|
The Siege Of Oxford
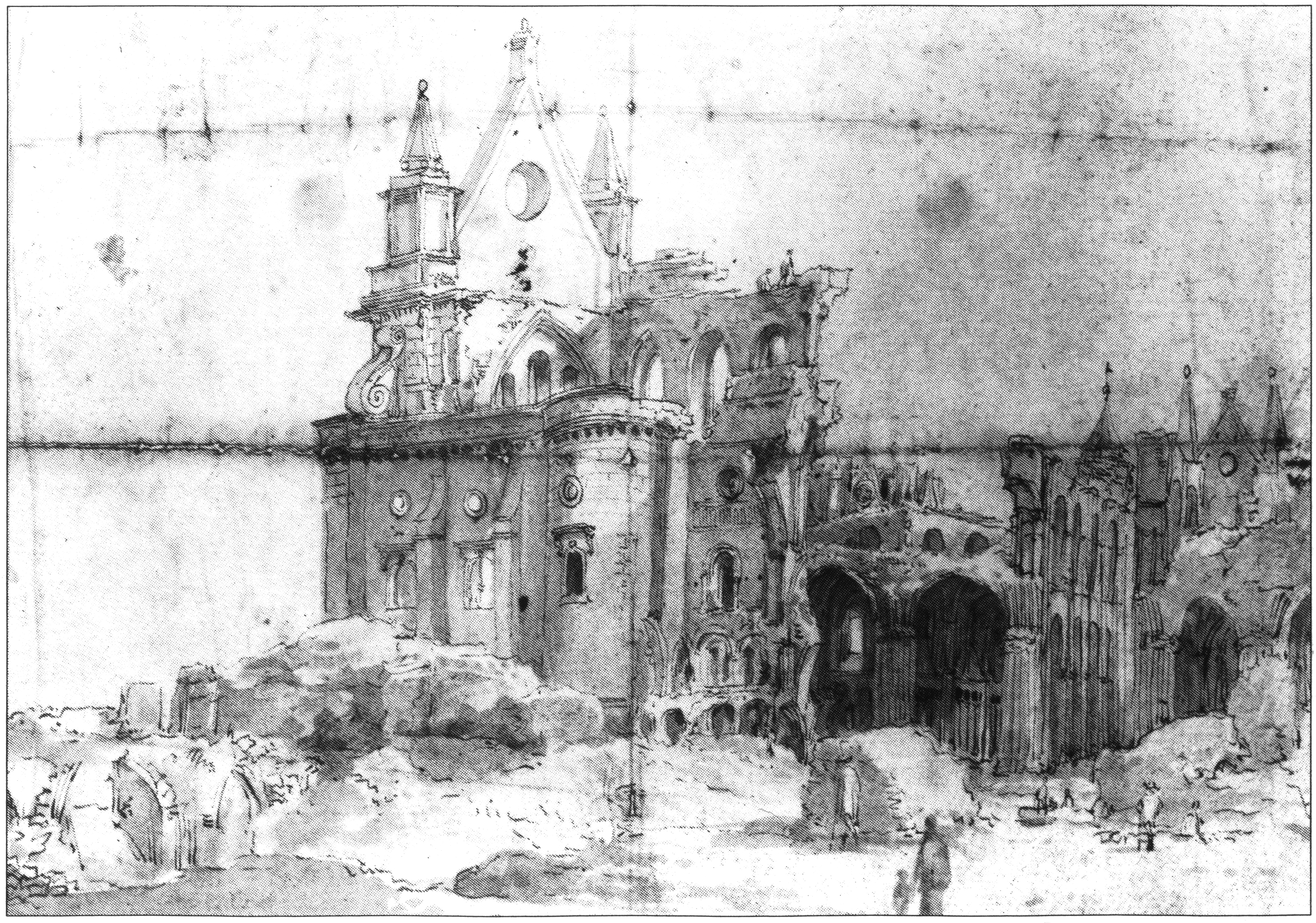
''The Siege of Oxford'' is a 1689 oil painting by the Dutch artist Jan Wyck. It depicts the Siege of Oxford in 1646 during the First English Civil War. Oxford had functioned as the Royalist capital throughout the war as London was in Parliamentary hands. Following the Battle of Naseby a more concerted attack on Oxford was launched, with artillery batteries established on Headington Hill to bombard the town into submission. It provides an unusual, panoramic view of the many fortifications defending the city. It is today in the Museum of Oxford The Museum of Oxford (MOX) is a history museum in Oxford, England, covering the history of Oxford and its people. The museum includes both permanent and temporary displays featuring artefacts relating to Oxford's history from prehistoric times ....https://artuk.org/discover/artworks/the-siege-of-oxford-43359 References Bibliography * Black, Jeremy. ''The Cambridge Illustrated Atlas of Warfare: Renaissance to Revolution, 1492-1792''. C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jan Wyck
Jan Wyck (also Jan Wiyck or Jan Wick) (29 October 1645 – 17 May 1702) was a Dutch baroque painter, best known for his works on military subjects. There are still over 150 of his works known to be in existence. In an era when French artists dominated the genre, the arrival of Wyck and other Dutch and Flemish artists in Great Britain from 1660 onwards provided the catalyst for the development of military and naval art in Britain. Like other painters from the Low Countries such as Dirk Maas, Peter Tillemans and William van de Velde, Wyck moved to England and worked there throughout his life, often under royal patronage, producing many fine works of battle paintings, portraits, hunting scenes and landscapes as well as advancing the development of British art through teaching.Oxford Dictionary of National Biography:Wyck, Jan, by Katherine Gibson pp.615 Early life Jan Wyck was born on 29 October 1652, in Haarlem, then part of the Dutch Republic. The son of Thomas Wyck (1616-167 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roundhead
Roundheads were the supporters of the Parliament of England during the English Civil War (1642–1651). Also known as Parliamentarians, they fought against King Charles I of England and his supporters, known as the Cavaliers or Royalists, who claimed rule by absolute monarchy and the principle of the divine right of kings. The goal of the Roundheads was to give to Parliament the supreme control over executive branch, executive administration of England. Beliefs Most Roundheads sought constitutional monarchy in place of the absolute monarchy sought by Charles; however, at the end of the English Civil War in 1649, public antipathy towards the king was high enough to allow republican leaders such as Oliver Cromwell to abolish the monarchy completely and establish the Commonwealth of England. The Roundhead commander-in-chief of the first Civil War, Thomas Fairfax, remained a supporter of constitutional monarchy, as did many other Roundhead leaders such as Edward Montagu, 2nd Earl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
War Paintings
War is an armed conflict between the armed forces of states, or between governmental forces and armed groups that are organized under a certain command structure and have the capacity to sustain military operations, or between such organized groups. It is generally characterized by widespread violence, destruction, and mortality, using regular or irregular military forces. ''Warfare'' refers to the common activities and characteristics of types of war, or of wars in general. Total war is warfare that is not restricted to purely legitimate military targets, and can result in massive civilian or other non-combatant suffering and casualties. Etymology The English word ''war'' derives from the 11th-century Old English words and , from Old French ( as in modern French), in turn from the Frankish , ultimately deriving from the Proto-Germanic language">Proto-Germanic . The word is related to the Old Saxon , Old High German , and the modern German , meaning . History Anth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Paintings
History painting is a genre in painting defined by its subject matter rather than any artistic style or specific period. History paintings depict a moment in a narrative story, most often (but not exclusively) Greek and Roman mythology and Bible stories, opposed to a specific and static subject, as in portrait, still life, and landscape painting. The term is derived from the wider senses of the word ''historia'' in Latin and ''histoire'' in French, meaning "story" or "narrative", and essentially means "story painting". Most history paintings are not of scenes from history, especially paintings from before about 1850. In modern English, "historical painting" is sometimes used to describe the painting of scenes from history in its narrower sense, especially for 19th-century art, excluding religious, mythological, and allegorical subjects, which are included in the broader term "history painting", and before the 19th century were the most common subjects for history paintings. Hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paintings By Jan Wyck
Painting is a visual art, which is characterized by the practice of applying paint, pigment, color or other medium to a solid surface (called "matrix" or "support"). The medium is commonly applied to the base with a brush. Other implements, such as palette knives, sponges, airbrushes, the artist's fingers, or even a dripping technique that uses gravity may be used. One who produces paintings is called a painter. In art, the term "painting" describes both the act and the result of the action (the final work is called "a painting"). The support for paintings includes such surfaces as walls, paper, canvas, wood, glass, lacquer, pottery, leaf, copper and concrete, and the painting may incorporate other materials, in single or multiple form, including sand, clay, paper, cardboard, newspaper, plaster, gold leaf, and even entire objects. Painting is an important form of visual art, bringing in elements such as drawing, composition, gesture, narration, and abstraction. Paintings can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |