) is a dimensionless performance measure of a device that uses thermal energy, such as an internal combustion engine, steam turbine, steam engine, boiler, furnace, refrigerator, ACs etc. For a heat engine, thermal efficiency is the ratio of the net work output to the heat input; in the case of a heat pump, thermal efficiency (known as the '' coefficient of performance'' or COP) is the ratio of net heat output (for heating), or the net heat removed (for cooling) to the energy input (external work). The efficiency of a heat engine is fractional as the output is always less than the input while the COP of a heat pump is more than 1. These values are further restricted by the Carnot theorem. Overview In general, energy conversion efficiency is the ratio between the useful output of a device and the input, in energy terms. For thermal efficiency, the input, Q_, to the device is heat, or the heat-content of a fuel that is consumed. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heatsink
A heat sink (also commonly spelled heatsink) is a passive heat exchanger that transfers the heat generated by an electronic or a mechanical device to a fluid medium, often air or a liquid coolant, where it is dissipated away from the device, thereby allowing regulation of the device's temperature. In computers, heat sinks are used to cool CPUs, GPUs, and some chipsets and RAM modules. Heat sinks are used with other high-power semiconductor devices such as power transistors and optoelectronics such as lasers and light-emitting diodes (LEDs), where the heat dissipation ability of the component itself is insufficient to moderate its temperature. A heat sink is designed to maximize its surface area in contact with the cooling medium surrounding it, such as the air. Air velocity, choice of material, protrusion design and surface treatment are factors that affect the performance of a heat sink. Heat sink attachment methods and thermal interface materials also affect the die tempe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microprocessor
A microprocessor is a computer processor (computing), processor for which the data processing logic and control is included on a single integrated circuit (IC), or a small number of ICs. The microprocessor contains the arithmetic, logic, and control circuitry required to perform the functions of a computer's central processing unit (CPU). The IC is capable of interpreting and executing program instructions and performing arithmetic operations. The microprocessor is a multipurpose, Clock signal, clock-driven, Processor register, register-based, digital integrated circuit that accepts binary code, binary data as input, processes it according to instruction (computing), instructions stored in its computer memory, memory, and provides results (also in binary form) as output. Microprocessors contain both combinational logic and sequential logic, sequential digital logic, and operate on numbers and symbols represented in the binary number system. The integration of a whole CPU on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermal Transfer
Thermal-transfer printing is a digital printing method in which material is applied to paper (or some other material) by melting a coating of ribbon so that it stays glued to the material on which the print is applied. It contrasts with direct thermal printing, where no ribbon is present in the process. Thermal transfer is preferred over direct thermal printing on surfaces that are heat-sensitive or when higher durability of printed matter (especially against heat) is desired. Thermal transfer is a popular print process particularly used for the printing of identification labels. It is the most widely used printing process in the world for the printing of high-quality barcodes. Printers like label makers can laminate the print for added durability. Thermal transfer printing was invented by SATO corporation. The world's first thermal-transfer label printer SATO M-2311 was produced in 1981. Thermal-transfer printing process Thermal-transfer printing is done by melting wax within ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |