|
The Echo (London)
''The Echo'', founded in 1868 in London by Cassell, Petter, Galpin & Co., was London's first halfpenny evening newspaper (earlier provincial titles included Liverpool's ''Events'' and the ''South Shields Gazette'', both launched in 1855). It was published daily except on Sunday. Sometimes its Saturday edition appeared under the name ''The Cricket Echo'' or ''The Football Echo''. Issue Number 1 appeared on 8 December 1868. ''The Echo'' ceased publication with Issue Number 11,391 on 31 July 1905. History Arthur Arnold was the editor for Messrs. Cassell, Petter & Galpin, who owned ''The Echo'' from 1868 until they sold it to Albert Grant in 1875. Upon the purchase by Grant, Arnold resigned as editor and went on a long trip to Russia and Persia. In less than 12 months as owner, Grant sold the newspaper to John Passmore Edwards in 1876. Edwards was the editor until its eventual sale in 1896 to a syndicate created for the purpose of purchasing ''The Echo''. In 1884 Edwards sold ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cassell (publisher)
Cassell is a British book publishing house founded in 1848 by John Cassell (1817–1865), which became in the 1890s an international publishing group company. In 1995, Cassell plc acquired Pinter Publishers. In December 1998, Cassell plc was bought by the Orion Publishing Group. In January 2002, Cassell imprints, including the Cassell Reference and Cassell Military, were joined with the Weidenfeld imprints to form a new division under the name of Weidenfeld & Nicolson Ltd. Cassell Illustrated survives as an imprint of the Octopus Publishing Group. History John Cassell (1817–1865), who was in turn a carpenter, temperance preacher, tea and coffee merchant, finally turned to publishing. His first publication was on 1 July 1848, a weekly newspaper called ''The Standard of Freedom'', advocating religious, political, and commercial freedom. '' The Working Man's Friend'' became another popular publication. In 1849 Cassell was dividing his time between his publishing and his groc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
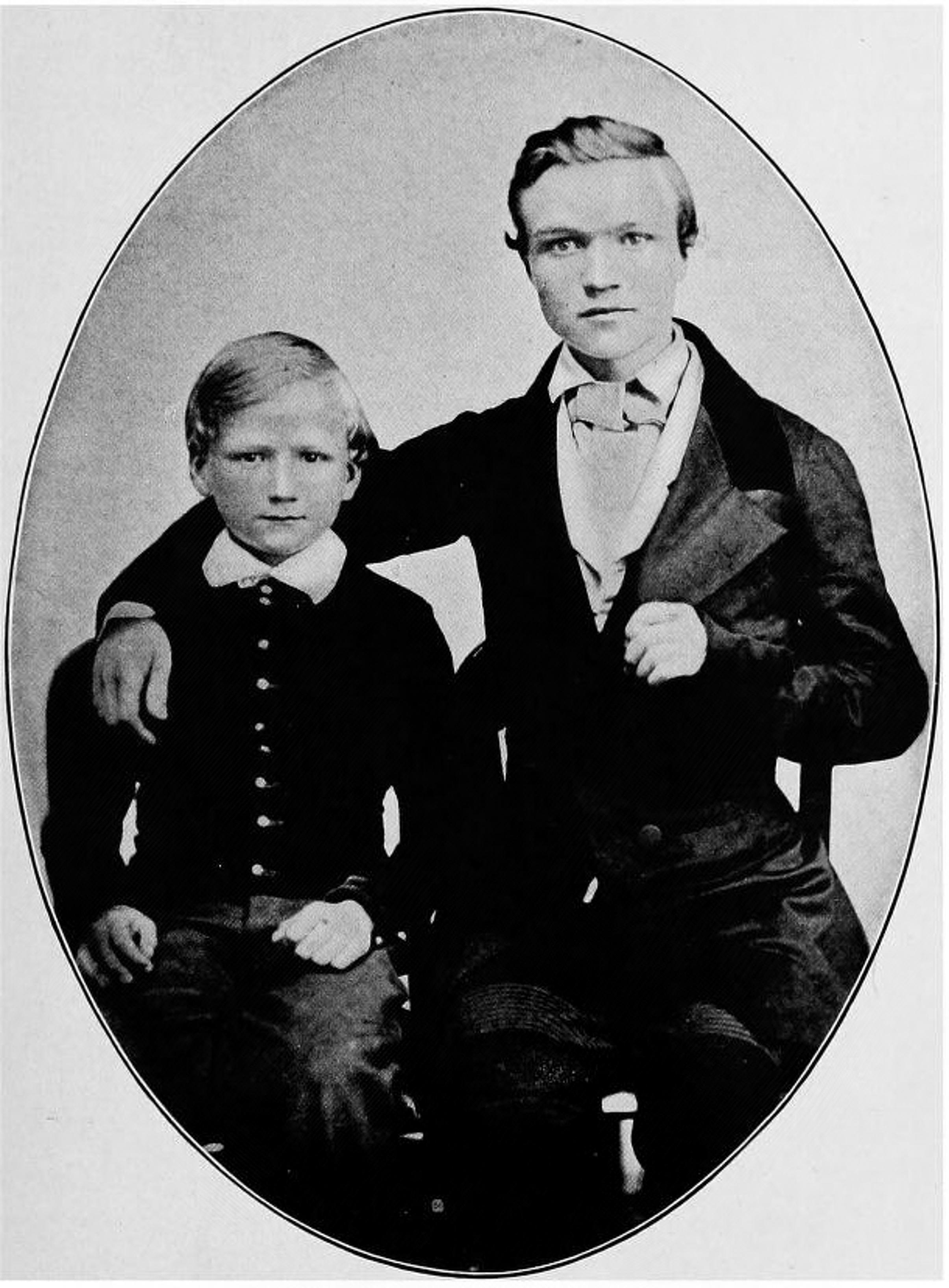
Arthur Arnold
Sir (Robert) Arthur Arnold (28 May 1833 – 20 May 1902) was a British Liberal politician and author. Biography He was the third son of Robert Coles Arnold, a justice of the peace of Framfield, Sussex, and the younger brother of poet Sir Edwin Arnold. Born in Gravesend, Kent,''Obituary: Sir Arthur Arnold'', The Times, 21 May 1902, p. 6 he was educated privately and trained as a surveyor and land agent.John Sutherland, ''The Stanford Companion to Victorian Fiction'', Stanford University Press, 1989. In 1861, he was involved in the surveying operations prior to the construction of the Thames Embankment. Two years later he was appointed under the 1863 Public Works (Manufacturing Districts) Act as an Assistant Commissioner (and later Inspector) of Public Works in Lancashire, during the Cotton Famine, and subsequently wrote ''A History of the Cotton Famine''. In his spare time he was a writer, and published two "sensation" novels: ''Ralph, or St Sepulchre's and St Stephen's'' (1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albert Grant (company Promoter)
Albert Grant (18 November 1831 – 30 August 1899) (born Abraham Gottheimer); Baron Grant in the nobility of Italy, was an Irish-born British company promoter and Conservative politician, unseated in 1874 for election offences. Early life Born in Dublin, Abraham was the son of Bernard Gottheimer, a poor Jewish pedlar from Central Europe. The family subsequently moved to London where his father became a partner in a business importing fancy goods. Abraham Gottheimer was educated in London and Paris, and assumed the name "Albert Grant" prior to his marriage to Emily Isabella Robinson in 1856. He entered employment as a clerk, later becoming a travelling salesman of wines. Company promotion In 1859 Grant established the first of a number of companies which were to fail at the expense of the shareholders. This was the Mercantile Discount Company which failed in 1861. In 1864 he established Crédit Foncier and Mobilier of England which was used as the vehicle to launch a number of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Passmore Edwards
John Passmore Edwards (24 March 1823 – 22 April 1911)ODNB article by A. J. A. Morris, 'Edwards, John Passmore (1823–1911)’, Oxford Dictionary of National Biography, Oxford University Press, Sept 2004; online edn, May 200 accessed 15 November 2007. was a British journalist, newspaper owner, and philanthropist who briefly served as a Liberal Party Member of Parliament. Early life According to his autobiography Passmore Edwards was born in Blackwater, a small village between Redruth and Truro in Cornwall, England. He had three brothers, William, Richard and James. His father was a Cornishman, a brewer by trade. His mother's maiden name was Passmore, and she had been born in Newton Abbot, Devon. He reported that in his youth there were few books available to him, and they were mostly theological in nature. At age twelve, the first book he managed to purchase for himself was Newton's ''Opticks'', and he declared that he "was just as wise at the end as I was at the beginni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrew Carnegie
Andrew Carnegie ( , ; November 25, 1835August 11, 1919) was a Scottish-American industrialist and philanthropist. Carnegie led the expansion of the History of the iron and steel industry in the United States, American steel industry in the late-19th century and became one of the List of richest Americans in history, richest Americans in history. He became a leading philanthropist in the United States, Great Britain, and the British Empire. During the last 18 years of his life, he gave away around $350 million (equivalent to $ billion in ), almost 90 percent of his fortune, to charities, foundations and universities. His 1889 article proclaiming "The Gospel of Wealth" called on the rich to use their wealth to improve society, expressed support for progressive taxation and an Inheritance tax, estate tax, and stimulated a wave of philanthropy. Carnegie was born in Dunfermline, Scotland. He immigrated to what is now Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, United States with his parents in 1848 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samuel Storey (Liberal Politician)
Samuel Storey (1841–1925) was a British politician born in County Durham. He became a Member of Parliament for Sunderland and the main founder of the ''Sunderland Echo'' newspaper. Early life Samuel Storey was born in Sherburn, near Durham, on 13 January 1841. He was the sixth son of County Durham farmer Robert Storey. When Robert died in 1843, his mother moved to Newcastle, where Samuel Storey was educated at ''St Andrew’s School''. He became a pupil-teacher there when he was 13 and then attended Durham Diocesan Training College from 1858 to 1859.''Sunderland Echo'' archive story After leaving college, Storey worked as a master at ''Birtley Church of England School'' from 1860 to 1864. However, when his mother moved from Newcastle to Monkwearmouth, Sunderland, in around 1858, he became increasingly involved in events in the town, helping to establish Sunderland Working Men's Club in 1863. Storey married Mary Ann Addison, daughter of John Addison of Monkwearmouth, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frederick Pethick-Lawrence, 1st Baron Pethick-Lawrence
Frederick William Pethick-Lawrence, 1st Baron Pethick-Lawrence, PC (né Lawrence; 28 December 1871 – 10 September 1961) was a British Labour politician who, among other things, campaigned for women's suffrage. Background and education Born in London as Frederick William Lawrence, he was the son of wealthy Unitarians who were members of the Liberal Party. Three of his father's brothers, William, James, and Edwin, were politically active in various roles, including as Lord Mayor of London and as members of parliament. Frederick was educated at Wixenford, Eton, and Trinity College, Cambridge, where he was a member of Cambridge University Liberal Club. He then became a barrister. Political career Lawrence met and fell in love with Emmeline Pethick, an active socialist and campaigner for women's votes. They finally married in 1901 after Lawrence converted to socialism. They kept separate bank accounts and they both took the surname 'Pethick Lawrence' (later Pethick-La ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frances Power Cobbe
Frances Power Cobbe (4 December 1822 – 5 April 1904) was an Anglo-Irish writer, philosopher, religious thinker, social reformer, anti-vivisection activist and leading women's suffrage campaigner. She founded a number of animal advocacy groups, including the National Anti-Vivisection Society (NAVS) in 1875 and the British Union for the Abolition of Vivisection (BUAV) in 1898, and was a member of the executive council of the London National Society for Women's Suffrage. Life Frances Power Cobbe was a member of the prominent Cobbe family, descended from Archbishop Charles Cobbe, Primate of Ireland. She was born in Newbridge House in the family estate in present-day Donabate, County Dublin. Cobbe was educated mainly at home by governesses with a brief period at a school in Brighton. She studied English literature, French, German, Italian, music, and the Bible. She then read heavily in the family library especially in religion and theology, joined several subscription libra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Percy Alden
Sir Percy Alden (6 June 1865 – 30 June 1944) was a British social worker, land reformer and radical Liberal Party politician. Born in Oxford, he was the third son of Isaac Alden, a master butcher and Harriet ''née'' Kemp. After serving twice as a member of parliament, he was killed in June 1944 by a German V-1 flying bomb. Education At the age of 15, while working as a messenger for the local examinations board, he met the philosopher T. H. Green. Green encouraged him to enter the University of Oxford. In 1884 he was admitted to Balliol College, graduating with a third in classical moderations in 1886 and '' literae humaniores'' in 1888. He subsequently began studies for the Congregational ministry at Mansfield House, Oxford. Here, he became involved in social work, and was appointed in 1891 as the first warden of the Mansfield House settlement in Canning Town, West Ham, a post he held until 1901, later serving as honorary warden and vice-president. Municipal politics From 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London Newspapers ...
This list of newspapers in London is divided into papers sold throughout the region and local publications. It is further divided into paid for and free titles. The newspaper industry in England is dominated by national newspapers, all of which are edited in London, although ''The Guardian'' began as the '' Manchester Guardian''. For a list of the national newspapers available in London see List of newspapers in the United Kingdom. Regional Local Paid for Free Defunct Printed papers moved online See also * Media in LondonDirectory of London Newspapers with Logos References {{London newspapers London Newspapers A newspaper is a Periodical literature, periodical publication containing written News, information about current events and is often typed in black ink with a white or gray background. Newspapers can cover a wide variety of fields such as poli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newspapers Established In 1868
A newspaper is a Periodical literature, periodical publication containing written News, information about current events and is often typed in black ink with a white or gray background. Newspapers can cover a wide variety of fields such as politics, business, sports, art, and science. They often include materials such as opinion columns, weather forecasts, reviews of local services, Obituary, obituaries, birth notices, crosswords, editorial cartoons, comic strips, and advice columns. Most newspapers are businesses, and they pay their expenses with a mixture of Subscription business model, subscription revenue, Newsagent's shop, newsstand sales, and advertising revenue. The journalism organizations that publish newspapers are themselves often Metonymy, metonymically called newspapers. Newspapers have traditionally been published Printing, in print (usually on cheap, low-grade paper called newsprint). However, today most newspapers are also Electronic publishing, published on webs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Publications Disestablished In 1905
To publish is to make content available to the general public.Berne Convention, article 3(3) URL last accessed 2025-05-23.Universal Copyright Convention, Geneva text (1952), article VI . URL last accessed 2010-05-10. While specific use of the term may vary among countries, it is usually applied to , images, or other |