|
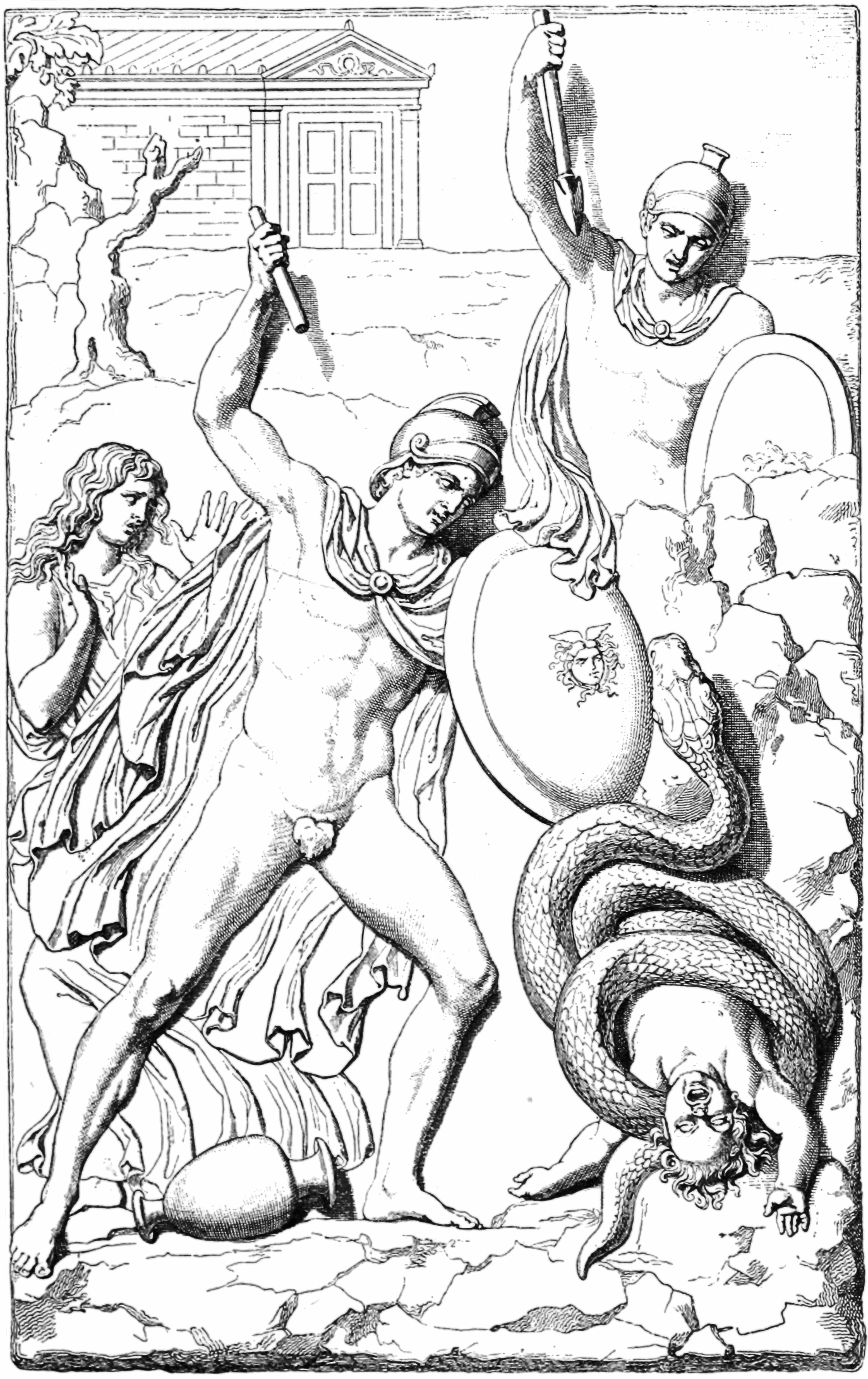
Thebaid (Greek Poem)
The ''Thebaid'' or ''Thebais'' (, ''Thēbais''), also called the Cyclic ''Thebaid'', is an Ancient Greek epic poem of uncertain authorship (see Cyclic poets) sometimes attributed by early writers to Homer, for example, by the poet Callinus and the historian Herodotus. It told the story of the war between the brothers Eteocles and Polynices, and was regarded as forming part of a Theban Cycle __NOTOC__ The Theban Cycle () is a collection of four lost epics of ancient Greek literature which tells the mythological history of the Boeotian city of Thebes.West, M.L. (2003), ''Greek Epic Fragments'', Loeb Classical Library, no. 497, Cambr .... Only fragments of the text survive. See also * ''Thebaid'' (Latin poem) Select editions and translations Critical editions * . * . * . * . Translations * . (The link is to the 1st edition of 1914.) English translation with facing Greek text; now obsolete except for its translations of the ancient quotations. * . Greek text with facing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antikensammlung Wuerzburg 1016
The Antikensammlung Berlin (Berlin antiquities collection) is one of the most important collections of classical art in the world, now held in the Altes Museum and Pergamon Museum in Berlin, Germany. It contains thousands of ancient archaeological artefacts from the ancient Greek, Roman, Etruscan and Cypriot civilizations. Its main attraction is the Pergamon Altar and Greek and Roman architectural elements from Priene, Magnesia, Baalbek and Falerii. In addition, the collection includes a large number of ancient sculptures, vases, terracottas, bronzes, sarcophagi, engraved gems and metalwork. History of the collection Foundation The collection's foundations were laid in the time of the Brandenburg Elector Friedrich Wilhelm I by ancient sculptures looted in 1656 from the ''Villa Regia'' Palace in Warsaw. The obtained sculptures were purchased in Italy by Polish kings Sigismund III Vasa and Władysław IV Vasa. This core of the collection, originally housed at the Berlin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greece
Ancient Greece () was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity (), that comprised a loose collection of culturally and linguistically related city-states and communities. Prior to the Roman period, most of these regions were officially unified only once under the Kingdom of Macedon from 338 to 323 BC. In Western history, the era of classical antiquity was immediately followed by the Early Middle Ages and the Byzantine period. Three centuries after the decline of Mycenaean Greece during the Bronze Age collapse, Greek urban poleis began to form in the 8th century BC, ushering in the Archaic period and the colonization of the Mediterranean Basin. This was followed by the age of Classical Greece, from the Greco-Persian Wars to the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC, and which included the Golden Age of Athens and the Peloponnesian War. The u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epic Poem
In poetry, an epic is a lengthy narrative poem typically about the extraordinary deeds of extraordinary characters who, in dealings with gods or other superhuman forces, gave shape to the mortal universe for their descendants. With regard to oral tradition, epic poems consist of formal speech and are usually learnt word for word, and are contrasted with narratives that consist of everyday speech where the performer has the license to recontextualize the story to a particular audience, often to a younger generation. Influential epics that have shaped Western literature and culture include Homer's ''Iliad'' and ''Odyssey''; Virgil's ''Aeneid''; and the anonymous ''Beowulf'' and ''Epic of Gilgamesh''. The genre has inspired the adjective '' epic'' as well as derivative works in other mediums (such as epic films) that evoke or emulate the characteristics of epics. Etymology The English word ''epic'' comes from Latin , which itself comes from the Ancient Greek adjective () ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homer
Homer (; , ; possibly born ) was an Ancient Greece, Ancient Greek poet who is credited as the author of the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Despite doubts about his authorship, Homer is considered one of the most revered and influential authors in history. The ''Iliad'' centers on a quarrel between King Agamemnon and the warrior Achilles during the last year of the Trojan War. The ''Odyssey'' chronicles the ten-year journey of Odysseus, king of Homer's Ithaca, Ithaca, back to his home after the fall of Troy. The epics depict man's struggle, the ''Odyssey'' especially so, as Odysseus perseveres through the punishment of the gods. The poems are in Homeric Greek, also known as Epic Greek, a literary language that shows a mixture of features of the Ionic Greek, Ionic and Aeolic Greek, Aeolic dialects from different centuries; the predominant influence is Eastern Ionic. Most researchers believe that the poems w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Callinus
Callinus (, ''Kallinos''; fl. mid-7th c. BC) was an ancient Greek elegiac poet who lived in the city of Ephesus in Asia Minor in the mid-7th century BC. His poetry is representative of the genre of martial exhortation elegy in which Tyrtaeus also specialized and which both Archilochus and Mimnermus appear to have composed. Along with these poets, all his near contemporaries, Callinus was considered the inventor of the elegiac couplet by some ancient critics. He resided in Ephesus in Asia Minor. He is supposed to have flourished between the invasion of Asia Minor by the Cimmerians and their expulsion by Alyattes (630–560 BC). During his lifetime his own countrymen were also engaged in a life-and-death struggle with the Magnesians. These two events give the key to his poetry, in which he endeavours to rouse the indolent Ionians to a sense of patriotism. Only a few fragments of the Callinus' poetry have survived. One of the longest fragments, consisting of 21 lines of verse, is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herodotus
Herodotus (; BC) was a Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus (now Bodrum, Turkey), under Persian control in the 5th century BC, and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria, Italy. He wrote the '' Histories'', a detailed account of the Greco-Persian Wars, among other subjects such as the rise of the Achaemenid dynasty of Cyrus. He has been described as " The Father of History", a title conferred on him by the ancient Roman orator Cicero, and the " Father of Lies" by others. The ''Histories'' primarily cover the lives of prominent kings and famous battles such as Marathon, Thermopylae, Artemisium, Salamis, Plataea, and Mycale. His work deviates from the main topics to provide a cultural, ethnographical, geographical, and historiographical background that forms an essential part of the narrative and provides readers with a wellspring of additional information. Herodotus was criticized in his times for his inclusion of "legends an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eteocles
In Greek mythology, Eteocles (; ) was a king of Ancient Thebes (Boeotia), Thebes, the son of Oedipus and either Jocasta or Euryganeia. Oedipus killed his father Laius and married his mother without knowing his relationship to either. When the relationship was revealed, he was expelled from Thebes. The rule passed to his sons Eteocles and Polynices. However, because of a curse from their father, the two brothers did not share the rule peacefully and died as a result, ultimately killing each other in battle for control of the city. Upon his death, Eteocles was succeeded by his uncle, Creon of Thebes, Creon. Etymology The name translates as "truly glorious", from ''eteós'' “true” and ''kleos'' “glory”. The name appears in earlier form ''*Etewoklewes'' (), attested in Mycenaean Greek tablets as ''E-te-wo-ke-le-we''. ''Tawagalawas'' is thought to be the Hittite language, Hittite rendition of the Greek name. Oedipus's curse In the ''Thebaid (Greek poem), Thebaid'', the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polynices
In Greek mythology, Polynices (also Polyneices) (; ) was the son of Oedipus and either Jocasta or Euryganeia and the older brother of Eteocles. When Oedipus was discovered to have killed his father and married his mother, Oedipus was expelled from Thebes, leaving Eteocles and Polynices to rule. Because of a curse put on them by their father, the two sons did not share the rule peacefully. During a battle for control over Thebes, the brothers killed each other. Mythology Oedipus's curse In the ''Thebaid'', the brothers were cursed by their father for their disrespect towards him on two occasions. The first of these occurred when they served him using the silver table of Cadmus and a golden cup, which he had forbidden. The brothers then sent him the haunch of a sacrificed animal, rather than the shoulder, which he deserved. Enraged, Oedipus prayed to Zeus that the brothers would die by each other's hand. However, in Sophocles' '' Oedipus at Colonus'', Oedipus desired to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theban Cycle
__NOTOC__ The Theban Cycle () is a collection of four lost epics of ancient Greek literature which tells the mythological history of the Boeotian city of Thebes.West, M.L. (2003), ''Greek Epic Fragments'', Loeb Classical Library, no. 497, Cambridge, MA, . They were composed in dactylic hexameter verse and believed to be recorded between 750 and 500 BC. The epics took place before the Trojan War and centered around the Theban royal family. The epics of the Theban Cycle were the '' Oedipodea'', the ''Thebaid'', the '' Epigoni'', and the '' Alcmeonis''. Overview In the collection, the precise sequence of events and the handling of characters and plots are difficult to reconstruct. There are very few fragments for the ''Oedipodea''. For the ''Epigoni'' there are less than ten fragments and only three verbatim fragments totaling four lines. In addition, unlike the poetry of the Trojan cycle, there is no prose summary. * The ''Oedipodea'': There are a total of 6,600 verses, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thebaid (Latin Poem)
The ''Thebaid'' (; ) is a Latin epic poem written by the Roman poet Statius. Published in the early 90s AD, it contains 9748 lines arranged in 12 books, and recounts the clash of two brothers, Eteocles and Polynices, over the throne of the Greek city of Thebes, Greece, Thebes. After Polynices is sent into exile, he forges an alliance of Seven against Thebes, seven Greek princes and embarks on a military campaign against his brother. Although its source material derives predominantly from the Ancient Greek literature, Greek literary tradition, the ''Thebaid'' has close ties with other Latin texts such as Virgil's ''Aeneid'' and Senecan tragedy, the tragedies of Seneca the Younger. The poem's central themes include the relationship between politics and the family, civil war, and the amoral acts to which it gives rise. Critics have also noted the poem's innovative depiction of Roman mythology. Following in the footsteps of Ovid, Ovid's ''Metamorphoses'', Statius used an episodic w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loeb Classical Library
The Loeb Classical Library (LCL; named after James Loeb; , ) is a monographic series of books originally published by Heinemann and since 1934 by Harvard University Press. It has bilingual editions of ancient Greek and Latin literature, with the original Greek or Latin text on the left-hand page and a fairly literal translation on the facing page. History Under the inspiration drawn from the book series specializing in publishing classical texts exclusively in the original languages, such as the Bibliotheca Teubneriana, established in 1849 or the Oxford Classical Texts book series, founded in 1894, the Loeb Classical Library was conceived and initially funded by the Jewish-German-American banker and philanthropist James Loeb (1867–1933). The first volumes were edited by Thomas Ethelbert Page, W. H. D. Rouse, and Edward Capps, and published by William Heinemann, Ltd. (London) in 1912, already in their distinctive green (for Greek text) and red (for Latin) hardco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |