|
Thamudic B
Thamudic B is a Central Semitic language and script concentrated in northwestern Arabia, with attestations in Syria, Egypt, and Yemen. As a poorly understood form of Ancient North Arabian, it is included in the Thamudic category. Mentions of the king of Babylon and the Nabataean god Dushara show that Thamudic B was written over a span of centuries, ranging at least from the seventh or sixth to fourth centuries BCE. Characteristics Thamudic B is mostly written horizontally, from right to left. Salient linguistic features include the following: # The suffix morpheme of the prefix conjugation in the first person is ''-t'', as in Arabic and Northwest Semitic Northwest Semitic is a division of the Semitic languages comprising the indigenous languages of the Levant. It emerged from Proto-Semitic language, Proto-Semitic in the Early Bronze Age. It is first attested in proper names identified as Amorite l ..., as opposed to the ''-k'' of Ancient South Arabian and Ethiopic. # The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Afroasiatic Languages
The Afroasiatic languages (also known as Afro-Asiatic, Afrasian, Hamito-Semitic, or Semito-Hamitic) are a language family (or "phylum") of about 400 languages spoken predominantly in West Asia, North Africa, the Horn of Africa, and parts of the Sahara and Sahel. Over 500 million people are native speakers of an Afroasiatic language, constituting the fourth-largest language family after Indo-European, Sino-Tibetan, and Niger–Congo. Most linguists divide the family into six branches: Berber (Amazigh), Chadic, Cushitic, Egyptian, Omotic, and Semitic. The vast majority of Afroasiatic languages are considered indigenous to the African continent, including all those not belonging to the Semitic branch (which originated in West Asia). The five most spoken languages are; Arabic (of all varieties) which is by far the most widely spoken within the family, with around 411 million native speakers concentrated primarily in West Asia and North Africa, the Chadic Hausa language w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semitic Languages
The Semitic languages are a branch of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family. They include Arabic, Amharic, Tigrinya language, Tigrinya, Aramaic, Hebrew language, Hebrew, Maltese language, Maltese, Modern South Arabian languages and numerous other ancient and modern languages. They are spoken by more than 330 million people across much of Western Asia, West Asia, North Africa, the Horn of Africa, Malta, and in large Immigration, immigrant and Expatriate, expatriate communities in North America, Europe, and Australasia. The terminology was first used in the 1780s by members of the Göttingen school of history, who derived the name from Shem, one of the three Generations of Noah, sons of Noah in the Book of Genesis. Semitic languages List of languages by first written account, occur in written form from a very early historical date in West Asia, with East Semitic languages, East Semitic Akkadian language, Akkadian (also known as Ancient Assyrian language, Assyrian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Semitic Languages
The West Semitic languages are a proposed major sub-grouping of Semitic languages. The term was first coined in 1883 by Fritz Hommel.The Semitic Languages: An International Handbook, Chapter V page 425 The grouping supported by Semiticists like Robert Hetzron and John Huehnergard divides the Semitic language family into two branches: Eastern and Western. The West Semitic languages consist of the clearly defined sub-groups: |
Central Semitic Languages
Central Semitic languages are one of the three groups of West Semitic languages, alongside Modern South Arabian languages and Ethiopian Semitic languages. Central Semitic can itself be further divided into two groups: Arabic and Northwest Semitic. Northwest Semitic languages largely fall into the Canaanite languages (such as Ammonite, Phoenician and Hebrew) and Aramaic. Overview Distinctive features of Central Semitic languages include the following: * An innovative negation marker *bal, of uncertain origin. * The generalization of ''t'' as the suffix conjugation past tense marker, levelling an earlier alternation between *k in the first person and *t in the second person. * A new prefix conjugation for the non-past tense, of the form ''ya-qtulu'', replacing the inherited ''ya-qattal'' form (they are schematic verbal forms, as if derived from an example triconsonantal root ''q-t-l''). * Pharyngealization of the emphatic consonants, which were previously articulated as eje ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classification Of Arabic Languages
The Arabic language family is divided into several categories which are: Old Arabic ( pre-Islamic Arabic), the literary varieties (Classical Arabic and Modern Standard Arabic), and the modern vernaculars. The genealogical position of Arabic within the group of the Semitic languages has long been a problem. Views on Arabic classification Semitic languages were confined in a relatively small geographic area (the region of Syria, Mesopotamia and the Arabian desert) and often spoken in contiguous regions. Permanent contacts between the speakers of these languages facilitated borrowing between them. Borrowing disrupts historical processes of change and makes it difficult to reconstruct the genealogy of languages. In the traditional classification of the Semitic languages, Arabic was in the Southwest Semitic group, based on some affinities with Modern South Arabian and Geʽez. Most scholars reject the Southwest Semitic subgrouping because it is not supported by any ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
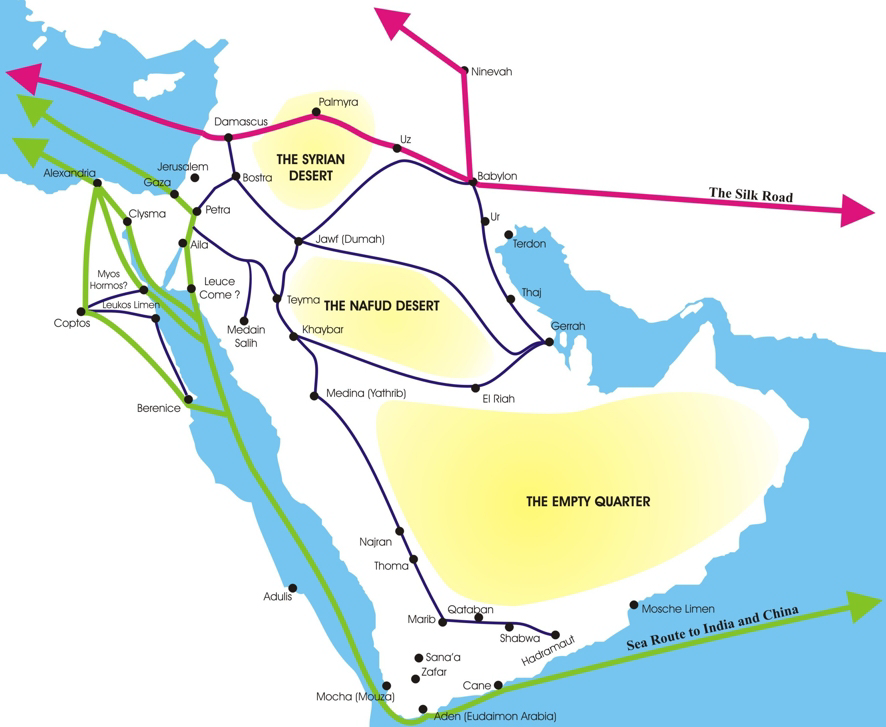
Ancient North Arabian
Languages and scripts in the 1st Century Arabia Ancient North Arabian (ANA) is a collection of scripts and a language or family of languages under the North Arabian languages branch along with Old Arabic that were used in north and central Arabia and south Syria from the 8th century BCE to the 4th century CE. The term "Ancient North Arabian" is defined negatively. It refers to all of the South Semitic scripts except Ancient South Arabian (ASA) regardless of their genetic relationships. Classification Many scholars believed that the various ANA alphabets were derived from the ASA script, mainly because the latter was employed by a major civilization and exhibited more angular features. Others believed that the ANA and ASA scripts shared a common ancestor from which they both developed in parallel. Indeed, it seems unlikely that the various ANA scripts descend from the monumental ASA alphabet, but that they collectively share a common ancestor to the exclusion of ASA is also s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabian Peninsula
The Arabian Peninsula (, , or , , ) or Arabia, is a peninsula in West Asia, situated north-east of Africa on the Arabian plate. At , comparable in size to India, the Arabian Peninsula is the largest peninsula in the world. Geographically, the Arabian Peninsula comprises Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates (UAE) and Yemen, as well as southern Iraq and Jordan. The largest of these is Saudi Arabia. In the Roman era, the Sinai Peninsula was also considered a part of Arabia. The Arabian Peninsula formed as a result of the rifting of the Red Sea between 56 and 23 million years ago, and is bordered by the Red Sea to the west and south-west, the Persian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman to the north-east, the Levant and Mesopotamia to the north and the Arabian Sea and the Indian Ocean to the south-east. The peninsula plays a critical geopolitical role in the Arab world and globally due to its vast reserves of petroleum, oil and natural gas. Before the mod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thamudic
Thamudic, named for the Thamud tribe, is a group of Epigraphy, epigraphic scripts known from large numbers of inscriptions in Ancient North Arabian (ANA) alphabets, which have not yet been properly studied. These texts are found over a huge area from southern Syria to Yemen. In 1937, Fred V. Winnett divided those known at the time into five rough categories A, B, C, D, E. In 1951, some 9,000 more inscriptions were recorded in south-west Saudi Arabia which have been given the name Southern Thamudic. Thamudic A is now known as Taymanitic. Thamudic E is now known as Hismaic. Southern Thamudic is also known as Thamudic F. Varieties Thamudic B The Thamudic B inscriptions are concentrated in Northwest Arabia, but can be occasionally found in Syria, Egypt, and Yemen. Thamudic C The Thamudic C inscriptions are concentrated in the Najd, but can be found elsewhere across western Arabia as well. They typically contain the word ''wdd'', of unknown meaning. Thamudic D Thamudic D i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Babylon
Babylon ( ) was an ancient city located on the lower Euphrates river in southern Mesopotamia, within modern-day Hillah, Iraq, about south of modern-day Baghdad. Babylon functioned as the main cultural and political centre of the Akkadian-speaking region of Babylonia. Its rulers established two important empires in antiquity, the 19th–16th century BC Old Babylonian Empire, and the 7th–6th century BC Neo-Babylonian Empire. Babylon was also used as a regional capital of other empires, such as the Achaemenid Empire. Babylon was one of the most important urban centres of the ancient Near East, until its decline during the Hellenistic period. Nearby ancient sites are Kish, Borsippa, Dilbat, and Kutha. The earliest known mention of Babylon as a small town appears on a clay tablet from the reign of Shar-Kali-Sharri (2217–2193 BC), of the Akkadian Empire. Babylon was merely a religious and cultural centre at this point and neither an independent state nor a large city, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nabataean Kingdom
The Nabataean Kingdom (Nabataean Aramaic: 𐢕𐢃𐢋𐢈 ''Nabāṭū''), also named Nabatea () was a political state of the Nabataeans during classical antiquity. The Nabataean Kingdom controlled many of the trade routes of the region, amassing large wealth and drawing the envy of its neighbors. It stretched south along the Tihamah into the Hejaz, up as far north as Damascus, which it controlled for a short period (85–71 BC). Nabataea remained an independent political entity from the mid-3rd century BC until it was annexed in AD 106 by the Roman Empire, which renamed it to Arabia Petraea. History Nabataeans The Nabataeans were one among several formerly Bedouin, nomadic Arab tribes that roamed (later settled) the Arabian Desert and moved with their herds to wherever they could find pasture and water. They became familiar with their area as seasons passed, and they struggled to survive during bad years when seasonal rainfall diminished. The origin of the specific tribe of Arab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dushara
Dushara (Nabataean Arabic: 𐢅𐢈𐢝𐢛𐢀 ''dwšrʾ''), also transliterated as Dusares or Dhu Shara, is a pre-Islamic Arabian god worshipped by the Nabataeans at Petra and Madain Saleh (of which city he was the patron). Safaitic inscriptions imply he was the son of the goddess Al-Lat, and that he assembled in the heavens with other deities. He is called "Dushara from Petra" in one inscription. Dushara was expected to bring justice if called by the correct ritual. Etymology Dushara is known first from epigraphic Nabataean sources who invariably spell the name ''dwšrʾ'', the Nabataean script denoting only consonants. He appears in Classical Greek sources as Δουσάρης (''Dousárēs'') and in Latin as ''Dusares''. The original meaning is disputed, but early Muslim historian Hisham ibn al-Kalbi in his " Book of Idols" explains the name as ''Dhū l-Šarā'' (), "etymologically probably 'the one of the Shara (mountains north of Petra)'", referring to a mountain rang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Right-to-left Script
A writing system comprises a set of symbols, called a ''script'', as well as the rules by which the script represents a particular language. The earliest writing appeared during the late 4th millennium BC. Throughout history, each independently invented writing system gradually emerged from a system of proto-writing, where a small number of ideographs were used in a manner incapable of fully encoding language, and thus lacking the ability to express a broad range of ideas. Writing systems are generally classified according to how its symbols, called ''graphemes'', relate to units of language. Phonetic writing systemswhich include alphabets and syllabariesuse graphemes that correspond to sounds in the corresponding spoken language. Alphabets use graphemes called '' letters'' that generally correspond to spoken phonemes. They are typically divided into three sub-types: ''Pure alphabets'' use letters to represent both consonant and vowel sounds, ''abjads'' generally only use let ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |