|
Thanchi Upazila
Thanchi () is an upazila of Bandarban District in the Division of Chittagong, Bangladesh. Geography Thanchi is located at . It has 4,872 households and a total area of 1020.82 km2. Thanchi upazila is bordered by Ruma upazila and Rangamati district to the north, Lama and Alikadam upazilas to the west, Rakhine State of Myanmar to the south and Chin State of Myanmar to the east. At the boundary with Ali Kadam Upazila, the Alikadam-Thanchi Road ascends hill Dim Pahar, making it one of the highest motorable roads in Bangladesh. Demographics As of the 2022 Bangladeshi census, Thanchi upazila had a population of 29,790. The ethnic population was 26,103 (87.62%), of which Marma were 9,345, Mru 7,021,Tripura 6,336, Khumi 1,829, Bom 685, Chakma 488 and Khyang 359. Administration Thanchi Upazila is divided into four union parishads: Balipara, Remakry, Thanchi, and Tindu. The union parishads are subdivided into 12 mauzas and 178 villages. Gallery File:Remakri রেম ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upazilas Of Bangladesh
An ''upazila'' ( pronounced: ), formerly called ''thana'', is an administrative division in Bangladesh, functioning as a sub-unit of a districts of Bangladesh, district. It can be seen as an analogous to a county or a borough of Western countries. Rural upazilas are further administratively divided into Union councils of Bangladesh, union council areas (union parishads). Bangladesh has 495 upazilas. The upazilas are the second lowest tier of regional administration in Bangladesh. The administrative structure consists of divisions (8), districts (64), upazilas (495) and union parishads (UPs). This system of devolution was introduced by the former military ruler and president of Bangladesh, Hossain Mohammad Ershad, Lt-Gen Hossain Muhammad Ershad, in an attempt to strengthen local government. Below UPs, villages (''gram'') and ''para'' exist, but these have no administrative power and elected members. The Local Government local ordinance, Ordinance of 1982 was amended a year lat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rakhine State
Rakhine State ( ; , ; ), formerly known as Arakan State, is a Administrative divisions of Myanmar, state in Myanmar (Burma). Situated on the western coast, it is bordered by Chin State to the north, Magway Region, Bago Region and Ayeyarwady Region to the east, the Bay of Bengal to the west and the Chittagong Division, Chattogram Division of Bangladesh to the northwest. It is located approximately between latitudes 17°30' north and 21°30' north and longitudes 92°10' east and 94°50' east. The north–south Arakan Mountains or Rakhine Yoma separate Rakhine State from central Myanmar. Off the coast of Rakhine State there are some fairly large islands such as Ramree Island, Ramree, Cheduba and Myingun Island, Myingun. Rakhine State has an area of and its capital is Sittwe (formerly known as Akyab). Names The state was historically known as Arakan in English until the Burmese government adopted the English name Rakhine in 1989. History The history of the region of Arakan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khyang People
Kheyang is the exonym of the Hyow. There Kheyang or the Hyow (খিয়াং), are a group of indigenous people inhabiting in the Chittagong Hill Tracts of Bangladesh and the Rakhine State of Myanmar. The Khyang are one of the smallest ethnic groups in Bangladesh with a population of only 4,826 according to the 2022 census. Etymology The word "Kheyang" is originated from the term "''khlɔng"'', which means ''person ''in the language. The endonym "''Hyow"'' means ''Chin.'' History According to Kheyang chronicles, the Khyangs with their king entered Chittagong Hill Tracts when their kingdom in Burma Myanmar, officially the Republic of the Union of Myanmar; and also referred to as Burma (the official English name until 1989), is a country in northwest Southeast Asia. It is the largest country by area in Mainland Southeast Asia and ha ... was overrun by the Burmese. But afterwards the king decided to go back to Burma. But his younger queen being pregnant could not acco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chakma People
The Chakma or Changhma people (, 𑄌𑄇𑄴𑄟), are an ethnic group and nation native to the Indian subcontinent and Western Myanmar. They are the largest indigenous group and as well as the second largest ethnic group of the Chittagong Hill Tracts region of southeastern Bangladesh. They also form the majority in Chakma Autonomous District Council of Mizoram. Significant Chakma populations are found in the northeast Indian states of Arunachal Pradesh, Tripura, Assam and Rakhine State of Myanmar. The Chakma possess strong ethnic affinities to Tibeto-Burman-speaking groups in Northeast India. Because of a language shift in the past to consolidate power among the tribes, they adopted an Indo-Aryan language Chakma, which is closely related to Pali and the Chittagonian language, predominant near the areas in which they live. Most modern Chakma people practice Theravada Buddhism, due to 19th-century reforms and institutionalisation by Queen regnant Rani Kalindi. In Myanmar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bom People
The Bom, Bawm or Bawmzo (), are an ethnic community inhabiting the Chittagong Hill Tracts of Bangladesh. According to the 2022 Bangladeshi census the population of Bawms in Bangladesh is 13,193. In 2004, around 10,000 Bawm inhabited India. 2,500 Bawms reside in Myanmar.Kim, Roy & Sangma. 2011. ''The Kuki-Chin Communities of Bangladesh: A sociolinguistic survey''. SIL International. They speak the Sino-Tibetan Bawm language. The Bawm are victims in the Chittagong Hill Tracts conflict, especially in the continuation of it. Bawms are targeted by the Bangladesh Army as well as by the Arakan Army,According to the prayer list of AKREF, a working group of the German Evangelical Alliance, from May 16th, 2024archived. History The origin of Bawm is traced to the founding of a village called Tiphul in Chin State Bawm people were among the earlier settlers in the Lushai Hills, along with Tlanglau, Khiang and Chawrai. These groups of people entered Lushai Hills through an area south of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khumi People
The Khumis () are a community inhabiting in the Chittagong Hill Tracts of Bangladesh. The Khumis are one of smallest ethnic groups in Bangladesh with a population of only 1214 according to the 1991 census (in the census of 1981 their population was recorded as 1258), though there are another 120,000 across the border in Myanmar (Burma). History Among the ethnic groups in Chittagong Hill Tracts the Khumis were the war like people. Earlier they were very often engaged in internecine or intertrinal warfare with the Bawms and the Mros. The Khumis used to live in Arakan; when there was fierce battle between them and the Mros, the latter being defeated fled to Chittagong Hill Tracts. But later the Khumis themselves entered Chittagong Hill Tracts after being defeated by Arakan. The term "Khumi" might have originated from a combination of two words in the Khumi language: "Kha," meaning "man," and "Ma," meaning "the best race." Together, they signify "the man who excels in racing." Bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tripuri People
The Tripuri people (Kokborok language, Kókborok: ''Tripuri dópha rok''), also known as Tripura, Tipra, Twipra, Tipperah, are a Tibeto-Burman-speaking ethnic group of Northeast India, Indian state of Tripura and Bangladesh. They are the descendants of the inhabitants of the Twipra/Tripura Kingdom in North-East India, North-East India and Bangladesh. The Tripuri people through the Manikya dynasty ruled the Twipra Kingdom, Kingdom of Tripura for over 600 years starting from 1400 A.D. until the kingdom joined the Dominion of India, Indian Union on 15 October 1949. Ancestral origins The Tripuri are part of the Tibeto-Burman ethnic group. Historical accounts suggest that they migrated from the upper courses of the Yangzi River, Yangtze and Yellow River, Hwang Ho rivers in Western China. Over time, they moved through the Himalayas, eventually settling in the region now known as Tripura. Ethnically, Tripuris belong to the Indo-Mongoloid origin and linguistically fall within the Tibeto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mru People
The Mru (Mru language, Mru: 𖩃𖩓𖩑) also known as the Mro, Murong, Taung Mro, Mrung, and Mrucha, refer to the tribes who live in the border regions between Myanmar (Burma), Bangladesh, and India. The Mru are a sub-group of the Chin people, a few of whom live in western Myanmar. They are also found in the northern Rakhine State. In Bangladesh, they reside in the Chittagong Hills in southeast Bangladesh, primarily in Bandarban District and Rangamati Hill District. In India, they reside in West Bengal. The Mru people are divided into five distinct linguistic and cultural sub-groups: the Anok, Tshüngma, Dömrong, Dopteng, and Rümma. Origin The Mru of Bangladesh and Myanmar are known as the Mro, Mrucha and Taung-Mro, respectively. The Mru claim that their ancestors lived at the source of the Kaladan River, but are unsure about when their people migrated to the region. They have no division of different exogamous clans or groups of clans, nor do they have a chieftain clas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marma People
The Marma () are the second-largest ethnic community in Bangladesh's Chittagong Hill Tracts, primarily residing in the Bandarban District, Bandarban, Khagrachhari District, Khagrachari and Rangamati Hill Districts. They belong to the same community as the Rakhine people. There are three endogamous groups of Marma within the Magh Community which are known as i) The Thongtha, Khyongtha, Mrokpatha, ii) The Marma, Mayamma, or Rakhaing Magh, iii) The Maramagri, otherwise called the Barua people, Barua maghs. Ethnonyms Between the 17th and 18th centuries, the Rakhine began calling themselves Mranma (မြန်မာ) and its derivatives like Marama (မရမာ), as attested by texts like the ''Rakhine Min Razagyi, Minrazagri Ayedaw Sadan'' and the ''Dhanyawaddy Ayedawbon''. This endonym continues to be used by the Marma. The term "Marma" is derived from "Myanmar," which was first used in the early 1100s. In the Marma and Arakanese language, Arakanese, Myanmar is pronounced ''M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
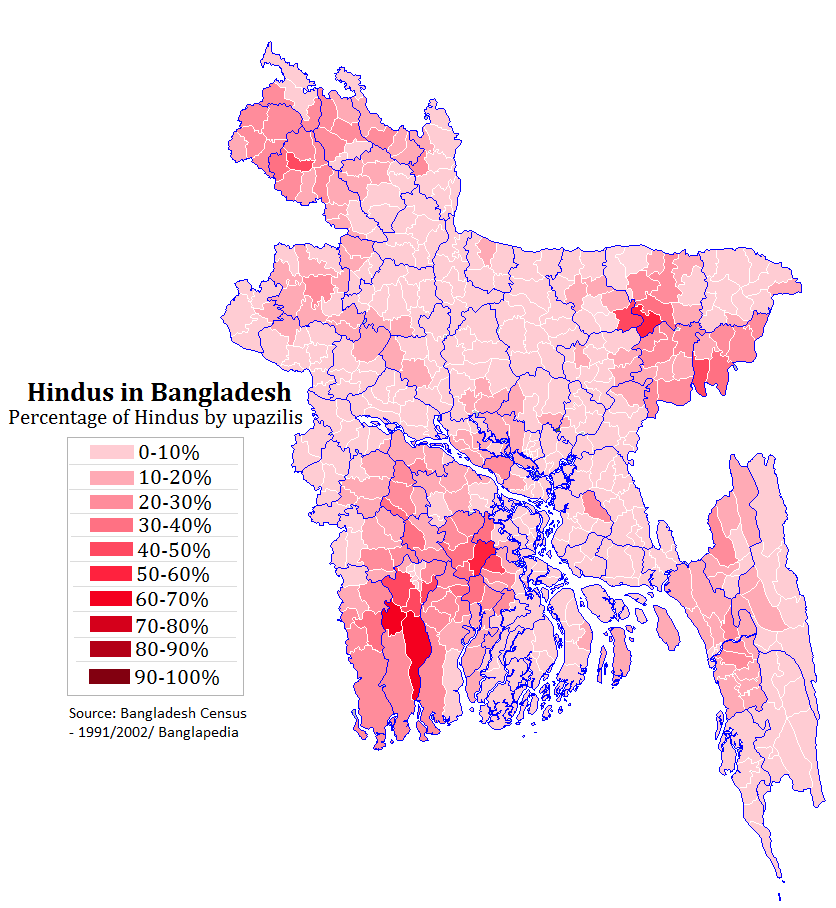
Hinduism In Bangladesh
Hinduism is the second largest religion in Bangladesh, as according to the 2022 Census of Bangladesh, approximately 13.1 million people responded as Hindus, constituting 7.95% of the nation. Bangladesh is the third-largest Hindu populated country in the world, after India and Nepal. Hinduism is the Religion in Bangladesh, second-largest religion in 61 of 64 districts in Bangladesh, but there are no Hindu majority districts in Bangladesh. Demographics According to the 2001 Bangladesh census, there were around 11.82 million Hindus in Bangladesh constituting 9.6% of the population, which at the time was 123.15 million. The 2011 Bangladesh census, Bangladesh 2011 census states, that approximately 12.73 million people responded that they were Hindus, constituting 8.54% of the total 149.77 million. While 2022 Census of Bangladesh, put the number of Hindus in Bangladesh at 13.1 million out of total 165.1 million population, thus constituting 7.95% of the population. According to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islam In Bangladesh
Islam is the largest and the state religion of the People's Republic of Bangladesh. According to the 2022 census, Bangladesh had a population of about 150 million Muslims, or 91.04% of its total population of million. Muslims of Bangladesh are predominant native Bengali Muslims. The majority of Bangladeshis are ''Sunni'', and follow the '' Hanafi'' school of ''Fiqh''. Bangladesh is a ''de facto'' secular country. The Bengal region was a supreme power of the medieval Islamic East. In the late 7th century, Muslims from Arabia established commercial as well as religious connection within the Bengal region before the conquest, mainly through the coastal regions as traders and primarily via the ports of Chittagong. In the early 13th century, Muhammad bin Bakhtiyar Khalji conquered Western and part of Northern Bengal and established the first Muslim kingdom in Bengal. During the 13th century, Sufi missionaries, mystics and saints began to preach Islam in villages. The Islamic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christianity In Bangladesh
Christians in Bangladesh () account for 0.30% (accurately 488,583) of the nation's population according to the 2022 census in Bangladesh. Together with Buddhism in Bangladesh, Buddhism (plus other minority groups such as Irreligion in Bangladesh, Atheism, Sikhism in Bangladesh, Sikhism, the Bahá'í Faith and others), Christianity accounts for 1% of the population. Islam in Bangladesh, Islam accounts for 91.04% of the country's population, followed by Hinduism in Bangladesh, Hinduism at 7.95% according to the 2022 census. History The introduction and development of Christianity in the Indian subcontinent can be traced back to several periods, with the help of several countries and denominations. The earliest connection to Christianity can be linked back to the arrival of the Thomas the Apostle, Apostle Thomas to the Malabar Coast during the first century, in 52 A.D. In addition, the Apostle had managed to convert several thousands of Hindu Brahmins, as they were "attracted" to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |