|
The Lucifer Effect
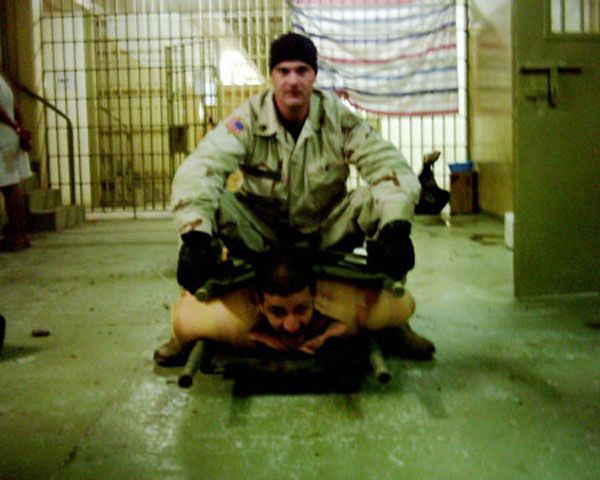
''The Lucifer Effect: Understanding How Good People Turn Evil'' is a 2007 book which includes professor Philip Zimbardo's first detailed, written account of the events surrounding the 1971 Stanford prison experiment (SPE) – a prison simulation study which had to be discontinued after only six days due to several distressing outcomes and mental breaks of the participants. The book includes over 30 years of subsequent research into the psychological and social factors which result in immoral acts being committed by otherwise moral people. It also examines the prisoner abuse at Abu Ghraib in 2003, which has similarities to the Stanford experiment. The title takes its name from the biblical story of the favored angel of God, Lucifer, his fall from grace, and his assumption of the role of Satan, the embodiment of evil. The book was briefly on ''The New York Times'' Non-Fiction Best Seller and won the American Psychological Association's 2008 William James Book Award. Overview The f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philip Zimbardo
Philip George Zimbardo (; March 23, 1933 – October 14, 2024) was an American psychologist and a professor at Stanford University. He was an internationally known educator, researcher, author and media personality in psychology who authored more than 500 articles, chapters, textbooks, and trade books covering a wide range of topics, including time perspective, cognitive dissonance, the psychology of evil, persuasion, cults, deindividuation, shyness, and heroism. He became known for his 1971 Stanford prison experiment, which was later criticized. He authored various widely used, introductory psychology textbooks for college students, and other notable works, including ''Shyness'', '' The Lucifer Effect'', and ''The Time Paradox''. He was the founder and president of the Heroic Imagination Project, a non-profit organization dedicated to promoting heroism in everyday life by training people how to resist bullying, bystanding, and negative conformity. He pioneered The Stanford Sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milgram Experiment
Beginning on August 7, 1961, a series of social psychology experiments were conducted by Yale University psychologist Stanley Milgram, who intended to measure the willingness of study participants to obey an authority figure who instructed them to perform acts conflicting with their personal conscience. Participants were led to believe that they were assisting a fictitious experiment, in which they had to administer electric shocks to a "learner". These fake electric shocks gradually increased to levels that would have been fatal had they been real. The experiments unexpectedly found that a very high proportion of subjects would fully obey the instructions, with every participant going up to 300 volts, and 65% going up to the full 450 volts. Milgram first described his research in a 1963 article in the ''Journal of Abnormal and Social Psychology'' [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Psychology
Social psychology is the methodical study of how thoughts, feelings, and behaviors are influenced by the actual, imagined, or implied presence of others. Although studying many of the same substantive topics as its counterpart in the field of sociology, psychological social psychology places more emphasis on the individual, rather than society; the influence of social structure and culture on individual outcomes, such as personality, behavior, and one's position in social hierarchies. Social psychologists typically explain human behavior as a result of the relationship between mental states and social situations, studying the social conditions under which thoughts, feelings, and behaviors occur, and how these variables influence social interactions. History 19th century In the 19th century, social psychology began to emerge from the larger field of psychology. At the time, many psychologists were concerned with developing concrete explanations for the different aspe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rose McDermott
Rose McDermott is an American political scientist who is the David and Marianna Fisher University Professor of International Relations at Brown University. She has also taught at Cornell, UCSB, and Harvard. She is a member of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences and the recipient of numerous awards and fellowships. Her work is situated at the intersection of several disciplines including political science, psychology, biology, methods, development, and gender studies. Early life and education McDermott was raised in Hawaii, United States. Her father was in the Navy. She has a B.A. in Political Science from Stanford University (1984), M.A. in Political Science from Columbia University (1986), M.A. in Experimental Social Psychology from Stanford University (1988), M.A. in Political Science from Stanford University (1990) and a PhD in Political Science from Stanford University (1991). At Columbia University, she was strongly influenced by Robert Jervis. Research McDermott ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christina Maslach
Christina Maslach (born January 21, 1946) is an American social psychology, social psychologist and Emeritus, professor emerita of psychology at the University of California, Berkeley, known for her research on occupational burnout. She is a co-author of the Maslach Burnout InventoryMaslach, C.; Jackson, S.E. (1981). "The measurement of experienced burnout". ''Journal of Occupational Behavior, 2,'' 99–113. and Areas of Worklife Survey. Early in her professional career, Maslach was instrumental in stopping the Stanford prison experiment. In 1997, she was awarded the U.S. Professor of the Year. Education and career Maslach graduated from Berkeley High School (California) (1963), Radcliffe College (1967) and earned a Doctor of Philosophy, Ph.D. in psychology at Stanford University (1971).Curriculum vitae , retrieved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whistleblower
Whistleblowing (also whistle-blowing or whistle blowing) is the activity of a person, often an employee, revealing information about activity within a private or public organization that is deemed illegal, immoral, illicit, unsafe, unethical or fraudulent. Whistleblowers can use a variety of internal or external channels to communicate information or allegations. Over 83% of whistleblowers report internally to a supervisor, human resources, compliance, or a neutral third party within the company, hoping that the company will address and correct the issues. A whistleblower can also bring allegations to light by communicating with external entities, such as the media, government, or law enforcement. Some countries legislate as to what constitutes a protected disclosure, and the permissible methods of presenting a disclosure. Whistleblowing can occur in the private sector or the public sector. Whistleblowers often face retaliation for their disclosure, including termination of emp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joe Darby
Sergeant Joseph M. Darby (born c. 1979) is a former U.S. Army reservist known as the whistleblower in the Abu Ghraib torture and prisoner abuse scandal. Darby is a graduate of North Star High School, near his hometown at the time, Jenners, Pennsylvania. At the time, Darby served as an M.P. at the Abu Ghraib prison, in Abu Ghraib, Iraq. After learning of the abuse, Darby was the first person to take steps to alert the U.S. military command. Disclosure of abuses at Abu Ghraib In January 2004, Darby provided two CD-ROMs of photographs to Special Agent Tyler Pieron of the U.S. Army Criminal Investigation Command, who was stationed at Abu Ghraib Prison, triggering an investigation that led to the implication of several soldiers violating the Geneva Convention. Darby initially wanted to remain anonymous, and had been assured of anonymity — he and those implicated all served in the 372nd Military Police Company, but became known when ''The New Yorker'' published his name and whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ivan Frederick
Ivan "Chip" Frederick II (born 1966) is an American former soldier who was court-martialed for prisoner abuse after the 2003–2004 Abu Ghraib prisoner abuse scandal. Along with other soldiers of his Army Reserve unit, the 372nd Military Police Company, Frederick was accused of allowing and inflicting sexual, physical, and psychological abuse on Iraqi detainees in Abu Ghraib prison, a notorious prison in Baghdad during the United States' occupation of Iraq. In May 2004, Frederick pleaded guilty to conspiracy, dereliction of duty, maltreatment of detainees, assault, and indecent acts. He was sentenced to 8 years' confinement and loss of rank and pay, and he received a dishonorable discharge. He was released on parole in October 2007, after spending four years in prison. Frederick was a staff sergeant and the senior enlisted soldier at the prison from October to December 2003. Prior to his deployment to Iraq, Frederick was a corrections officer at Buckingham Correctional Cente ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attica Prison Riot
The Attica Prison riot took place at the state prison in Attica, New York; it started on September 9, 1971, and ended on September 13 with the highest number of fatalities in the history of United States prison uprisings. Of the 43 men who died (33 inmates and 10 correctional officers and employees), all but one guard and three inmates were killed by law enforcement gunfire when the state retook control of the prison on the final day of the uprising. The Attica Uprising has been described as a historic event in the prisoners' rights movement. Prisoners revolted to seek better living conditions and political rights, claiming that they were treated as beasts. On September 9, 1971, 1,281 of the approximately 2,200 men incarcerated in the Attica Correctional Facility rioted and took control of the prison, taking 42 staff hostage. During the four days of negotiations, authorities agreed to 28 of the prisoners' demands, but did not accept the demand for the removal of Attica's ward ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deindividuation
Deindividuation is a concept in social psychology that is generally thought of as the loss of self-awareness in groups, although this is a matter of contention (see below). For the social psychologist, the level of analysis is the individual in the context of a social situation. As such, social psychologists emphasize the role of internal psychological processes. Other social scientists, such as sociologists, are more concerned with broad social, economic, political, and historical factors that influence events in a given society.Aronson, Wilson, and Akert. Social Psychology. 7th ed. Rentice Hall:2010. Overview Theories of deindividuation propose that it is a psychological state of decreased self-evaluation and decreased evaluation apprehension causing antinormative and disinhibited behavior. Deindividuation theory seeks to provide an explanation for a variety of antinormative collective behavior, such as violent crowds, lynch mobs, etc. Deindividuation theory has also been a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bibb Latané
Bibb Latané (; born July 19, 1937) is an American social psychologist. He worked with John M. Darley on bystander intervention in emergencies. He has also published many articles on social attraction in animals, social loafing in groups, and the spread of social influence in populations. Biography Latané received his B.A. from Yale in 1958 and his Ph.D. (under the mentorship of Stanley Schachter) from the University of Minnesota in 1963. He taught at Columbia University, the Ohio State University, Florida Atlantic University, and the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. In the 1980s, he was director of UNC's Institute for Research in Social Science (now the Odum Institute). He is currently director of the Center for Human Science in Chapel Hill, NC, which he founded. Latané's work with Darley involved a series of experiments that staged emergencies so that the social psychologists could observe how the presence of inactive bystanders affect the subjects' helpin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John M
John is a common English name and surname: * John (given name) * John (surname) John may also refer to: New Testament Works * Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John * First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John * Second Epistle of John, often shortened to 2 John * Third Epistle of John, often shortened to 3 John People * John the Baptist (died ), regarded as a prophet and the forerunner of Jesus Christ * John the Apostle (died ), one of the twelve apostles of Jesus Christ * John the Evangelist, assigned author of the Fourth Gospel, once identified with the Apostle * John of Patmos, also known as John the Divine or John the Revelator, the author of the Book of Revelation, once identified with the Apostle * John the Presbyter, a figure either identified with or distinguished from the Apostle, the Evangelist and John of Patmos Other people with the given name Religious figures * John, father of Andrew the Apostle and Saint Peter * Pope John ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |