|
The Diamond Bar
The Diamond Bar, formerly known as Long's Pub, is a historical site in Béal na Bláth in the townland of Glannarouge (''Gleann na Ruaige''), County Cork. The ambush that led to the death of the Irish leader Michael Collins was planned in a storehouse behind The Diamond Bar. The Michael Collins Memorial, close to where Michael Collins was shot, is located one kilometre south of The Diamond Bar. History During the Irish Civil War, Michael Collins was on his way from Macroom to Bandon, County Cork, on the morning of 22 August 1922. The travelling convoy included a Crossley tender, motorcyclist, armoured car and Michael Collins' staff car. A meeting of Anti-Treaty Republicans had been scheduled for the same day in Murray's farmhouse, behind the Diamond Bar, which is on the road to Bandon. A chauffeur was hired by Collins' convoy to show them an alternative route, as other roads were blocked due to bridges being destroyed. However, the convoy temporarily lost sight of the chauff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Béal Na Bláth
Béal na Bláth or Béal na Blá (anglicised Bealnablath or Bealnabla)"Béal na Blá/Bealnablath" . is a small village on the R585 road in , . The area is best known as the site of the ambush and death of the Irish revolutionary leader [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
County Cork
County Cork ( ga, Contae Chorcaí) is the largest and the southernmost county of Ireland, named after the city of Cork, the state's second-largest city. It is in the province of Munster and the Southern Region. Its largest market towns are Mallow, Macroom, Midleton, and Skibbereen. the county had a population of 581,231, making it the third- most populous county in Ireland. Cork County Council is the local authority for the county, while Cork City Council governs the city of Cork and its environs. Notable Corkonians include Michael Collins, Jack Lynch, Roy Keane, Sonia O'Sullivan and Cillian Murphy. Cork borders four other counties: Kerry to the west, Limerick to the north, Tipperary to the north-east and Waterford to the east. The county contains a section of the Golden Vale pastureland that stretches from Kanturk in the north to Allihies in the south. The south-west region, including West Cork, is one of Ireland's main tourist destinations, known for it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael Collins (Irish Leader)
Michael Collins ( ga, Mícheál Ó Coileáin; 16 October 1890 – 22 August 1922) was an Irish revolutionary, soldier and politician who was a leading figure in the early-20th century struggle for Irish independence. During the War of Independence he was Director of Intelligence of the Irish Republican Army (IRA) and a government minister of the self-declared Irish Republic. He was then Chairman of the Provisional Government of the Irish Free State from January 1922 and commander-in-chief of the National Army from July until his death in an ambush in August 1922, during the Civil War. Collins was born in Woodfield, County Cork, the youngest of eight children. He moved to London in 1906 to become a clerk in the Post Office Savings Bank at Blythe House. He was a member of the London GAA, through which he became associated with the Irish Republican Brotherhood and the Gaelic League. He returned to Ireland in January 1916 and fought in the Easter Rising. He was taken prisoner ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irish Civil War
The Irish Civil War ( ga, Cogadh Cathartha na hÉireann; 28 June 1922 – 24 May 1923) was a conflict that followed the Irish War of Independence and accompanied the establishment of the Irish Free State, an entity independent from the United Kingdom but within the British Empire. The civil war was waged between the Provisional Government of Ireland and the Irish Republican Army (IRA) over the Anglo-Irish Treaty. The Provisional Government (which became the Free State in December 1922) supported the terms of the treaty, while the anti-treaty opposition saw it as a betrayal of the Irish Republic which had been proclaimed during the Easter Rising of 1916. Many of those who fought on both sides in the conflict had been members of the IRA during the War of Independence. The Civil War was won by the pro-treaty Free State forces, who benefited from substantial quantities of weapons provided by the British Government. The conflict may have claimed more lives than the War of Independ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
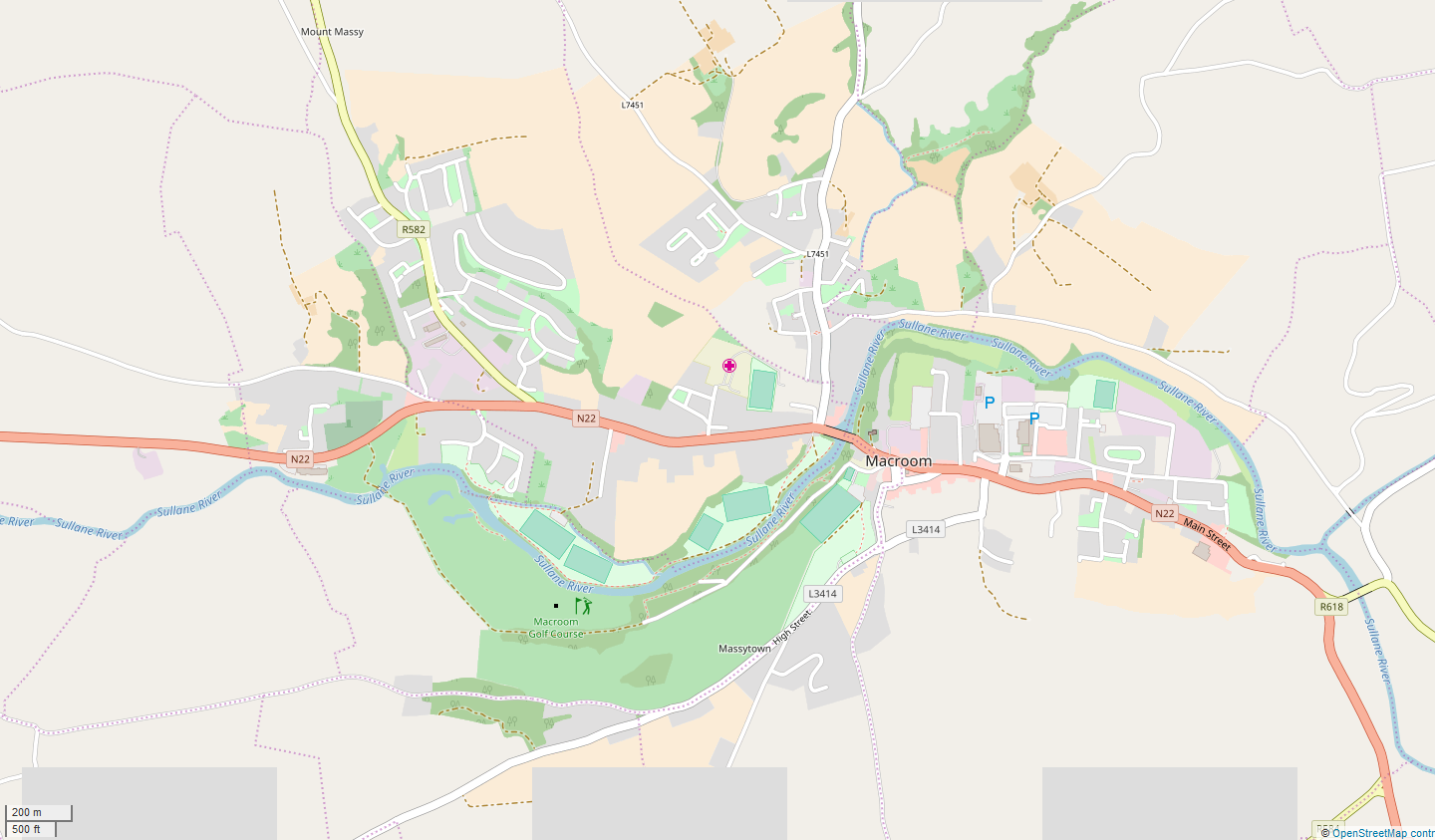
Macroom
Macroom (; ga, Maigh Chromtha) is a market town in County Cork, Ireland, located in the valley of the River Sullane, halfway between Cork city and Killarney. Its population has grown and receded over the centuries as it went through periods of war, famine and workhouses, forced emigration and intermittent prosperity. The 2011 census gave an urban population of 3,879 people, while the 2016 census recorded 3,765 people. Macroom began as a meeting place for the druids of Munster. It is first mentioned is in 6th-century records, and the immediate area hosted a major battle involving the Irish king Brian Boru. During the middle ages, the town was invaded by a succession of warring clans, including the Murcheatach Uí Briain and Richard de Cogan families. In the early modern period the MacCarthy's took control and later the area found prosperity via milling. The MacCarthys built a series of tower houses, some of which survive. The family lost influence during the Williami ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bandon, County Cork
Bandon (; ) is a town in County Cork, Ireland. It lies on the River Bandon between two hills. The name in Irish means 'Bridge of the Bandon', a reference to the origin of the town as a crossing point on the river. In 2004 Bandon celebrated its quatercentenary. The town, sometimes called the Gateway to West Cork, had a population of 6,957 at the 2016 census. Bandon is in the Cork South-West (Dáil Éireann) constituency, which has three seats. History In September 1588, at the start of the Plantation of Munster, Phane Beecher of London acquired, as Undertaker, the seignory of Castlemahon. It was in this seignory that the town of Bandon was formed in 1604 by Phane Beecher's son and heir Henry Beecher, together with other English settlers John Shipward, William Newce and John Archdeacon. The original settlers in Beecher's seignory came from various locations in England. Originally the town proper was inhabited solely by Protestants, as a by-law had been passed stating "That no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staff Car
A staff car is a vehicle used by a senior military officer, and is part of their country's white fleet. The term is most often used in relation to the United Kingdom where they were first used in quantity during World War I, examples being the Vauxhall D-type and Crossley 20/25. Staff cars are often painted in camouflage colours, or plain black. In the U.S., Brazil and other American countries the frequent colour is flat olive-drab as used on the 1941 Buick Century Series 60, used during the Second World War. It was generally painted in khaki, with a white star on the front doors. Gen. Dwight D. Eisenhower, commander in chief of the Allied Forces on the Western Front during World War II, used a Packard Clipper 1942 staff car. The Plymouth P11 1941 was also used frequently. During the Second World War the German Wehrmacht (armed forces) also used staff cars for various purposes. These included military models with machine gun mounts like the Horch 108 and converted civi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irish Republican Army (1922–69)
The Irish Republican Army (IRA) is a name used by various paramilitary organisations in Ireland throughout the 20th and 21st centuries. Organisations by this name have been dedicated to irredentism through Irish republicanism, the belief that all of Ireland should be an independent republic free from British rule. The original Irish Republican Army (1919–1922), often now referred to as the "old IRA", was raised in 1917 from members of the Irish Volunteers and the Irish Citizen Army later reinforced by Irishmen formerly in the British Army in World War I, who returned to Ireland to fight against Britain in the Irish War of Independence. In Irish law, this IRA was the army of the revolutionary Irish Republic as declared by its parliament, Dáil Éireann, in 1919. In the century that followed, the original IRA was reorganised, changed and split on multiple occasions, to such a degree that many subsequent paramilitary organisations have been known by that title – most notabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tom Hales (Irish Republican)
Thomas Hales (5 March 1892 – 29 April 1966) was an Irish Republican Army (IRA) volunteer and politician from West Cork. Early years and childhood Thomas Hales was born at Knocknacurra, Ballinadee, near Bandon on a family farm owned by his father, Robert Hales, an activist in the Irish Land War and a reputed member of the Irish Republican Brotherhood (IRB) and his wife, Margaret ( Fitzgerald), Hales was the sixth of nine children (five sons and four daughters). He was educated at Ballinadee national school and Warner's Lane school, Bandon. After leaving school he worked at Harte's timber yard, Bandon. Irish War of Independence Tom Hales joined the Irish Volunteers in 1913. He was a part of a group of volunteers who planned to rise up in Cork during the 1916 Easter Rising, however they received last minute orders to stand down. By May 1916 Tom Hales and his brothers, Seán, Bob, and William, were fighting with the IRA in west Cork during the Irish War of Independence. Tom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Éamon De Valera
Éamon de Valera (, ; first registered as George de Valero; changed some time before 1901 to Edward de Valera; 14 October 1882 – 29 August 1975) was a prominent Irish statesman and political leader. He served several terms as head of government and head of state and had a leading role in introducing the 1937 Constitution of Ireland. Prior to de Valera's political career, he was a commandant of Irish Volunteers at Boland's Mill during the 1916 Easter Rising. He was arrested and sentenced to death but released for a variety of reasons, including the public response to the British execution of Rising leaders. He returned to Ireland after being jailed in England and became one of the leading political figures of the War of Independence. After the signing of the Anglo-Irish Treaty, de Valera served as the political leader of Anti-Treaty Sinn Féin until 1926, when he, along with many supporters, left the party to set up Fianna Fáil, a new political party which abandoned the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Inventory Of Architectural Heritage
The National Inventory of Architectural Heritage (NIAH) maintains a central database of the architectural heritage of the Republic of Ireland covering the period since 1700 in complement to the Archaeological Survey of Ireland, which focuses on archaeological sites of the pre-1700 period. As of 2022, there are over 50,000 records in the database, including buildings, monuments, street furniture and other structures. It does not cover Northern Ireland. Buildings recorded in the database are given a rating, either national or regional. Formation The NIAH is a unit of the Heritage Division within the Department of Housing, Local Government and Heritage. The unit was founded in 1990 to address the obligations of the Convention for the Protection of the Architectural Heritage of Europe of which Ireland is signatory. Initially, the NIAH existed only on a non-statutory basis with the task to create and maintain an inventory of to be protected buildings and sites. The legal framework fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)
