|
The Zetkin Collective
The Zetkin Collective is a research group made up of activists and academics. It focuses on analyzing and explaining the political ecology of the far-right, including ecofascism and Malthusianism as well as climate change denial and eco-nationalism. The group began within the human ecology department of Lund University in Sweden. The collective is named after Clara Zetkin, a German Marxist theorist who studied the Italian fascist movement in 1923. Its work draws on the definition of fascism created by Zetkin. The collective authored the book ''White Skin, Black Fuel: On the Danger of Fossil Fascism'', which was published by Verso press. In 2020, the French-language French ( or ) is a Romance language of the Indo-European family. It descended from the Vulgar Latin of the Roman Empire, as did all Romance languages. French evolved from Gallo-Romance, the Latin spoken in Gaul, and more specifically in No ... edition ''Fascisme fossile:'' ''L'extrême droite, l'énergie, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sweden
Sweden, ; fi, Ruotsi; fit, Ruotti; se, Ruoŧŧa; smj, Svierik; sje, Sverji; sju, Sverje; sma, Sveerje or ; yi, שוועדן, Shvedn; rmu, Svedikko; rmf, Sveittiko. formally the Kingdom of Sweden, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. It borders Norway to the west and north, and Finland to the east. At , Sweden is the largest Nordic country and the List of European countries by area, fifth-largest country in Europe. The Capital city, capital and largest city is Stockholm. Sweden has a population of 10.5 million, and a low population density of ; around 87% of Swedes reside in urban areas in the central and southern half of the country. Sweden’s urban areas together cover 1.5% of its land area. Because the country is so long, ranging from 55th parallel north, 55°N to 69th parallel north, 69°N, the climate of Sweden is diverse. Sweden has been inhabited since Prehistoric Sweden, prehistoric times, . T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Le Devoir
''Le Devoir'' (, "Duty") is a French-language newspaper published in Montreal and distributed in Quebec and throughout Canada. It was founded by journalist and politician Henri Bourassa in 1910. ''Le Devoir'' is one of few independent large-circulation newspapers in Quebec (and one of the few in Canada) in a market dominated by the media conglomerate Quebecor (including '' Le Journal de Montréal''). Historically ''Le Devoir'' was considered Canada's francophone newspaper of record, although in the 21st century it has been challenged for that title by the increased status of competitor '' La Presse''. History Henri Bourassa, a young Liberal Party MP from Montreal, rose to national prominence in 1899 when he resigned his seat in Parliament in protest at the Liberal government's decision to send troops to support the British in the South African War of 1899–1902. Bourassa was opposed to all Canadian participation in British wars and would go on to become a key figure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Language
French ( or ) is a Romance language of the Indo-European family. It descended from the Vulgar Latin of the Roman Empire, as did all Romance languages. French evolved from Gallo-Romance, the Latin spoken in Gaul, and more specifically in Northern Gaul. Its closest relatives are the other langues d'oïl—languages historically spoken in northern France and in southern Belgium, which French (Francien) largely supplanted. French was also influenced by native Celtic languages of Northern Roman Gaul like Gallia Belgica and by the ( Germanic) Frankish language of the post-Roman Frankish invaders. Today, owing to France's past overseas expansion, there are numerous French-based creole languages, most notably Haitian Creole. A French-speaking person or nation may be referred to as Francophone in both English and French. French is an official language in 29 countries across multiple continents, most of which are members of the '' Organisation internationale de la Francopho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London Review Of Books
The ''London Review of Books'' (''LRB'') is a British literary magazine published twice monthly that features articles and essays on fiction and non-fiction subjects, which are usually structured as book reviews. History The ''London Review of Books'' was founded in 1979, when publication of ''The Times Literary Supplement'' was suspended during the year-long lock-out at ''The Times''. Its founding editors were Karl Miller, then professor of English at University College London; Mary-Kay Wilmers, formerly an editor at ''The Times Literary Supplement''; and Susannah Clapp, a former editor at Jonathan Cape. For its first six months, it appeared as an insert in ''The New York Review of Books''. It became an independent publication in May 1980. Its political stance has been described by Alan Bennett Alan Bennett (born 9 May 1934) is an English actor, author, playwright and screenwriter. Over his distinguished entertainment career he has received numerous awards and honou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Definitions Of Fascism
What constitutes a definition of fascism and fascist governments has been a complicated and highly disputed subject concerning the exact nature of fascism and its core tenets debated amongst historians, political scientists, and other scholars since Benito Mussolini first used the term in 1915. Historian Ian Kershaw once wrote that "trying to define 'fascism' is like trying to nail jelly to the wall". A significant number of scholars agree that a "fascist regime" is foremost an authoritarian form of government, although not all authoritarian regimes are fascist. Authoritarianism is thus a defining characteristic, but most scholars will say that more distinguishing traits are needed to make an authoritarian regime fascist. Similarly, ''fascism'' as an ideology is also hard to define. Originally, it referred to a totalitarian political movement linked with corporatism which existed in Italy from 1922 to 1943 under the leadership of Benito Mussolini. Many scholars use the word "fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
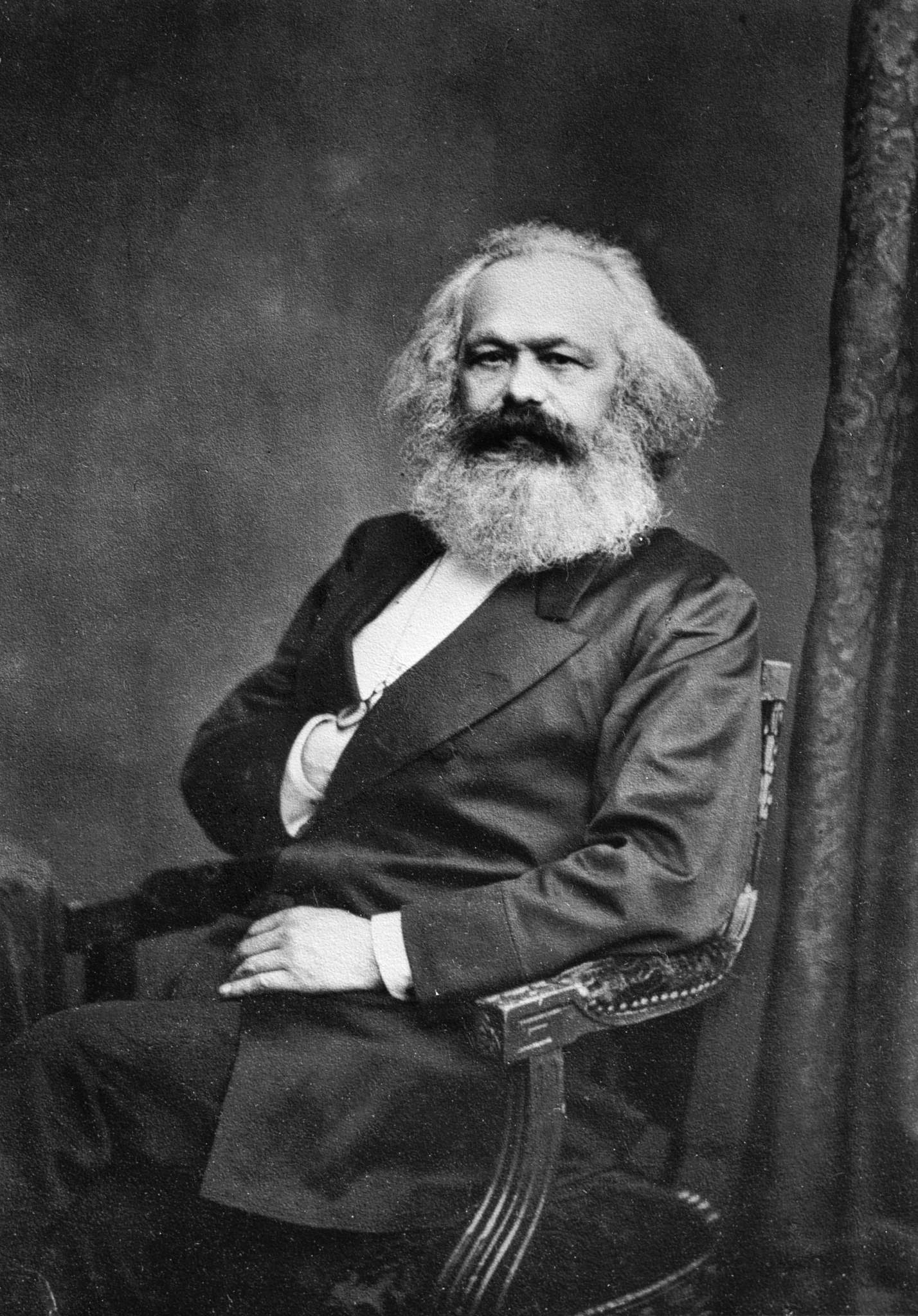
Marxism
Marxism is a left-wing to far-left method of socioeconomic analysis that uses a materialist interpretation of historical development, better known as historical materialism, to understand class relations and social conflict and a dialectical perspective to view social transformation. It originates from the works of 19th-century German philosophers Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels. As Marxism has developed over time into various branches and schools of thought, no single, definitive Marxist theory exists. In addition to the schools of thought which emphasize or modify elements of classical Marxism, various Marxian concepts have been incorporated and adapted into a diverse array of social theories leading to widely varying conclusions. Alongside Marx's critique of political economy, the defining characteristics of Marxism have often been described using the terms dialectical materialism and historical materialism, though these terms were coined after Marx's death and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
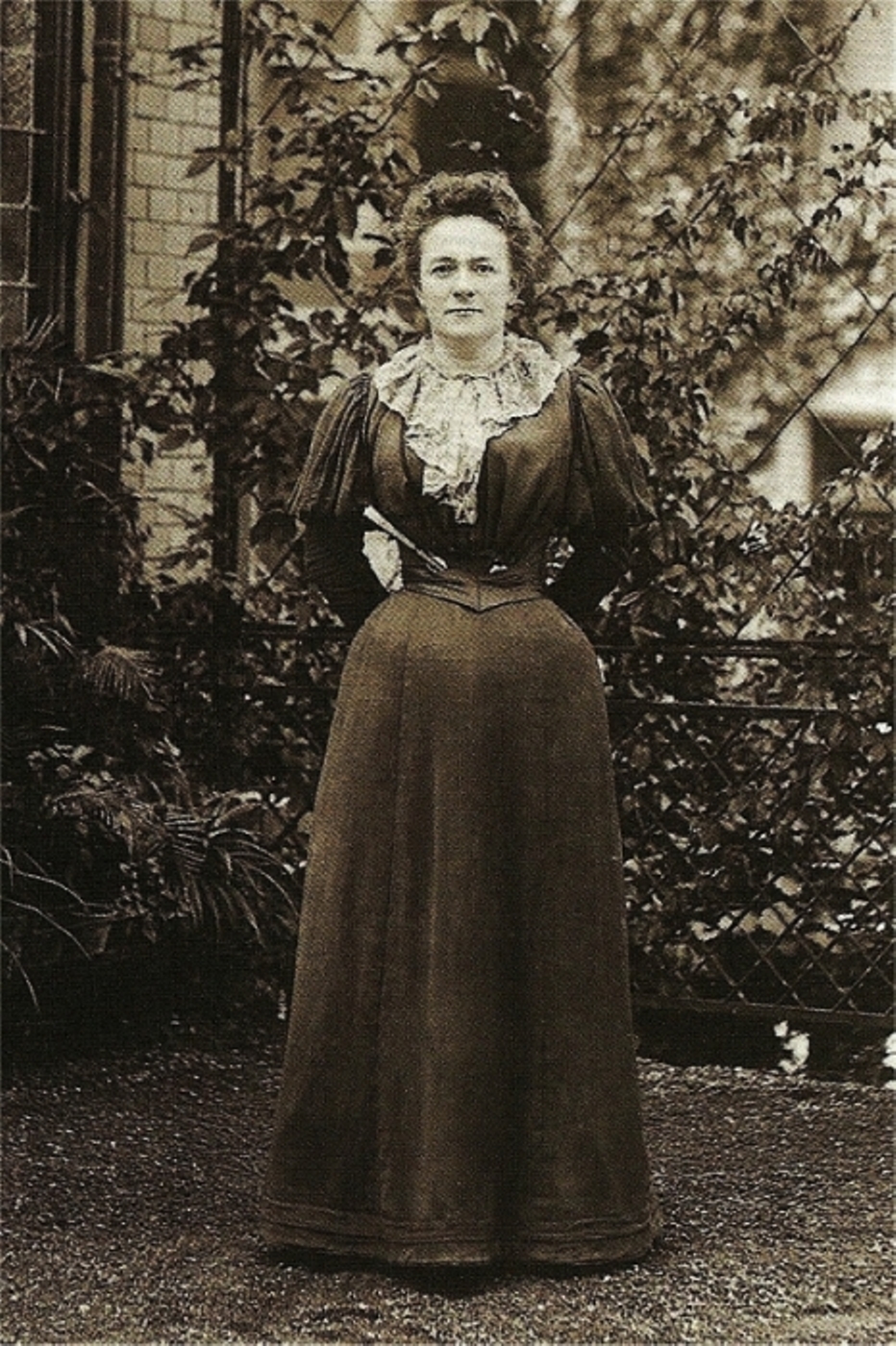
Clara Zetkin
Clara Zetkin (; ; ''née'' Eißner ; 5 July 1857 – 20 June 1933) was a German Marxist theorist, communist activist, and advocate for women's rights. Until 1917, she was active in the Social Democratic Party of Germany. She then joined the Independent Social Democratic Party of Germany (USPD) and its far-left wing, the Spartacist League. This later became the Communist Party of Germany (KPD), which she represented in the Reichstag during the Weimar Republic from 1920 to 1933. Biography Background and education Clara Josephine Eißner (Eissner) was born the eldest of three children in , a peasant village in Saxony, now part of the municipality Königshain-Wiederau. Her father, Gottfried Eissner, was a schoolmaster, church organist and a devout Protestant, while her mother, Josephine Vitale, had French roots, came from a middle-class family from Leipzig and was highly educated. In 1872, her family moved to Leipzig, where she was educated at the Leipzig Teachers’ Coll ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lund University
, motto = Ad utrumque , mottoeng = Prepared for both , established = , type = Public research university , budget = SEK 9 billion Facts and figures Lund University web site. , head_label = Vice Chancellor , head = Erik Renström , academic_staff = 4,780 (2022) (academic staff, researchers and employed research students) , administrative_staff = 2,890 (2022) , students = 46 000 (29 000 full-time equivalents) [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Ecology
Human ecology is an interdisciplinary and transdisciplinary study of the relationship between humans and their natural, social, and built environments. The philosophy and study of human ecology has a diffuse history with advancements in ecology, geography, sociology, psychology, anthropology, zoology, epidemiology, public health, and home economics, among others. Historical development The roots of ecology as a broader discipline can be traced to the Greeks and a lengthy list of developments in natural history science. Ecology also has notably developed in other cultures. Traditional knowledge, as it is called, includes the human propensity for intuitive knowledge, intelligent relations, understanding, and for passing on information about the natural world and the human experience. The term ecology was coined by Ernst Haeckel in 1866 and defined by direct reference to ''the economy of nature''. Like other contemporary researchers of his time, Haeckel adopted his terminology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Climate Change Denial
Climate change denial, or global warming denial, is Denial (Freud), denial, dismissal, or doubt that contradicts the scientific consensus on climate change, including the extent to which it is Attribution of recent climate change, caused by humans, its Effects of global warming, effects on nature and human society, or the potential of adaptation to global warming by human actions. Many who deny, dismiss, or hold doubt about the scientific consensus on Anthropogenic hazard, anthropogenic global warming self-label as "climate change skeptics", which several scientists have noted is misnomer, an inaccurate description. Climate change denial can also be implicit when individuals or social groups accept the science but fail to come to terms with it or to translate their acceptance into action. Several social science studies have analyzed these positions as forms of denial or denialism,: "There is debate over which term is most appropriate ... Those involved in challenging climate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)