|
Thalattosaur
Thalattosauria (Greek for "sea lizards") is an extinct order of marine reptiles that lived during the Triassic Period. Thalattosaurs were diverse in size and shape, and are divided into two superfamilies: Askeptosauroidea and Thalattosauroidea. Askeptosauroids were endemic to the Tethys Ocean, their fossils have been found in Europe and China, and they were likely semiaquatic fish eaters with straight snouts and decent terrestrial abilities. Thalattosauroids were more specialized for aquatic life and most had unusual downturned snouts and crushing dentition. Thalattosauroids lived along the coasts of both Panthalassa and the Tethys Ocean, and were most diverse in China and western North America. The largest species of thalattosaurs grew to over 4 meters (13 feet) in length, including a long, flattened tail utilized in underwater propulsion. Although thalattosaurs bore a superficial resemblance to lizards, their exact relationships are unresolved. They are widely accepted as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thalattosaurus Alexandrae
''Thalattosaurus'' (pronounced: , from and ) is an extinct genus of marine reptile in the family Thalattosauroidea. Known exclusively from the Triassic period, it was a long shellfish-eating diapsid with paddle-like limbs and a down-turned rostrum. Fossils were recovered in the Lower and Middle Triassic Sulphur Mountain Formation of British Columbia as well as the Upper Triassic Hosselkus Limestone of California. It has gained notoriety as a result of studies on general diapsid phylogeny. Although originally described as four distinct species by Merriam in 1905, one was proven to be ''T. alexandrae'' upon further inspection and another has a missing type specimen. Currently it is believed to include two known species; ''Thalattosaurus alexandrae'' and ''T. borealis''. Discovery and naming In summer 1903, Annie Alexander led an expedition with Miss Edna Wemple, Eustace Furlong, Merriam John C, W.B. Esterly, and Mr. F.S. Ray to Shasta County where they discovered what the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thalattosauroidea
Thalattosauroidea is a superfamily (zoology), superfamily of thalattosaurs, a Triassic group of marine reptiles. It was named in 1904 by paleontologist John Campbell Merriam to include the genus ''Thalattosaurus'' from California. Thalattosauroids are one of two groups of Thalattosauria, the other being Askeptosauroidea. Thalattosauroids make up the "traditional" thalattosaurs with large downturned snouts, short necks, and long, paddle-like tails. Classification Thalattosauria includes North American genera such as ''Thalattosaurus'' and ''Nectosaurus'' as well as recently described China, Chinese forms such as ''Xinpusaurus''. A 1999 study of thalattosaurs, which established much of the currently accepted phylogeny of the group, referred to Thalattosauroidea as Thalattosauria, while calling the larger group Thalattosauriformes. More recent phylogenetic studies have come upon the same conclusions, but refer to the group as Thalattosauroidea in order to contrast it with another sup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
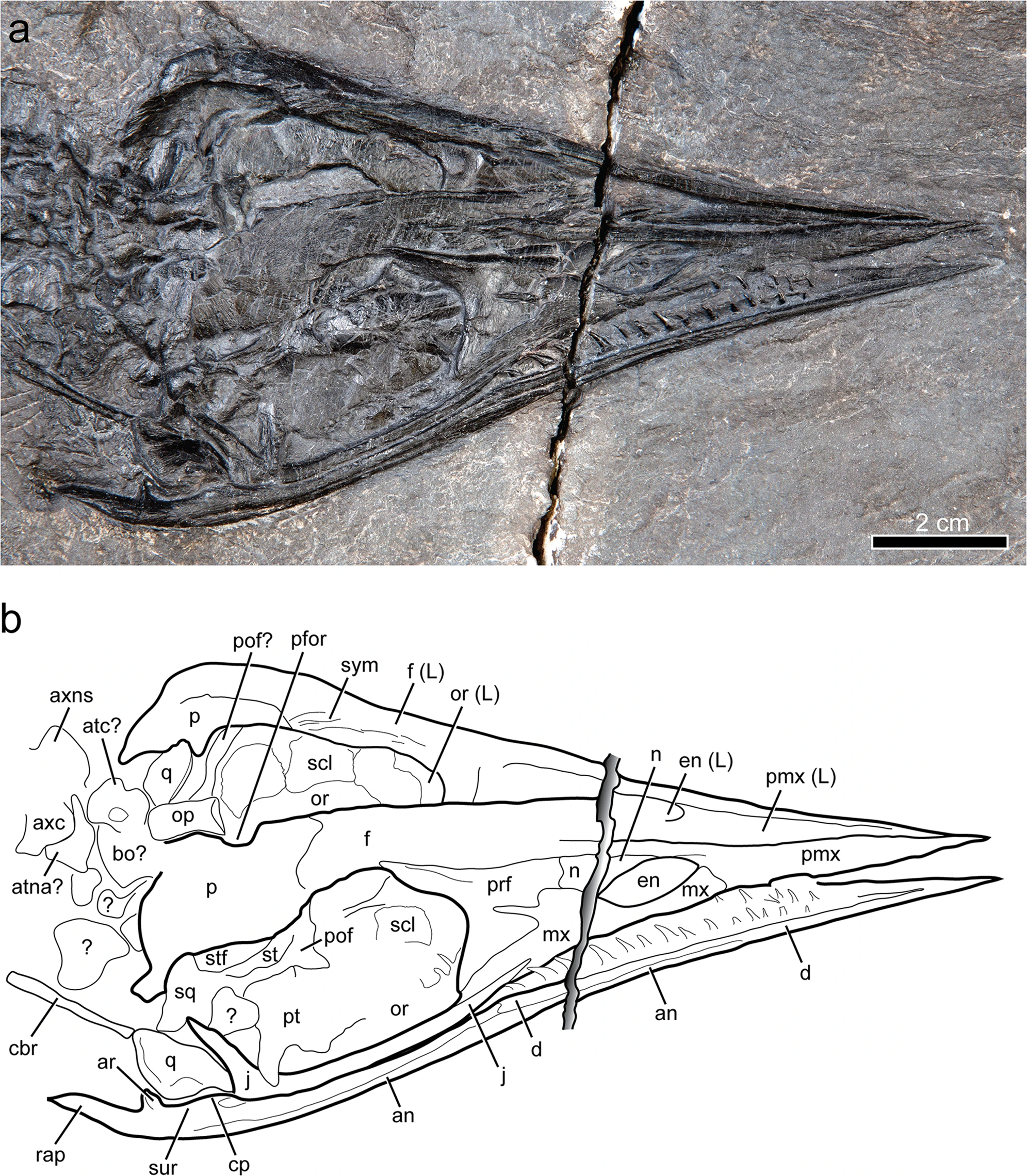
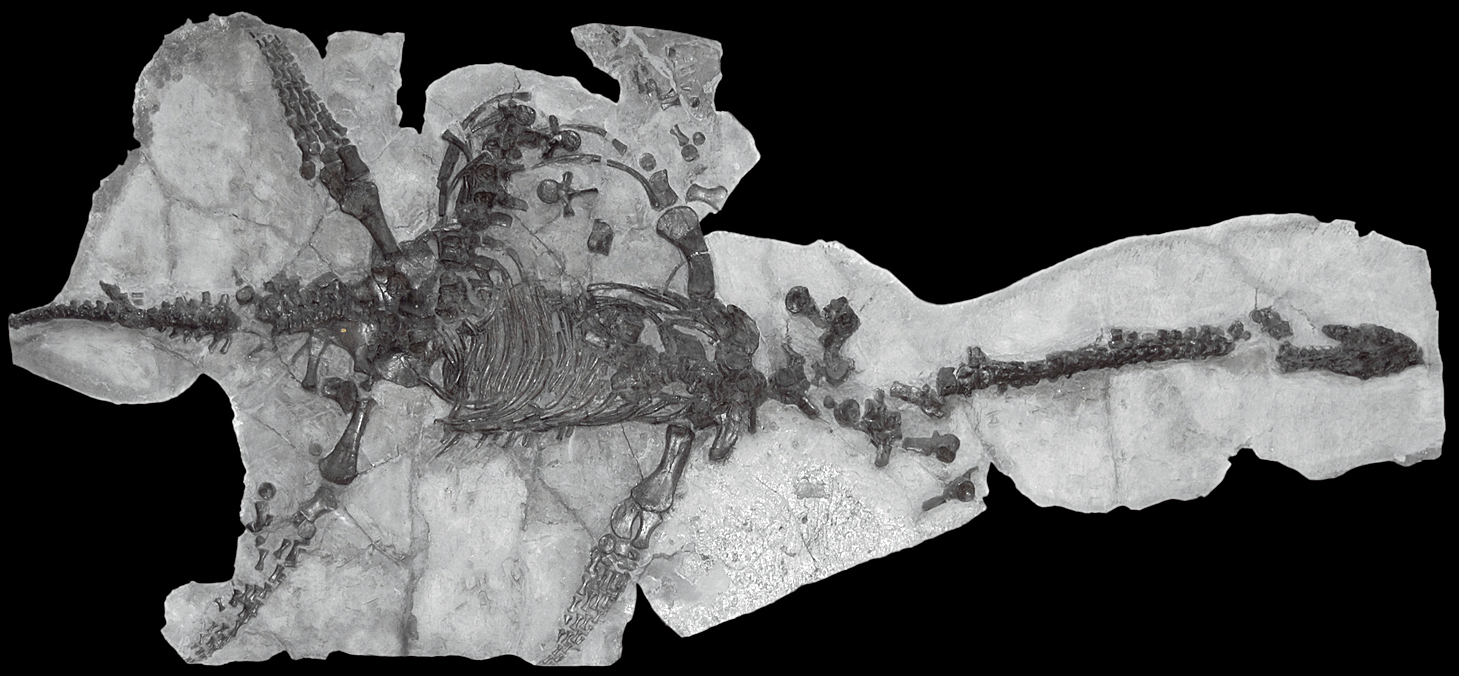
Gunakadeit Joseeae
''Gunakadeit'' is an extinct genus of thalattosaur. It is known from a single species, ''Gunakadeit joseeae'', which is based on an articulated and mostly complete skeleton from the late Triassic (middle Norian) Hound Island Volcanics of Alaska. ''Gunakadeit'' possessed a variety of features from the two major suborders of thalattosaurs, Askeptosauroidea and Thalattosauroidea, and it is considered the most Basal (phylogenetics), basal member of the latter group. Despite this, it is also the youngest known thalattosaur genus, with the group going extinct at the end of the Triassic. ''Gunakadeits basal position and relatively recent occurrence implies a 20-million-year ghost lineage connecting it to the rest of Thalattosauria. The skull ends in a sharply pointed and toothless tip like the askeptosauroid ''Endennasaurus'', but unlike ''Endennasaurus'', ''Gunakadeit'' had poorly developed joints and was likely exclusively aquatic in behavior. Discovery The holotype, University of A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Askeptosauroidea
Askeptosauroidea is a superfamily of thalattosaurs, a Triassic group of marine reptiles. Askeptosauroidea is one of two major subgroups of Thalattosauria, the other being Thalattosauroidea. It includes the family Askeptosauridae and a more basal form called ''Endennasaurus''. Phylogeny Below is a cladogram from Wu ''et al.'' (2009) showing the phylogenetic In biology, phylogenetics () is the study of the evolutionary history of life using observable characteristics of organisms (or genes), which is known as phylogenetic inference. It infers the relationship among organisms based on empirical dat ... relationships of Askeptosauroidea: References Thalattosauria Triassic first appearances Triassic extinctions {{triassic-reptile-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Askeptosaurus Italicus
''Askeptosaurus'' is an extinct genus of askeptosauroid, a marine reptile from the extinct order Thalattosauria. ''Askeptosaurus'' is known from several well-preserved fossils found in Middle Triassic marine strata in what is now Italy and Switzerland. History of discovery ''Askeptosaurus,'' and its only known species ''Askeptosaurus italicus,'' were first named and described in 1925 by Hungarian paleontologist Franz Nopcsa von Felső-Szilvás. It was most recently redescribed by Dr. Johannes Müller in 2005. ''Askeptosaurus'' is known from several disarticulated and articulated skeletons preserved at the MSNM (Museo Civico di Storia Naturale di Milano) in Milan, Italy, and the PIMUZ ('' Paläontologisches Institut und Museum der Universität Zürich'', Paleontological Institute and of the University of Zurich) in Zurich, Switzerland. These specimens were discovered in the Grenzbitumenzone of Monte San Giorgio, a UNESCO World Heritage Site on the Swiss-Italian border. Also kn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sauropterygian
Sauropterygia ("lizard Flipper (anatomy), flippers") is an extinct taxon of diverse, aquatic diapsid reptiles that developed from terrestrial ancestors soon after the Permian–Triassic extinction event, end-Permian extinction and flourished during the Triassic before all except for the Plesiosauria became extinct at the end of that period. The plesiosaurs would continue to diversify until the end of the Mesozoic, when they became extinct as part of the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, end-Cretaceous mass extinction. Sauropterygians are united by a radical adaptation of their pectoral girdle, adapted to support powerful flipper strokes. Some later sauropterygians, such as the pliosaurs, developed a similar mechanism in their pelvis. Other than being diapsids, their affinities to other reptiles have long been contentious. Sometimes suggested to be closely related to turtles, other proposals have considered them most closely related to Lepidosauromorpha or Archosauromorpha, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diapsid
Diapsids ("two arches") are a clade of sauropsids, distinguished from more primitive eureptiles by the presence of two holes, known as temporal fenestrae, in each side of their skulls. The earliest traditionally identified diapsids, the araeoscelidians, appeared about three hundred million years ago during the late Carboniferous period. All diapsids other than the most primitive ones in the clade Araeoscelidia are often placed into the clade Neodiapsida. The diapsids are extremely diverse, and include birds and all modern reptile groups, including turtles, which were historically thought to lie outside the group. All modern reptiles and birds are placed within the neodiapsid subclade Sauria. Although some diapsids have lost either one hole (lizards), or both holes (snakes and turtles), or have a heavily restructured skull (modern birds), they are still classified as diapsids based on their ancestry. At least 17,084 species of diapsid animals are extant: 9,159 birds, and 7,925 s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blezingeria
''Blezingeria'' is an extinct genus of marine reptile from the Middle Triassic of Germany. The type and only species ''Blezingeria ichthyospondyla'' was named by German paleontologist Eberhard Fraas in 1896. It is known from many isolated bones that come from a deposit in southwestern Germany called the Upper Muschelkalk, which dates back to the Ladinian stage. The relationships of ''Blezingeria'' are uncertain. Fraas identified it as a nothosaur, but it has also been classified as a cymbospondylid ichthyosaur, and most recently a thalattosaur. Many thalattosaur fossils have been found in a slightly olderLate Ladinian-age rock unit in Monte San Giorgio, Switzerland, so if ''Blezingeria'' is a thalattosaur, it may represent an early stage in an evolutionary radiation An evolutionary radiation is an increase in taxonomic diversity that is caused by elevated rates of speciation, that may or may not be associated with an increase in morphological disparity. A significantly la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archosauromorpha
Archosauromorpha ( Greek for "ruling lizard forms") is a clade of diapsid reptiles containing all reptiles more closely related to archosaurs (such as crocodilians and dinosaurs, including birds) than to lepidosaurs (such as tuataras, lizards, and snakes). Archosauromorphs first appeared during the late Middle Permian or Late Permian, though they became much more common and diverse during the Triassic period. Although Archosauromorpha was first named in 1946, its membership did not become well-established until the 1980s. Currently Archosauromorpha encompasses four main groups of reptiles: the stocky, herbivorous allokotosaurs and rhynchosaurs, the hugely diverse Archosauriformes, and a polyphyletic grouping of various long-necked reptiles including '' Protorosaurus'', tanystropheids, and '' Prolacerta''. Other groups including pantestudines (turtles and their extinct relatives) and the semiaquatic choristoderes have also been placed in Archosauromorpha by some authors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endennasaurus Acutirostris
''Endennasaurus'' is an extinct genus of thalattosaurian from the Upper Triassic of Italy. It was found in and named after the Endenna cave, composed of Zorzino Limestone in Lombardia. at Fossilworks
Fossilworks was a portal which provides query, download, and analysis tools to facilitate access to the Paleobiology Database, a large relational database assembled by hundreds of paleontologists from around the world.
History
Fossilworks was cr ... .org
Gallery References Thalattosauria[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marine Reptile
Marine reptiles are reptiles which have become secondarily adapted for an aquatic or semiaquatic life in a marine environment. Only about 100 of the 12,000 extant reptile species and subspecies are classed as marine reptiles, including marine iguanas, sea snakes, sea turtles and saltwater crocodiles. The earliest marine reptile was '' Mesosaurus'' (not to be confused with '' Mosasaurus''), which arose in the Permian period of the Paleozoic era. During the Mesozoic era, many groups of reptiles became adapted to life in the seas, including such familiar clades as the ichthyosaurs, plesiosaurs (these two orders were once thought united in the group "Enaliosauria", a classification now cladistically obsolete), mosasaurs, nothosaurs, placodonts, sea turtles, thalattosaurs and thalattosuchians. Most marine reptile groups became extinct at the end of the Cretaceous period, but some still existed during the Cenozoic, most importantly the sea turtles. Other Cenozoic marine r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triassic
The Triassic ( ; sometimes symbolized 🝈) is a geologic period and system which spans 50.5 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.4 Mya. The Triassic is the first and shortest period of the Mesozoic Era and the seventh period of the Phanerozoic Eon. Both the start and end of the period are marked by major extinction events. The Triassic Period is subdivided into three epochs: Early Triassic, Middle Triassic and Late Triassic. The Triassic began in the wake of the Permian–Triassic extinction event, which left the Earth's biosphere impoverished; it was well into the middle of the Triassic before life recovered its former diversity. Three categories of organisms can be distinguished in the Triassic record: survivors from the extinction event, new groups that flourished briefly, and other new groups that went on to dominate the Mesozoic Era. Reptiles, especially archosaurs, were the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |