|
The Quality Of Nationality Index
The Quality of Nationality Index (QNI) ranks the quality of nationalities based on internal and external factors. Each nationality receives an aggregated score based on economic strength, human development, ease of travel, political stability and overseas employment opportunities for their citizens. The QNI was created by Dimitry Kochenov and Christian Kälin, chairman of Henley & Partners. Significance The phenomenon of being a native of any country was described as 'a birthright lottery' by Ayelet Shachar, Professor of Law, Political Science, and Global Affairs at the University of Toronto. At the same time, the QNI shows that nationalities diverge greatly in their practical value, which is not always parallel with the characteristics of those countries, such as economic power or level of human development. Applying the methodology of the QNI, some economically strong countries have relatively unattractive nationalities. For example, Indian nationality shares 106th place wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christian Kälin
Christian H. Kälin or Kaelin (born 1971) is a Swiss businessperson, author, government advisor and lawyer who is the chairman of Henley & Partners, an architect of citizenship-by-investment programs that allow wealthy individuals to obtain additional passports. Early life and education Kälin was born in 1971 in Zürich. In his teenage years, he began collecting immigration and citizenship laws from different countries, writing to embassies to request copies of their legislation and keeping the documents in a big binder. He told writer and journalist Atossa Araxia Abrahamian of this time in his life: "What always fascinated me was the inclusionary and exclusionary aspect of citizenship....I wanted to understand how different countries handled this." Kälin studied in Paris, Auckland, and Zurich. He earned master's and PhD degrees in law from the University of Zurich. His doctoral thesis was published under the title ''Ius Doni: The Acquisition of Citizenship by Investment. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mahbub Ul Haq
Mahbub ul-Haq (; ) was a Pakistani economist, international development theorist, and politician who served as the minister of Finance from 10 April 1985 to 28 January 1986, and again from June to December 1988 as a caretaker. Regarded as one of the greatest economists of his time, Haq devised the Human Development Index, widely used to gauge the development of nations. After graduating with a degree in economics from the Government College University in Lahore, he won a scholarship to the University of Cambridge in England, where he obtained a second higher degree in the same field. He later received his PhD from Yale University in the United States and conducted postdoctoral research at the Harvard Kennedy School. Haq returned to Pakistan to serve as the chief economist of the Planning Commission throughout the 1960s. In 1970, after the fall of Ayub Khan, Haq moved to Washington, D.C. to serve at the World Bank as Director of Policy Planning until 1982, where he played ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economic Community Of West African States
The Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS; also known as CEDEAO in French and Portuguese) is a regional political and economic union of twelve countries of West Africa. Collectively, the present and former members comprise an area of and have an estimated population of over 424.34 million. Considered one of the pillar regional blocs of the continent-wide African Economic Community (AEC), the stated goal of ECOWAS is to achieve "collective self-sufficiency" for its member states by creating a single large trade bloc by building a full economic and trading union. Additionally, ECOWAS aims to raise living standards and promote economic development. The union was established on 28 May 1975, with the signing of the Treaty of Lagos, with its stated mission to promote economic integration across the region. A revised version of the treaty was agreed and signed on 24 July 1993 in Cotonou, the largest city in Benin. ECOWAS's published principles include equality and int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
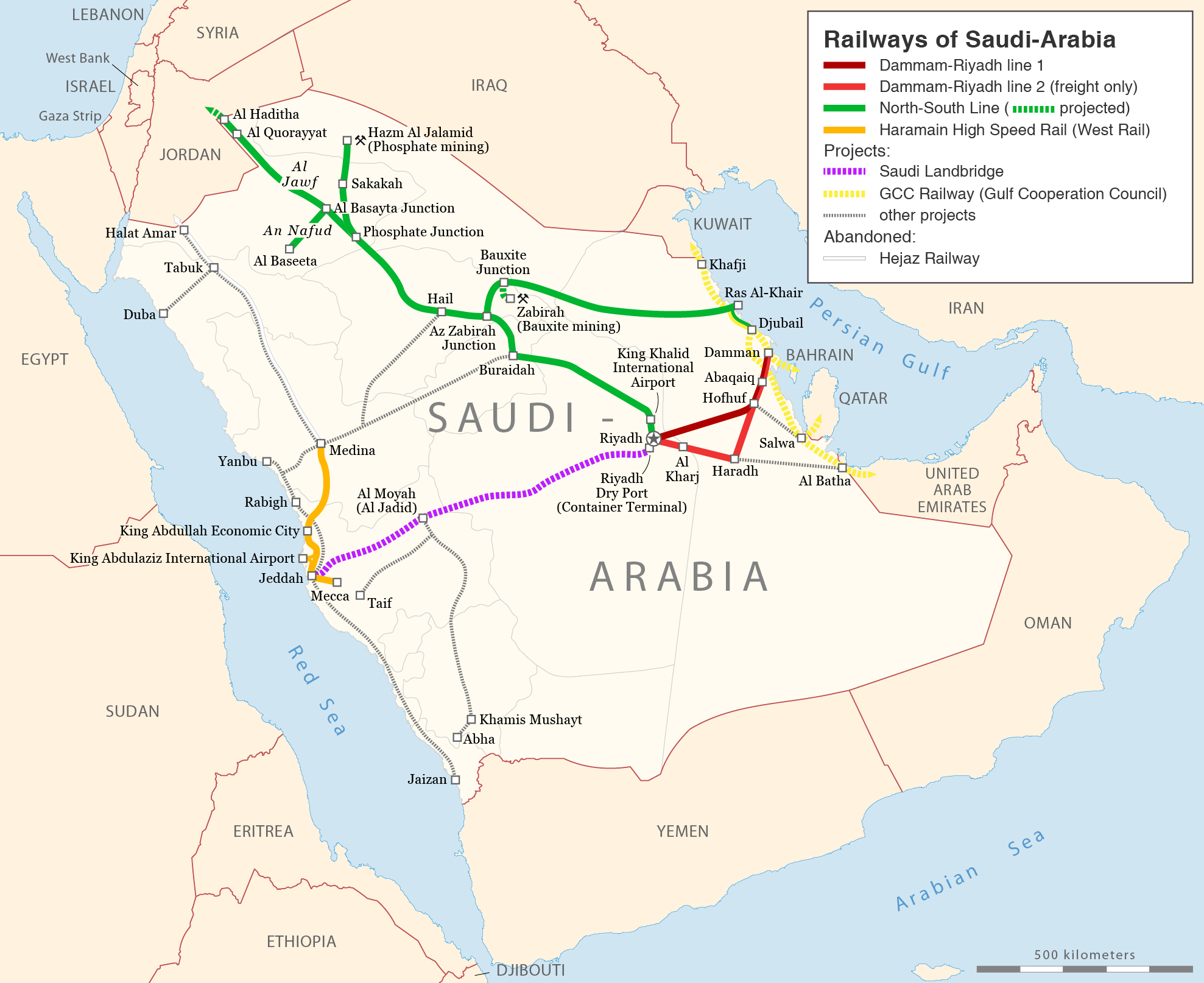
Gulf Cooperation Council
The Cooperation Council for the Arab States of the Gulf (), also known as the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC; ), is a Regional integration, regional, intergovernmental organization, intergovernmental, political, and economic union comprising Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, and the United Arab Emirates. The council's main headquarters is located in Riyadh, the capital of Saudi Arabia. The Charter of the GCC was signed on 25 May 1981, formally establishing the institution. All current member states are monarchy, monarchies, including three Constitutional monarchy, constitutional monarchies (Qatar, Kuwait, and Bahrain), two absolute monarchies (Saudi Arabia and Oman), and one federal monarchy (the United Arab Emirates, which is composed of seven member states, each of which is an absolute monarchy with its own emir). There have been discussions regarding the future membership of Jordan, Morocco, and Yemen. Iraq is the only Arab states of the Persian Gulf, Gulf Arab stat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mercosur
The Southern Common Market (commonly known by abbreviation ''Mercosur'' in Spanish and ''Mercosul'' in Portuguese) is a South American trade bloc established by the Treaty of Asunción in 1991 and Protocol of Ouro Preto in 1994. Its full members are Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Paraguay, and Uruguay. Venezuela is a full member but has been suspended since 1 December 2016. Chile, Colombia, Ecuador, Guyana, Panama, Peru, and Suriname are associate countries. Mercosur's origins are linked to the discussions for the constitution of a regional economic market for Latin America, which go back to the treaty that established the Latin American Free Trade Association in 1960, which was succeeded by the Latin American Integration Association in the 1980s. At the time, Argentina and Brazil made progress in the matter, signing the Iguaçu Declaration (1985), which established a bilateral commission, which was followed by a series of trade agreements the following year. The Integration, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated population of over 449million as of 2024. The EU is often described as a ''sui generis'' political entity combining characteristics of both a federation and a confederation. Containing 5.5% of the world population in 2023, EU member states generated a nominal gross domestic product (GDP) of around €17.935 trillion in 2024, accounting for approximately one sixth of global economic output. Its cornerstone, the European Union Customs Union, Customs Union, paved the way to establishing European Single Market, an internal single market based on standardised European Union law, legal framework and legislation that applies in all member states in those matters, and only those matters, where the states ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Air Transport Association
The International Air Transport Association (IATA ) is an airline trade association founded in 1945. IATA has been described as a cartel since, in addition to setting technical standards for airlines, IATA also organized tariff conferences that served as a forum for price fixing. According to IATA, the trade association represents 317 airlines, including major carriers, from over 120 countries. The IATA's member airlines account for carrying approximately 82% (2020) of total available seat miles air traffic. IATA supports airline activity and helps formulate industry policy and standards. It is headquartered in Montreal, Canada, with executive offices in Geneva, Switzerland. History IATA was formed in April 1945 in Havana, Cuba. It is the successor to the International Air Traffic Association, which was formed in 1919 at The Hague, Netherlands. At its founding, IATA consisted of 57 airlines from 31 countries. Much of IATA's early work was technical and IATA provided input to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Institute For Economics And Peace
The Institute for Economics and Peace (IEP) is a global think tank headquartered in Sydney, Australia with branches in New York City, Mexico City and Oxford. IEP studies the relationship between peace, business, and prosperity, and seeks to promote understanding of the cultural, economic, and political factors that drive peacefulness. It is a registered Australian charity and works in partnership with the Aspen Institute, Economists for Peace and Security, the United Nations Global Compact, Center for Strategic and International Studies and Cranfield University. It also collaborates with the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, the Commonwealth Secretariat, UNDP and UN Peacebuilding Support Office. It is chaired by technology entrepreneur Steve Killelea, founder of IR. Global Peace Index The main index produced by IEP is the Global Peace Index (GPI), a widely cited benchmark measuring peace. The GPI has been incorporated into the Stockholm International ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
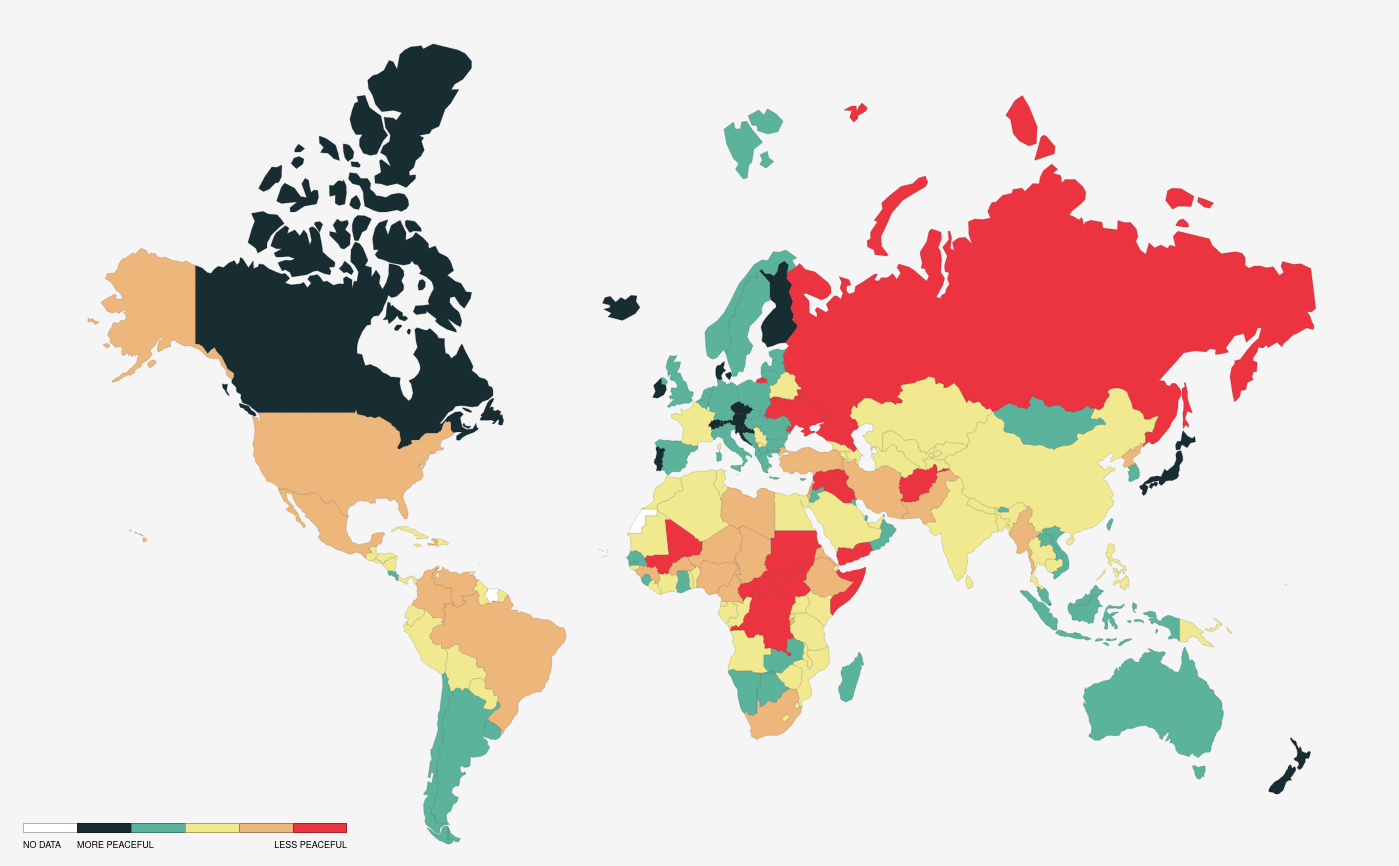
Global Peace Index
The Global Peace Index (GPI) is a report produced by the Australia-based NGO Institute for Economics & Peace (IEP) which measures the relative position of nations' and regions' peacefulness. The GPI ranks 163 independent states and territories (collectively accounting for 99.7 per cent of the world's population) according to their levels of peacefulness. In the past decade, the GPI has presented trends of increased global violence and less peacefulness. The GPI (Global Peace Index) is developed in consultation with an international panel of peace experts from peace institutes and think tanks with data collected by the Economist Intelligence Unit. The Index was first launched in 2007, with subsequent reports being released annually. In 2015 it ranked 165 countries, up from 121 in 2007. The study was conceived by Australian technology entrepreneur Steve Killelea, and is endorsed by individuals such as former UN Secretary-General Kofi Annan, the Dalai Lama, and 2008 Nobel Peace P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans and Grant (money), grants to the governments of Least developed countries, low- and Developing country, middle-income countries for the purposes of economic development. The World Bank is the collective name for the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD) and International Development Association (IDA), two of five international organizations owned by the World Bank Group. It was established along with the International Monetary Fund at the 1944 Bretton Woods Conference. After a slow start, its first loan was to France in 1947. In its early years, it primarily focused on rebuilding Europe. Over time, it focused on providing loans to developing world countries. In the 1970s, the World Bank re-conceptualized its mission of facilitating development as being oriented around poverty reduction. For the last 30 years, it has included NGOs and environmental groups in its loan portfolio. Its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Monetary Fund
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) is a major financial agency of the United Nations, and an international financial institution funded by 191 member countries, with headquarters in Washington, D.C. It is regarded as the global lender of last resort to national governments, and a leading supporter of exchange-rate economic stability, stability. Its stated mission is "working to foster global monetary cooperation, secure financial stability, facilitate international trade, promote high employment and sustainable economic growth, and poverty reduction, reduce poverty around the world." Established in July 1944 at the Bretton Woods Conference, primarily according to the ideas of Harry Dexter White and John Maynard Keynes, it started with 29 member countries and the goal of reconstructing the international monetary systems, international monetary system after World War II. In its early years, the IMF primarily focused on facilitating fixed exchange rates across the developed worl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Purchasing Power Parity
Purchasing power parity (PPP) is a measure of the price of specific goods in different countries and is used to compare the absolute purchasing power of the countries' currency, currencies. PPP is effectively the ratio of the price of a market basket at one location divided by the price of the basket of goods at a different location. The PPP inflation and exchange rate may differ from the Exchange rate, market exchange rate because of tariffs, and other transaction costs. The purchasing power parity indicator can be used to compare economies regarding their gross domestic product (GDP), labour productivity and actual individual consumption, and in some cases to analyse price convergence and to compare the cost of living between places. The calculation of the PPP, according to the OECD, is made through a ''basket of goods'' that contains a "final product list [that] covers around 3,000 consumer goods and services, 30 occupations in government, 200 types of equipment goods and about ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |