|
Theodore Parker
Theodore Parker (August 24, 1810 – May 10, 1860) was an American transcendentalist and reforming minister of the Unitarian church. A reformer and abolitionist, his words and popular quotations would later inspire speeches by Abraham Lincoln and Martin Luther King Jr. Early life and education Parker was born in Lexington, Massachusetts, the youngest child in a large farming family. His paternal grandfather was John Parker, the leader of the Lexington militia at the Battle of Lexington. Among his colonial Yankee ancestors were Thomas Hastings, who came from the East Anglia region of England to the Massachusetts Bay Colony in 1634, and Deacon Thomas Parker, who came from England in 1635 and was one of the founders of Reading. Most of Theodore's family had died by the time he was 27, probably due to tuberculosis. Out of eleven siblings, only five remained: three brothers, including Theodore, and two sisters. His mother, to whom he was emotionally close, died when he was el ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Reverend
The Reverend (abbreviated as The Revd, The Rev'd or The Rev) is an honorific style (form of address), style given to certain (primarily Western Christian, Western) Christian clergy and Christian minister, ministers. There are sometimes differences in the way the style is used in different countries and church traditions. ''The Reverend'' is correctly called a ''style'', but is sometimes referred to as a title, form of address, or title of respect. Etymology The term is an anglicisation of the Latin , the style originally used in Latin documents in medieval Europe. It is the gerundive or future passive participle of the verb ("to respect; to revere"), meaning "[one who is] to be revered/must be respected". ''The Reverend'' is therefore equivalent to ''the Honourable'' or ''the Venerable''. Originating as a general term of respectful address in the 15th century, it became particularly associated with clergy by the 17th century, with variations associated with certain ranks in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reading, Massachusetts
Reading ( ) is a New England town, town in Middlesex County, Massachusetts, United States, north of central Boston. The population was 25,518 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. History Settlement Many of the Massachusetts Bay Colony's original settlers arrived from England in the 1630s through the ports of Lynn, Massachusetts, Lynn and Salem, Massachusetts, Salem. In 1639, some citizens of Lynn petitioned the government of the colony for a "place for an inland plantation". They were initially granted six square miles, followed by an additional four. The first settlement in this grant was at first called "Lynn Village" and was located on the south shore of the "Great Pond", now known as Lake Quannapowitt. On June 10, 1644, the settlement was incorporated as the town of Reading, taking its name from the town of Reading, Berkshire, Reading in England. The first church was organized soon after the settlement, and the first parish separated and became the town of "South ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin (language)
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area around Rome, Italy. Through the expansion of the Roman Republic, it became the dominant language in the Italian Peninsula and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. It has greatly influenced many languages, including English, having contributed many words to the English lexicon, particularly after the Christianization of the Anglo-Saxons and the Norman Conquest. Latin roots appear frequently in the technical vocabulary used by fields such as theology, the sciences, medicine, and law. By the late Roman Republic, Old Latin had evolved into standardized Classical Latin. Vulgar Latin refers to the less prestigious colloquial registers, attested in inscriptions and some literary works such as those of the comic playwrights Plautus and Terence and the author Petronius. While ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ralph Waldo Emerson
Ralph Waldo Emerson (May 25, 1803April 27, 1882), who went by his middle name Waldo, was an American essayist, lecturer, philosopher, minister, abolitionism, abolitionist, and poet who led the Transcendentalism, Transcendentalist movement of the mid-19th century. He was seen as a champion of individualism and critical thinking, as well as a prescient critic of the countervailing pressures of society and conformity. Friedrich Nietzsche thought he was "the most gifted of the Americans," and Walt Whitman called Emerson his "master". Emerson gradually moved away from the religious and social beliefs of his contemporaries, formulating and expressing the philosophy of Transcendentalism in his 1836 essay, "Nature (Emerson), Nature". His speech "The American Scholar," given in 1837, was called America's "intellectual Declaration of Independence" by Oliver Wendell Holmes Sr.Richardson, p. 263. Emerson wrote most of Essays (Emerson), his important essays as lectures and then revised them ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Carlyle
Thomas Carlyle (4 December 17955 February 1881) was a Scottish essayist, historian, and philosopher. Known as the "Sage writing, sage of Chelsea, London, Chelsea", his writings strongly influenced the intellectual and artistic culture of the Victorian era. Carlyle was born in Ecclefechan, a village in Dumfriesshire. He attended the University of Edinburgh where he excelled in mathematics and invented the Carlyle circle. After finishing the arts course, he prepared to become a minister in the Burgher (Church history), Burgher Church while working as a schoolmaster. He quit these and several other endeavours before settling on literature, writing for the ''Edinburgh Encyclopædia'' and working as a translator. He initially gained prominence in English-language literary circles for his extensive writing on German Romanticism, German Romantic literature and philosophy. These themes were explored in his first major work, a semi-autobiographical philosophical novel entitled ''Sartor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samuel Taylor Coleridge
Samuel Taylor Coleridge ( ; 21 October 177225 July 1834) was an English poet, literary critic, philosopher, and theologian who was a founder of the Romantic Movement in England and a member of the Lake Poets with his friend William Wordsworth. He also shared volumes and collaborated with Charles Lamb, Robert Southey, and Charles Lloyd (poet), Charles Lloyd. He wrote the poems ''The Rime of the Ancient Mariner'' and "Kubla Khan", as well as the major prose work ''Biographia Literaria''. His critical works were highly influential, especially in relation to William Shakespeare, and he helped introduce German idealist philosophy to English-speaking cultures. Coleridge coined many familiar words and phrases, including "suspension of disbelief". He had a major influence on Ralph Waldo Emerson and American transcendentalism. Throughout his adult life, Coleridge had crippling bouts of anxiety and depression; it has been speculated that he had bipolar disorder, which had not been defin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harvard Divinity School
Harvard Divinity School (HDS) is one of the constituent schools of Harvard University in Cambridge, Massachusetts. The school's mission is to educate its students either in the religious studies, academic study of religion or for leadership roles in religion, government, and service. It also caters to students from other Harvard schools that are interested in the former field. HDS is among a small group of university-based, non-denominational Divinity (academic discipline), divinity schools in the United States. History Harvard College was founded in 1636 as a Puritan/Congregationalism in the United States, Congregationalist institution and trained ministers for many years. The separate institution of the Divinity School dates from 1816, when it was established as the first non-denominational divinity school in the United States. (Princeton Theological Seminary had been founded as a Presbyterian institution in 1812. Andover Theological Seminary was founded in 1807 by orthodox Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Faith
Faith is confidence or trust in a person, thing, or concept. In the context of religion, faith is " belief in God or in the doctrines or teachings of religion". According to the Merriam-Webster's Dictionary, faith has multiple definitions, including "something that is believed especially with strong conviction", "complete trust", "belief and trust in and loyalty to God", as well as "a firm belief in something for which there is no proof". Religious people often think of faith as confidence based on a perceived degree of warrant, or evidence, while others who are more skeptical of religion tend to think of faith as simply belief without evidence. In the Roman world, 'faith' (Latin: ) was understood without particular association with gods or beliefs. Instead, it was understood as a paradoxical set of reciprocal ideas: voluntary will and voluntary restraint in the sense of father over family or host over guest, whereby one party willfully surrenders to a party who could harm b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Octavius Brooks Frothingham
Octavius Brooks Frothingham (November 26, 1822 – November 27, 1895) was an American clergyman and author. Biography He was born in Boston, Massachusetts, the son of Nathaniel Langdon Frothingham (1793–1870), a prominent Unitarian preacher, and through his mother's family he was related to Phillips Brooks. He graduated from Harvard College in 1843 and from the Divinity School in 1846. On March 23, 1847, he married Caroline Martha Curtis (February 5, 1825 - June 8, 1900). Pastorates He was pastor of the North Unitarian church of Salem, Massachusetts, from 1847 to 1855. He broke with this congregation over the issue of slavery.George Harvey Genzmer, "Frothingham, Octavius Brooks," ''Dictionary of American Biography'', New York: Charles Scribner's Sons, 1961. From 1855 to 1860, he was pastor of a new Unitarian society in Jersey City. There he gave up the Lord's Supper, thinking that it ministered to self-satisfaction. It was as a radical Unitarian that he became pastor of ano ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Watertown, Massachusetts
Watertown is a city in Middlesex County, Massachusetts, United States, part of Greater Boston. The population was 35,329 in the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. Its neighborhoods include Bemis, Coolidge Square, East Watertown, Watertown Square, and the West End. Watertown was one of the first Massachusetts Bay Colony settlements organized by Puritans, Puritan settlers in 1630. The city is home to the Perkins School for the Blind, the Armenian Library and Museum of America, and the historic Watertown Arsenal, which produced military armaments from 1816 through World War II. History Archeological evidence suggests that Watertown was inhabited for thousands of years before European colonization of the Americas, colonization. In the 1600s, two groups of Massachusett, the Pequossette and the Nonantum, had settlements on the banks of the river later called the Charles, and a contemporary source lists "Pigsgusset" as the native name of "Water towne." The Pequossette built a fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
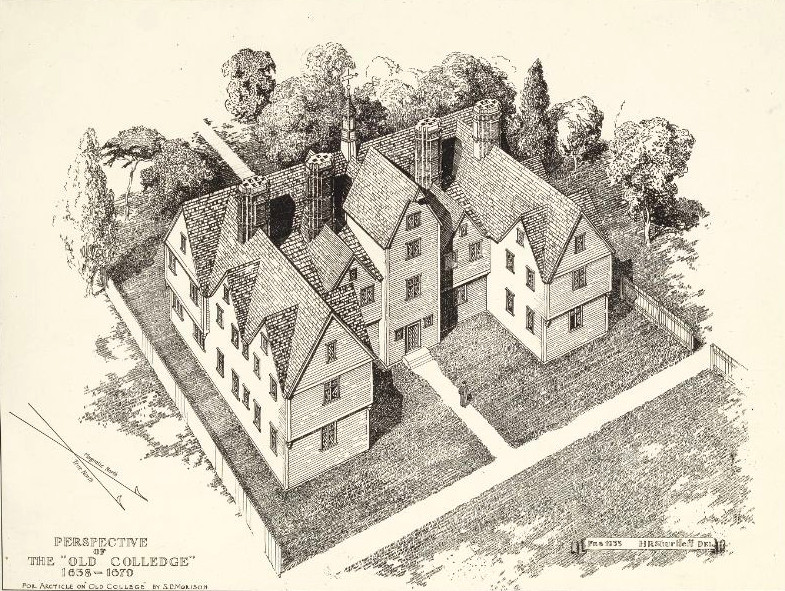
Harvard College
Harvard College is the undergraduate education, undergraduate college of Harvard University, a Private university, private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States. Part of the Harvard Faculty of Arts and Sciences, Faculty of Arts and Sciences, Harvard College is Harvard University's traditional undergraduate program, offering BA (Bachelor of Arts) and BS (Bachelor of Science) degrees. It is highly selective, with fewer than four percent of applicants being offered admission as of 2022. Harvard College students participate in over 450 extracurricular organizations and nearly all live on campus. First-year students reside in or near Harvard Yard while upperclass students reside in other on-campus housing. History Harvard College was founded in 1636 by vote of the Massachusetts General Court, Great and General Court of the Massachusetts Bay Colony. Two years later, the college became home to North America's first known printing press, carri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Houghton MS Am 1506 (14) - Cranch
Houghton may refer to: Places Australia * Houghton, South Australia, a town near Adelaide * Houghton Highway, the longest bridge in Australia, between Redcliffe and Brisbane in Queensland * Houghton Island (Queensland) Canada * Houghton Township, Ontario, a former township in Norfolk County, Ontario New Zealand * Houghton Bay South Africa * Houghton Estate, a suburb of Johannesburg United Kingdom * Hanging Houghton, Northamptonshire *Houghton, Cambridgeshire * Houghton, Cumbria * Houghton, East Riding of Yorkshire * Houghton, Hampshire *Houghton, Norfolk *Houghton Saint Giles, Norfolk * Houghton, Northumberland, a location in the United Kingdom * Houghton, Pembrokeshire *Houghton, West Sussex *Houghton-le-Side, Darlington *Houghton-le-Spring, Sunderland * Houghton Park, Houghton-le-Spring * Houghton Bank, Darlington *Houghton Conquest, Bedfordshire *Houghton on the Hill, Leicestershire *Houghton on the Hill, Norfolk *Houghton Regis, Bedfordshire *New Houghton, Derbyshire * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |