|
Than
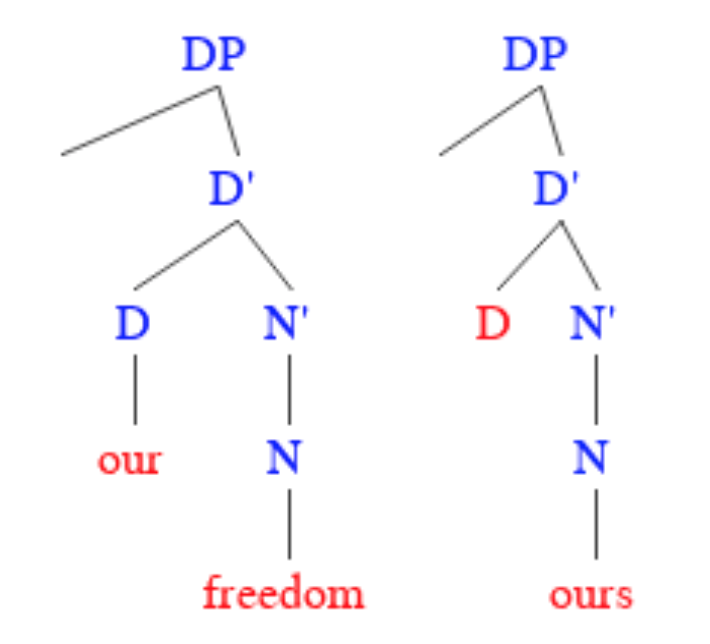
''Than'' is a grammatical particle analyzed as both a conjunction and a preposition in the English language. It introduces a comparison and is associated with comparatives and with words such as more, less, and fewer. Typically, it measures the force of an adjective or similar description between two predicates. Usage Case of pronouns following ''than'' According to the view of many English-language prescriptivists, including influential 18th-century grammarian Robert Lowth, ''than'' is exclusively a conjunction and therefore takes either nominative (or subjective) or oblique (or objective) pronouns, depending on context, rather than exclusively oblique pronouns as prepositions do. This rule is broken as often as it is observed. For instance, William Shakespeare's 1600 play ''Julius Caesar'' has an instance of an oblique pronoun following ''than'' where the nominative is also possible: :''A man no mightier than thyself or me...'' Likewise, Samuel Johnson wrote: :''No man ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grammatical Particle
In grammar, the term ''particle'' ( abbreviated ) has a traditional meaning, as a part of speech that cannot be inflected, and a modern meaning, as a function word (functor) associated with another word or phrase in order to impart meaning. Although a particle may have an intrinsic meaning and may fit into other grammatical categories, the fundamental idea of the particle is to add context to the sentence, expressing a mood or indicating a specific action. In English, for example, the phrase "oh well" has no purpose in speech other than to convey a mood. The word "up" would be a particle in the phrase "look up" (as in "look up this topic"), implying that one researches something rather than that one literally gazes skywards. Many languages use particles in varying amounts and for varying reasons. In Hindi, they may be used as honorifics, or to indicate emphasis or negation. In some languages, they are clearly defined; for example, in Chinese, there are three types of (; ): ''str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Lowth
Robert Lowth ( ; 27 November 1710 – 3 November 1787) was an English clergyman and academic who served as the Bishop of Oxford, Bishop of St Davids, Professor of Poetry and the author of one of the most influential textbooks of English grammar. Life Lowth was born in Hampshire, England, Great Britain, the son of Dr William Lowth, a clergyman and Biblical commentator. He was educated at Winchester College and became a scholar of New College, Oxford in 1729. Lowth obtained his BA in 1733 and his Master of Arts degree in 1737. In 1735, while still at Oxford, Lowth took orders in the Anglican Church and was appointed vicar of Ovington, Hampshire, a position he retained until 1741, when he was appointed Oxford Professor of Poetry. Bishop Lowth made a translation of the Book of Isaiah, first published in 1778. The Seventh-day Adventist theologian E. J. Waggoner said in 1899 that Lowth's translation of Isaiah was "without doubt, as a whole, the best English translation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pronoun
In linguistics and grammar, a pronoun (Interlinear gloss, glossed ) is a word or a group of words that one may substitute for a noun or noun phrase. Pronouns have traditionally been regarded as one of the part of speech, parts of speech, but some modern theorists would not consider them to form a single class, in view of the variety of functions they perform cross-linguistically. An example of a pronoun is "you", which can be either singular or plural. Sub-types include personal pronoun, personal and possessive pronouns, reflexive pronoun, reflexive and reciprocal pronoun, reciprocal pronouns, demonstrative pronouns, relative pronoun, relative and interrogative pronouns, and indefinite pronouns. The use of pronouns often involves anaphora (linguistics), anaphora, where the meaning of the pronoun is dependent on an antecedent (grammar), antecedent. For example, in the sentence ''That poor man looks as if he needs a new coat'', the meaning of the pronoun ''he'' is dependent on its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noun Case
A grammatical case is a category of nouns and noun modifiers (determiners, adjectives, participles, and numerals) that corresponds to one or more potential grammatical functions for a nominal group in a wording. In various languages, nominal groups consisting of a noun and its modifiers belong to one of a few such categories. For instance, in English, one says ''I see them'' and ''they see me'': the nominative pronouns ''I/they'' represent the perceiver, and the accusative pronouns ''me/them'' represent the phenomenon perceived. Here, nominative and accusative are cases, that is, categories of pronouns corresponding to the functions they have in representation. English has largely lost its inflected case system but personal pronouns still have three cases, which are simplified forms of the nominative, accusative (including functions formerly handled by the dative) and genitive cases. They are used with personal pronouns: subjective case (I, you, he, she, it, we, they, who, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samuel Johnson
Samuel Johnson ( – 13 December 1784), often called Dr Johnson, was an English writer who made lasting contributions as a poet, playwright, essayist, moralist, literary critic, sermonist, biographer, editor, and lexicographer. The ''Oxford Dictionary of National Biography'' calls him "arguably the most distinguished man of letters in English history". Born in Lichfield, Staffordshire, he attended Pembroke College, Oxford, until lack of funds forced him to leave. After working as a teacher, he moved to London and began writing for ''The Gentleman's Magazine''. Early works include '' Life of Mr Richard Savage'', the poems ''London'' and '' The Vanity of Human Wishes'' and the play '' Irene''. After nine years of effort, Johnson's '' A Dictionary of the English Language'' appeared in 1755, and was acclaimed as "one of the greatest single achievements of scholarship". Later work included essays, an annotated '' The Plays of William Shakespeare'', and the apologue '' The Hist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Julius Caesar (play)
''The Tragedy of Julius Caesar ''(First Folio title: ''The Tragedie of Ivlivs Cæsar''), often shortened to ''Julius Caesar'', is a history play and Shakespearean tragedy, tragedy by William Shakespeare first performed in 1599. In the play, Brutus the Younger, Brutus joins a conspiracy led by Gaius Cassius Longinus, Cassius to assassinate Julius Caesar, to prevent him from becoming a tyrant. Caesar's right-hand man Mark Antony, Antony stirs up hostility against the conspirators and Roman Empire, Rome becomes embroiled in a dramatic civil war. Synopsis The play opens with two tribunes Flavius and Gaius Epidius Marullus, Marullus (appointed leaders/officials of Rome) discovering the plebeians, commoners of Rome celebrating Julius Caesar's Roman triumph, triumphant return from Battle of Munda, defeating the sons of his military rival, Pompey. The tribunes, insulting the crowd for their change in loyalty from Pompey to Caesar, attempt to end the festivities and break up the commone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Shakespeare
William Shakespeare ( 23 April 1564 – 23 April 1616) was an English playwright, poet and actor. He is widely regarded as the greatest writer in the English language and the world's pre-eminent dramatist. He is often called England's national poet and the "Bard of River Avon, Warwickshire, Avon" or simply "the Bard". His extant works, including William Shakespeare's collaborations, collaborations, consist of some Shakespeare's plays, 39 plays, Shakespeare's sonnets, 154 sonnets, three long narrative poems and a few other verses, some of uncertain authorship. His plays List of translations of works by William Shakespeare, have been translated into every major modern language, living language and are performed more often than those of any other playwright. Shakespeare remains arguably the most influential writer in the English language, and his works continue to be studied and reinterpreted. Shakespeare was born and raised in Stratford-upon-Avon, Warwickshire. At the age of 18 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oblique Case
In grammar, an oblique ( abbreviated ; from ) or objective case ( abbr. ) is a nominal case other than the nominative case and, sometimes, the vocative. A noun or pronoun in the oblique case can generally appear in any role except as subject, for which the nominative case is used. The term ''objective case'' is generally preferred by modern English grammarians, where it supplanted Old English's dative and accusative. When the two terms are contrasted, they differ in the ability of a word in the oblique case to function as a possessive attributive; whether English has an oblique rather than an objective case then depends on how " proper" or widespread one considers the dialects where such usage is employed. An oblique case often contrasts with an unmarked case, as in English oblique ''him'' and ''them'' versus nominative ''he'' and ''they''. However, the term ''oblique'' is also used for languages without a nominative case, such as ergative–absolutive languages; in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nominative Case
In grammar, the nominative case ( abbreviated ), subjective case, straight case, or upright case is one of the grammatical cases of a noun or other part of speech, which generally marks the subject of a verb, or (in Latin and formal variants of English) a predicative nominal or adjective, as opposed to its object, or other verb arguments. Generally, the noun "that is doing something" is in the nominative, and the nominative is often the form listed in dictionaries. Etymology The English word ''nominative'' comes from Latin ''cāsus nominātīvus'' "case for naming", which was translated from Ancient Greek ὀνομαστικὴ πτῶσις, ''onomastikḗ ptôsis'' "inflection for naming", from ''onomázō'' "call by name", from ''ónoma'' "name". Dionysius Thrax in his The Art of Grammar refers to it as ''orthḗ'' or ''eutheîa'' "straight", in contrast to the oblique case, oblique or "bent" cases. Characteristics The reference form (more technically, the ''lea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prescription (linguistics)
Linguistic prescription is the establishment of rules defining publicly preferred usage of language, including rules of spelling, pronunciation, vocabulary, grammar, etc. Linguistic prescriptivism may aim to establish a standard language, teach what a particular society or sector of a society perceives as a correct or proper form, or advise on effective and stylistically apt communication. If usage preferences are conservative, prescription might appear resistant to language change; if radical, it may produce neologisms. Such prescriptions may be motivated by consistency (making a language simpler or more logical); rhetorical effectiveness; tradition; aesthetics or personal preferences; linguistic purism or nationalism (i.e. removing foreign influences); or to avoid causing offense (etiquette or political correctness). Prescriptive approaches to language are often contrasted with the descriptive approach of academic linguistics, which observes and records how language is actuall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grammatical Conjunction
In grammar, a conjunction (List of glossing abbreviations, abbreviated or ) is a part of speech that connects Word, words, phrases, or Clause, clauses'','' which are called its conjuncts. That description is vague enough to overlap with those of other parts of speech because what constitutes a "conjunction" must be defined for each language. In English language, English, a given word may have several Word sense, senses and in some contexts be a Preposition and postposition, preposition but a conjunction in others, depending on the syntax. For example, ''after'' is a preposition in "he left after the fight" but a conjunction in "he left after they fought". In general, a conjunction is an invariant (non-Inflection, inflecting) grammatical particle that stands between conjuncts. A conjunction may be placed at the beginning of a sentence, but some superstition about the practice persists. The definition may be extended to idiomatic phrases that behave as a unit and perform the same ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
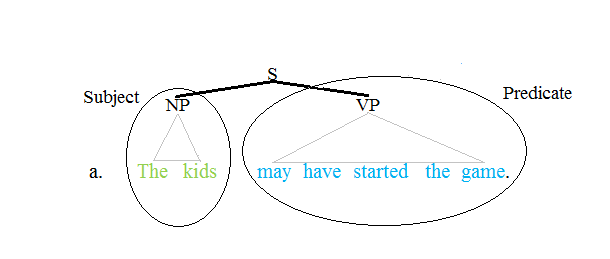
Predicate (grammar)
The term predicate is used in two ways in linguistics and its subfields. The first defines a predicate as everything in a standard declarative sentence except the subject (grammar), subject, and the other defines it as only the main content verb or associated predicative expression of a clause. Thus, by the first definition, the predicate of the sentence ''Frank likes cake'' is ''likes cake'', while by the second definition, it is only the content verb ''likes'', and ''Frank'' and ''cake'' are the argument (linguistics), arguments of this predicate. The conflict between these two definitions can lead to confusion. Syntax Traditional grammar The notion of a predicate in traditional grammar traces back to Aristotelian logic. A predicate is seen as a property that a subject has or is characterized by. A predicate is therefore an expression that can be ''true of'' something. Thus, the expression "is moving" is true of anything that is moving. This classical understanding of pred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |