|
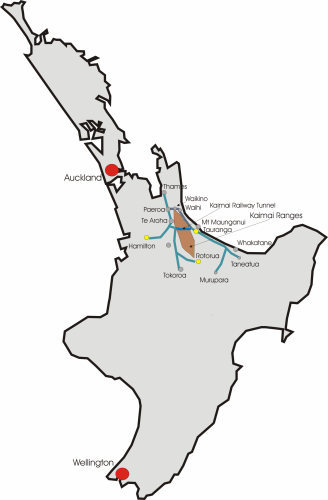
Thames Express
The ''Thames Express'' was an express passenger train operated by the New Zealand Railways Department between Auckland and Thames. It ran between 1908 and 1928. Introduction In the early 20th century, the railways that fanned out from Auckland were isolated from the national network. South of Auckland, apart from commuter services to suburbs and townships near the city, just one dedicated passenger train operated - the '' Rotorua Express'', which only became daily in October 1902. All other passenger services were "mixed" trains that involved one or more passenger carriages being attached to a freight service. In December 1908, just after the opening of the North Island Main Trunk railway connected the Auckland section to the rest of the North Island, the decision was taken to introduce a daily afternoon service south of Auckland to Frankton. This service continued on to Thames, with connecting trains to Cambridge and Waihi, and became known as the ''Thames Express''. Op ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inter-city Rail
Inter-city rail services are Express train, express trains that run services that connect cities over longer distances than Commuter rail, commuter or Regional rail, regional trains. They include rail services that are neither short-distance commuter rail trains within one city area nor slow regional rail trains stopping at all stations and covering local journeys only. An inter-city train is typically an express train with limited stops and comfortable carriages to serve long-distance travel. Inter-city rail sometimes provides international services. This is most prevalent in Europe because of the proximity of its 50 countries to a 10,180,000-square-kilometre (3,930,000-square-mile) area. Eurostar and EuroCity are examples. In many European countries, the word InterCity or Inter-City is an official brand name for a network of regular-interval and relatively long-distance train services that meet certain criteria of speed and comfort. That use of the term appeared in the United ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steam Locomotive
A steam locomotive is a locomotive that provides the force to move itself and other vehicles by means of the expansion of steam. It is fuelled by burning combustible material (usually coal, Fuel oil, oil or, rarely, Wood fuel, wood) to heat water in the locomotive's Boiler (power generation), boiler to the point where it becomes gaseous and its volume increases 1,700 times. Functionally, it is a steam engine on wheels. In most locomotives, the steam is admitted alternately to each end of its Steam locomotive components, cylinders in which pistons are mechanically connected to the locomotive's main wheels. Fuel and water supplies are usually carried with the locomotive, either on the locomotive itself or in a Tender (rail), tender coupled to it. #Variations, Variations in this general design include electrically powered boilers, turbines in place of pistons, and using steam generated externally. Steam locomotives were first developed in the United Kingdom of Great Britain an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otago University Press
Otago University Press is an academic publisher associated with the University of Otago. The press is located in Dunedin, New Zealand. The Otago University Press is the oldest academic publisher in New Zealand. The Otago University Press publishes non-fiction and poetry and is also the publisher of the literary journal Landfall. Otago University Press has published award-winning books, including ''Tumble'' by Joanna Preston, winner of the 2022 Ockham Award for Poetry. The press is currently a member of the Association of University Presses The Association of University Presses (AUPresses) is an association of nonprofit, mostly, but not exclusively, North American university presses. It is based in New York City. Until December 2017, it was known as the Association of American Univ .... As of 2024, the editorial board consists of: * Sue Wootton (publisher) * Chris Brickell, Professor in gender studies * Chris Prentice, Honorary Associate Professor in English and linguist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The New Zealand Herald
''The New Zealand Herald'' is a daily newspaper published in Auckland, New Zealand, owned by New Zealand Media and Entertainment, and considered a newspaper of record for New Zealand. It has the largest newspaper circulation in New Zealand, peaking at over 200,000 copies in 2006, although circulation of the daily ''Herald'' had declined to 100,073 copies on average by September 2019. The ''Herald''s publications include a daily paper; the ''Weekend Herald'', a weekly Saturday paper; and the ''Herald on Sunday'', which has 365,000 readers nationwide. The ''Herald on Sunday'' is the most widely read Sunday paper in New Zealand. The paper's website, nzherald.co.nz, is viewed 2.2 million times a week and was named Voyager Media Awards' News Website of the Year in 2020, 2021, 2022, and 2023. In 2023, the ''Weekend Herald'' was awarded Weekly Newspaper of the Year and the publication's mobile application was the News App of the Year. Its main circulation area is the Auckland R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taneatua Express
The ''Taneatua Express'' was an express passenger train operated by the New Zealand Railways Department that ran between Auckland and Taneatua in the Bay of Plenty, serving centres such as Tauranga and Te Puke. It commenced in 1929 and operated until 1959. Introduction The immediate precursor to the ''Taneatua Express'', and a victim of its introduction, was the ''Thames Express'', which operated from Auckland to Thames. The East Coast Main Trunk Railway, in its first incarnation, diverged from the Thames Branch in Paeroa (the Thames Branch later included the line from Morrinsville to Paeroa with the opening of the Kaimai Tunnel deviation), and when it opened in 1928, Thames swiftly declined in status as a railway terminus as services began operating through to the Bay of Plenty. A direct passenger service between Auckland and the Bay of Plenty terminus in Taneatua commenced upon the East Coast Main Trunk's opening, rendering the ''Thames Express'' superfluous as the ''Taneatu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bay Of Plenty
The Bay of Plenty () is a large bight (geography), bight along the northern coast of New Zealand's North Island. It stretches from the Coromandel Peninsula in the west to Cape Runaway in the east. Called ''Te Moana-a-Toitehuatahi'' (the Ocean of Toitehuatahi) in the Māori language after Toi-te-huatahi, an early ancestor, the name 'Bay of Plenty' was bestowed by James Cook in 1769 when he noticed the abundant food supplies at several Māori people, Māori villages there, in stark contrast to observations he had made earlier in Poverty Bay. Geography The bay is defined by of open coastline used for economic, recreational and cultural purposes. The coastline from Waihi Beach in the west to Opape is defined as sandy coast, while the coast from Opape to Cape Runaway is rocky shore. Sizeable harbours are located at Tauranga, Whakatāne and Ohiwa. Major estuaries include Maketu, Little Waihi, Whakatāne, Waiotahe and Waioeka River, Waioeka/Ōtara River, Ōtara. Eight major rivers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Coast Main Trunk Railway
The East Coast Main Trunk (ECMT) is a railway line in the North Island of New Zealand, originally running between Hamilton and Taneatua via Tauranga, connecting the Waikato with the Bay of Plenty. The ECMT now runs between Hamilton and Kawerau, with a branch line to Taneatua from the junction at Hawkens. The line is built to narrow gauge of , the uniform gauge in New Zealand. It was known as the East Coast Main Trunk Railway until 2011, when the word "Railway" was dropped. History Construction In 1880, the North Island Main Trunk railway had reached Frankton, Waikato, Frankton, Hamilton, New Zealand, Hamilton, from Auckland. From there, it was delayed by construction of the Claudelands Bridge, original Waikato River bridge (now carrying road traffic as part of Claudelands Road), before the line made its way to Morrinsville in October 1884, Te Aroha in March 1886 and Paeroa in 1898. There were also minor delays, such as in the delivery of Podocarpus totara, totara sleepers. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NZR RM Class (Sentinel-Cammell)
The NZR RM class Sentinel-Cammell was a steam-powered railcar operated by the New Zealand Railways Department (NZR). It was the only one of its type to operate in New Zealand, and one of only two steam railcars trialled in the country; the other was the Clayton steam railcar. Overview In the early 20th century, NZR began experiments with railcars as an option to replace unprofitable regional locomotive-hauled carriage expresses and to provide efficient passenger service on rural branch lines that were served solely by slow mixed trains that carried both goods and passengers. Such mixed trains had slow schedules as they had to load and unload freight regularly, making their stops longer than passenger service would normally require. In 1925, a steam railcar was ordered from the Sentinel Waggon Works of Shrewsbury and Metro-Cammell of Birmingham, and when it entered revenue service, it was the first railcar to do so in the Auckland Region. It subsequently operated outside this r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railcar
A railcar (not to be confused with the generic term railroad car or railway car) is a self-propelled railway vehicle designed to transport passengers. The term "railcar" is usually used in reference to a train consisting of a single coach (or carriage, car, unit), with a driver's cab at one or both ends. In its simplest form, a "railcar" may also be little more than a motorized railway handcar, draisine or railbus. Some railway companies, such as the Great Western, termed such vehicles " railmotors" (or "rail motors"). Self-powered railcars were once common in North America; and termed Doodlebugs. Self-propelled passenger vehicles also capable of hauling a train are, in technical rail usage, more usually called " rail motor coaches" or "motor cars" (not to be confused with the motor cars, otherwise known as automobiles, that operate on roads). Alternative use In Australia, the term is sometimes also used as an alternative name for the small types of multiple un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wellington
Wellington is the capital city of New Zealand. It is located at the south-western tip of the North Island, between Cook Strait and the Remutaka Range. Wellington is the third-largest city in New Zealand (second largest in the North Island), and is the administrative centre of the Wellington Region. It is the world's southernmost capital of a sovereign state. Wellington features a temperate maritime climate, and is the world's windiest city by average wind speed. Māori oral tradition tells that Kupe discovered and explored the region in about the 10th century. The area was initially settled by Māori iwi such as Rangitāne and Muaūpoko. The disruptions of the Musket Wars led to them being overwhelmed by northern iwi such as Te Āti Awa by the early 19th century. Wellington's current form was originally designed by Captain William Mein Smith, the first Surveyor General for Edward Wakefield's New Zealand Company, in 1840. Smith's plan included a series of inter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Night Limited
The ''Night Limited'' was an express passenger train that operated in New Zealand between Wellington and Auckland, utilising the entire length of the North Island Main Trunk. It commenced service on 15 December 1924 and was replaced by the Silver Star in September 1971 and supplemented by the '' Northerner'' express in November 1975. Introduction When the North Island Main Trunk railway was completed in 1908, services between Auckland and Wellington were slow and tedious, taking two days to complete the journey. The first expresses ran on 14 February 1909 and took 19 hours 13 minutes, though stopping only at Paekākāriki, Palmerston North, Feilding, Marton, Taihape, Ohakune, Taumarunui, Te Kuiti, and Frankton. The ''Night Limited'' was introduced in December 1924 to provide a quicker service. Its name stemmed from the fact it ran overnight and had limited stops at Palmerston North, Marton, Taihape, Ohakune, Taumarunui and Frankton. AB class steam locomotives were emp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |