|
Thallium Halides
The thallium halides include monohalides , where thallium has oxidation state +1, trihalides , where thallium generally has oxidation state +3, and some intermediate halides containing thallium with mixed +1 and +3 oxidation states. X is a halogen. These salts find use in specialized optical settings, such as focusing elements in research spectrophotometers. Compared to the more common zinc selenide-based optics, materials such as thallium bromoiodide enable transmission at longer wavelengths. In the infrared, this allows for measurements as low as 350 cm−1 (28 μm), whereas zinc selenide is opaque by 21.5 μm, and zinc sulfide optics are generally only usable to 650 cm−1 (15 μm). Monohalides The monohalides, also known as thallous halides, all contain thallium with oxidation state +1. Parallels can be drawn between the thallium(I) halides and their corresponding silver salts; for example, thallium(I) chloride and bromide are light-sensitive, and thal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halide
In chemistry, a halide (rarely halogenide) is a binary chemical compound, of which one part is a halogen atom and the other part is an element or radical that is less electronegative (or more electropositive) than the halogen, to make a fluoride, chloride, bromide, iodide, astatide, or theoretically tennesside compound. The alkali metals combine directly with halogens under appropriate conditions forming halides of the general formula, MX (X = F, Cl, Br or I). Many salts are halides; the ''hal-'' syllable in ''halide'' and '' halite'' reflects this correlation. A halide ion is a halogen atom bearing a negative charge. The common halide anions are fluoride (), chloride (), bromide (), and iodide (). Such ions are present in many ionic halide salts. Halide minerals contain halides. All these halide anions are colorless. Halides also form covalent bonds, examples being colorless TiF4, colorless TiCl4, orange TiBr4, and brown TiI4. The heavier members TiCl4, TiBr4 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Zeiss AG
Zeiss ( ; ) is a German manufacturer of optical systems and optoelectronics, founded in Jena, Germany, in 1846 by optician Carl Zeiss. Together with Ernst Abbe (joined 1866) and Otto Schott (joined 1884) he laid the foundation for today's multinational company. The current company emerged from a reunification of Carl Zeiss companies in East and West Germany with a consolidation phase in the 1990s. ZEISS is active in four business segments with approximately equal revenue (Industrial Quality and Research, Medical Technology, Consumer Markets and Semiconductor Manufacturing Technology) in almost 50 countries, has 30 production sites and around 25 development sites worldwide. Carl Zeiss AG is the holding of all subsidiaries within Zeiss Group, of which Carl Zeiss Meditec AG is the only one that is traded at the stock market. Carl Zeiss AG is owned by the foundation Carl-Zeiss-Stiftung. The Zeiss Group has its headquarters in southern Germany, in the small town of Oberkochen, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thallium Triiodide
Thallium triiodide, more precisely thallium(I) triiodide is a chemical compound of thallium and iodine with empirical formula . Unlike the other thallium trihalides, which contain thallium(III), is actually a thallium(I) salt containing thallium(I) cations and triiodide anions , and thus has the chemical formula . It is a black crystalline solid. An appreciation as to why is not oxidised to in the reaction: : can be gained by considering the standard reduction potentials of the half-cells which are: :;''Er''° = 1.252 :;''Er''° = 0.5355 The favoured reaction is therefore the reduction of to (1.252 > 0.5355). Using standard electrode potentials in this way must be done with caution as factors such as complex formation and solvation may affect the reaction. is no exception as it is possible to stabilise thallium(III) with excess forming the tetraiodothallate(III) ion (isoelectronic with the tetraiodomercurate anion and with lead(IV) iodide ). Structure and prepara ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water Of Crystallization
In chemistry, water(s) of crystallization or water(s) of hydration are water molecules that are present inside crystals. Water is often incorporated in the formation of crystals from aqueous solutions. In some contexts, water of crystallization is the total mass of water in a chemical substance, substance at a given temperature and is mostly present in a definite (stoichiometric) ratio. Classically, "water of crystallization" refers to water that is found in the Crystal structure, crystalline framework of a metal complex or a salt (chemistry), salt, which is not directly chemical bond, bonded to the metal cation. Upon crystallization from water, or water-containing solvents, many chemical compound, compounds incorporate water molecules in their crystalline frameworks. Water of crystallization can generally be removed by heating a sample but the crystalline properties are often lost. Compared to Inorganic compound, inorganic salts, proteins crystallize with large amounts of water i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromium(III) Chloride
Chromium(III) chloride (also called chromic chloride) is an inorganic chemical compound with the chemical formula . This crystalline salt forms several hydrates with the formula , among which are hydrates where ''n'' can be 5 (chromium(III) chloride pentahydrate ) or 6 (chromium(III) chloride hexahydrate ). The anhydrous compound with the formula are violet crystals, while the most common form of the chromium(III) chloride are the dark green crystals of hexahydrate, . Chromium chlorides find use as catalysts and as precursors to dyes for wool. Structure Anhydrous chromium(III) chloride adopts the structure, with occupying one third of the octahedral interstices in alternating layers of a pseudo- cubic close packed lattice of ions. The absence of cations in alternate layers leads to weak bonding between adjacent layers. For this reason, crystals of cleave easily along the planes between layers, which results in the flaky (micaceous) appearance of samples of chromium(III) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
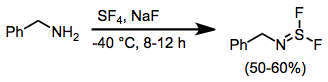
Sulfur Tetrafluoride
Sulfur tetrafluoride is a chemical compound with the formula S F4. It is a colorless corrosive gas that releases dangerous hydrogen fluoride gas upon exposure to water or moisture. Sulfur tetrafluoride is a useful reagent for the preparation of organofluorine compounds, some of which are important in the pharmaceutical and specialty chemical industries. Structure Sulfur in SF4 is in the +4 oxidation state, with one lone pair of electrons. The atoms in SF4 are arranged in a see-saw shape, with the sulfur atom at the center. One of the three equatorial positions is occupied by a nonbonding lone pair of electrons. Consequently, the molecule has two distinct types of F ligands, two axial and two equatorial. The relevant bond distances are = 164.3 pm and = 154.2 pm. It is typical for the axial ligands in hypervalent molecules to be bonded less strongly. The 19F NMR spectrum of SF4 reveals only one signal, which indicates that the axial and equatorial F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bromine Trifluoride
Bromine trifluoride is an interhalogen compound with the formula BrF3. At room temperature, it is a straw-coloured liquid with a pungent odor which decomposes violently on contact with water and organic compounds. It is a powerful fluorinating agent and an ionizing inorganic solvent. It is used to produce uranium hexafluoride (UF6) in the processing and reprocessing of nuclear fuel. Synthesis Bromine trifluoride was first described by Paul Lebeau in 1906, who obtained the material by the reaction of bromine with fluorine at 20 °C: : The disproportionation of bromine monofluoride also gives bromine trifluoride: : Structure Like ClF3 and IF3, the BrF3 molecule is T-shaped and planar. In the VSEPR formalism, the bromine center is assigned two electron lone pairs. The distance from the bromine atom to each axial fluorine atom is 1.81 Å and to the equatorial fluorine atom is 1.72 Å. The angle between an axial fluorine atom and the equatorial fluorine atom is slight ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thallium(III) Fluoride
Thallium trifluoride is the inorganic compound An inorganic compound is typically a chemical compound that lacks carbon–hydrogen bondsthat is, a compound that is not an organic compound. The study of inorganic compounds is a subfield of chemistry known as ''inorganic chemistry''. Inorgan ... with the formula TlF3. It is a white solid. Aside from being one of two thallium fluorides, the compound is only of theoretical interest. It adopts the same structure as bismuth trifluoride, featuring eight-coordinate Tl(III) centers. Some evidence exists for a second polymorph. References {{fluorides Fluorides Metal halides Thallium(III) compounds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CRC Press
The CRC Press, LLC is an American publishing group that specializes in producing technical books. Many of their books relate to engineering, science and mathematics. Their scope also includes books on business, forensics and information technology. CRC Press is now a division of Taylor & Francis, itself a subsidiary of Informa. History The CRC Press was founded as the Chemical Rubber Company (CRC) in 1903 by brothers Arthur, Leo and Emanuel Friedman in Cleveland, Ohio, based on an earlier enterprise by Arthur, who had begun selling rubber laboratory aprons in 1900. The company gradually expanded to include sales of laboratory equipment to chemist A chemist (from Greek ''chēm(ía)'' alchemy; replacing ''chymist'' from Medieval Latin ''alchemist'') is a graduated scientist trained in the study of chemistry, or an officially enrolled student in the field. Chemists study the composition of ...s. In 1913 the CRC offered a short (116-page) manual called the ''Rubber Handboo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frank Twyman
Frank Twyman (17 November 1876 – 6 March 1959) was a British designer of optical instruments and co-inventor of the Twyman–Green interferometer. Early life Twyman was born in Canterbury, Kent, England on 17 November 1876, the seventh child of nine to Jane Lefevre and ropemaker George Edmund Twyman. He attended Simon Langton School before doing an electrical engineering course at Finsbury Technical College, followed by a Siemens scholarship at Central Technical College in London. In 1897 he co-authored his first scientific paper. Career Twyman worked briefly for the Fowler Waring Cables Company testing telephone cables, before beginning work in 1898 for optical instrument manufacturing firm Adam Hilger as an assistant to Otto Hilger. Following the death of Otto Hilger, Twyman became managing director of the firm. He remained in post until 1946 when he became chairman. Until 1910 he managed the design and construction of all of the firms new equipment. This included a d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hygroscopic
Hygroscopy is the phenomenon of attracting and holding water molecules via either absorption (chemistry), absorption or adsorption from the surrounding Natural environment, environment, which is usually at normal or room temperature. If water molecules become suspended among the substance's molecules, adsorbing substances can become physically changed, e.g. changing in volume, boiling point, viscosity or some other physical characteristic or property of the substance. For example, a finely dispersed hygroscopic powder, such as a salt, may become clumpy over time due to collection of moisture from the surrounding environment. ''Deliquescent'' materials are sufficiently hygroscopic that they dissolve in the water they absorb, forming an aqueous solution. Hygroscopy is essential for many plant and animal species' attainment of hydration, nutrition, reproduction and/or seed dispersal. Biological evolution created hygroscopic solutions for water harvesting, filament tensile strength, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |