|
Texture (Musical)
Texture may refer to: Science and technology * Image texture, the spatial arrangement of color or intensities in an image * Surface texture, the smoothness, roughness, or bumpiness of the surface of an object * Texture (roads), road surface characteristics with waves shorter than road roughness * Texture (cosmology), a theoretical topological defect in the structure of spacetime * Crystallographic texture, distribution of crystallographic orientations in a polycrystalline material * Texture (geology), a physical appearance or character of a rock * Texture mapping, a bitmap image applied to a surface in computer graphics * Soil texture, a relative proportion of grain sizes of a soil Arts * Texture (visual arts), an element of design and its application in art Music * Texture (music), an overall sound created by the interaction of aspects of a piece of music * ''Textures'' (album), a 1989 album by Brian Eno * Textures (band), a metal band from the Netherlands, who formed in 2001 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Image Texture
An image texture is the small-scale structure perceived on an image, based on the spatial arrangement of color or intensities. It can be quantified by a set of metrics calculated in image processing. Image texture metrics give us information about the whole image or selected regions. Linda G. Shapiro and George C. Stockman, ''Computer Vision'', Upper Saddle River: Prentice–Hall, 2001 Image textures can be artificially created or found in natural scenes captured in an image. Image textures are one way that can be used to help in segmentation or classification of images. For more accurate segmentation the most useful features are spatial frequency and an average grey level. To analyze an image texture in computer graphics, there are two ways to approach the issue: Structured Approach and Statistical Approach. Structured Approach A structured approach sees an image texture as a set of primitive texels in some regular or repeated pattern. This works well when analyzing a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
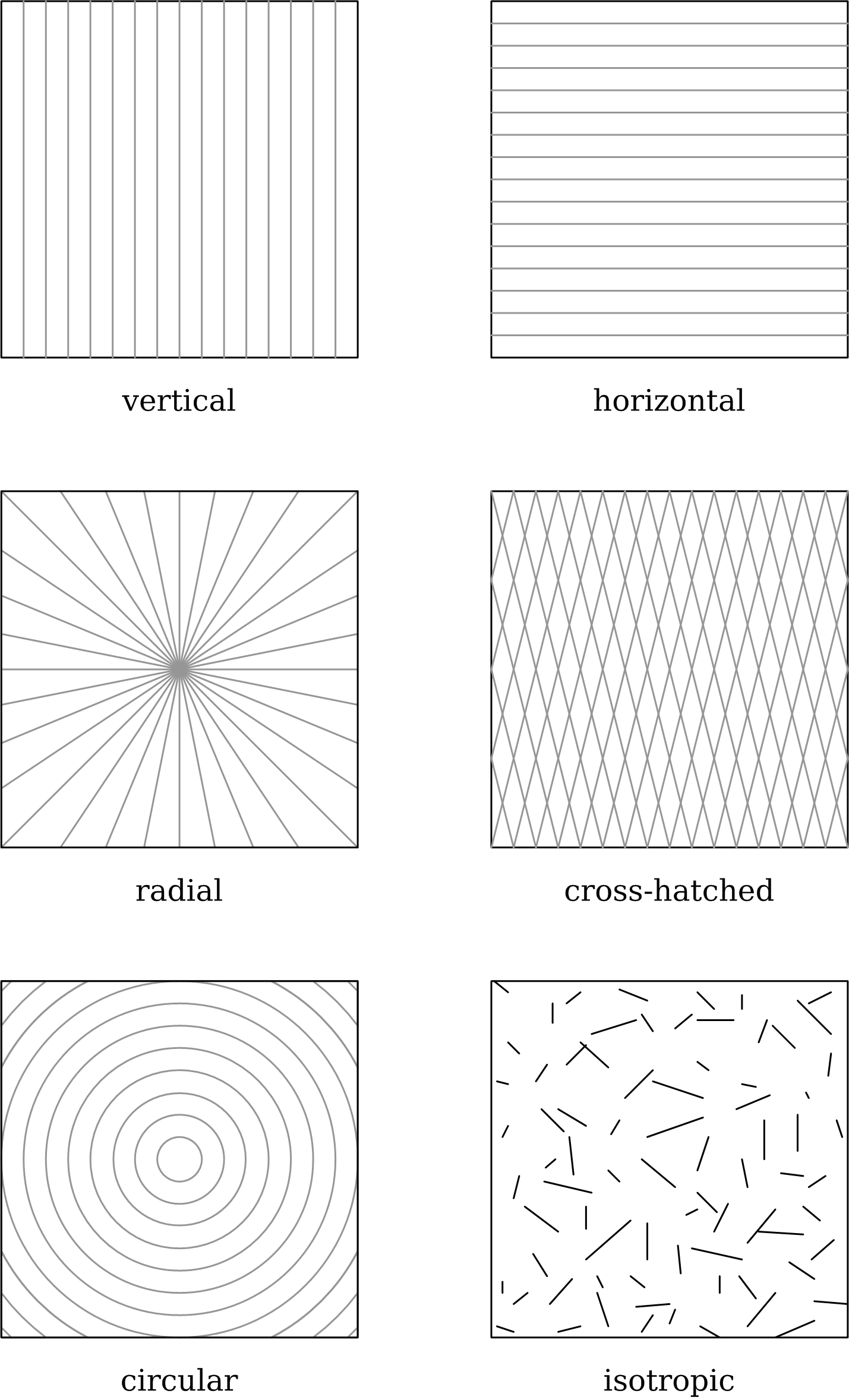
Surface Texture
Surface finish, also known as surface texture or surface topography, is the nature of a surface as defined by the three characteristics of lay, surface roughness, and waviness.. It comprises the small, local deviations of a surface from the perfectly flat ideal (a true plane). Surface texture is one of the important factors that control friction and transfer layer formation during sliding. Considerable efforts have been made to study the influence of surface texture on friction and wear during sliding conditions. Surface textures can be isotropic or anisotropic. Sometimes, stick-slip friction phenomena can be observed during sliding, depending on surface texture. Each manufacturing process (such as the many kinds of machining) produces a surface texture. The process is usually optimized to ensure that the resulting texture is usable. If necessary, an additional process will be added to modify the initial texture. The latter process may be grinding (abrasive cutting), polishi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Texture (roads)
Road surface textures are deviations from a planar and smooth surface, affecting the vehicle/tyre interaction. Pavement texture is divided into: microtexture with wavelengths from 0 mm to , macrotexture with wavelengths from to and megatexture with wavelengths from to . Microtexture Microtexture (MiTx) is the collaborative term for a material's crystallographic parameters and other aspects of microstructure: such as morphology, including size and shape distributions; chemical composition; and crystal orientation and relationships While vehicle suspension deflection and dynamic tire loads are affected by longer wavelength ( roughness), road texture affects the interaction between the road surface and the tire footprint. Microtexture has wavelengths shorter than 0.5 mm. It relates to the surface of the binder, of the aggregate, and of contaminants such as rubber deposits from tires. The mix of the road material contributes to dry road surface friction. Typically, r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Texture (cosmology)
In cosmology, a texture is a type of topological defect in the order parameter (typically a scalar field) of a field theory featuring spontaneous symmetry breaking. They are not as localized as the other defects, and are unstable. No textures have been definitively confirmed as having been detected, but their existence is compatible with current theories and observations of the universe. In late 2007 a cold spot in the cosmic microwave background The cosmic microwave background (CMB, CMBR), or relic radiation, is microwave radiation that fills all space in the observable universe. With a standard optical telescope, the background space between stars and galaxies is almost completely dar ... detected by the Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe was interpreted as possibly being a sign of a texture lying in that direction. A 2012 study found no evidence of textures. References Large-scale structure of the cosmos {{physical-cosmology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crystallographic Texture
In materials science and related fields, crystallographic texture is the distribution of crystallographic orientations of a polycrystalline sample. A sample in which these orientations are fully random or is amorphous and thus no crystallographic planes, is said to have no texture. If the crystallographic orientations are not random, but have some preferred orientation, then the sample may have a weak, moderate or strong texture. The degree is dependent on the percentage of crystals having the preferred orientation. Texture is seen in almost all engineered materials, and can have a great influence on materials properties. The texture forms in materials during thermo-mechanical processes, for example during production processes e.g. Rolling (metalworking), rolling. Consequently, the rolling process is often followed by a heat treatment to reduce the amount of unwanted texture. Controlling the production process in combination with the characterization of texture and the material's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Texture (geology)
In geology, texture or rock microstructure refers to the relationship between the materials of which a rock is composed. The broadest textural classes are crystalline (in which the components are intergrown and interlocking crystals), fragmental (in which there is an accumulation of fragments by some physical process), aphanitic (in which crystals are not visible to the unaided eye), and glassy (in which the particles are too small to be seen and amorphously arranged).Texture & Genesis of Rocks, Introductory Geology Laboratory, Christopher DiLeonardo, Ph.D., Marek Cichanski, Ph.D., Earth & Space Sciences, De Anza College The geometric aspects and relations amongst the component particles or crystals are referred to as the '' crystallographic texture'' or ''preferred orientation''. Textures can be quantified in many ways. A common parameter is the crystal size distribution. This creates the physical appearance or character of a rock, such as grain size, shape, arrangement, and ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Texture Mapping
Texture mapping is a term used in computer graphics to describe how 2D images are projected onto 3D models. The most common variant is the UV unwrap, which can be described as an inverse paper cutout, where the surfaces of a 3D model are cut apart so that it can be unfolded into a 2D coordinate space (UV Space). Semantic Texture mapping can both refer to the task of unwrapping a 3D model, the abstract that a 3D model has textures applied to it and the related algorithm of the 3D software. Texture map refers to a Raster graphics also called image, texture. If the texture stores a specific property it's also referred to as color map, roughness map, etc. The coordinate space which converts from the 3D space of a 3D model into a 2D space so that it can sample from the Texture map is called: UV Space, UV Coordinates, Texture Space. Algorithm A simplified explanation of how an algorithm could work to render an image: # For each pixel we trace the coordinates of the screen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soil Texture
Soil texture is a soil classification, classification instrument used both in the field and laboratory to determine soil classes based on their physical texture. Soil texture can be determined using qualitative methods such as texture by feel, and quantitative methods such as the hydrometer method based on Stokes' law. Soil texture has agricultural applications such as determining crop suitability and to predict the response of the soil to environmental and management conditions such as drought or calcium (lime) requirements. Soil texture focuses on the particles that are less than two millimeters in diameter which include sand, silt, and clay. The USDA soil taxonomy and World Reference Base for Soil Resources, WRB soil classification systems use 12 textural classes whereas the ADAS (company), UK-ADAS system uses 11. These classifications are based on the percentages of sand, silt, and clay in the soil. History The first classification, the international system, was first propos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Texture (visual Arts)
In the visual arts, texture refers to the perceived surface quality of a work of art. It is an element found in both two-dimensional and three-dimensional designs, and it is characterized by its visual and physical properties. The use of ''texture'', in conjunction with other design elements, can convey a wide range of messages and evoke various emotions. Physical The physical texture, also known as ''actual texture'' or ''tactile texture,'' refers to the patterns of variations found on a solid surface. These can encompass a wide range of materials, including but not limited to fur, canvas, wood grain, sand, leather, satin, eggshell, matte, or smooth surfaces like metal or glass. Physical texture differentiates itself from visual texture by having a ''physical quality'' that can be felt by touching the surface. The specific use of texture can impact the perceived smoothness or roughness conveyed by an artwork. For instance, ''rough surfaces'' can create a visually ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Texture (music)
In music, texture is how the tempo and the melodic and harmonic materials are combined in a musical composition, determining the overall quality of the sound in a piece. The texture is often described in regard to the density, or thickness, and range, or width, between lowest and highest pitches, in relative terms as well as more specifically distinguished according to the number of voices, or parts, and the relationship between these voices (see Common types below). For example, a thick texture contains many 'layers' of instruments. One of these layers could be a string section or another brass. The thickness also is changed by the amount and the richness of the instruments playing the piece. The thickness varies from light to thick. A piece's texture may be changed by the number and character of parts playing at once, the timbre of the instruments or voices playing these parts and the harmony, tempo, and rhythms used. The types categorized by number and relationship of parts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Textures (album)
Brian Peter George Jean-Baptiste de la Salle Eno (, born 15 May 1948), also mononymously known as Eno, is an English musician, songwriter, record producer, visual artist, and activist. He is best known for his pioneering contributions to ambient music and electronica, and for producing, recording, and writing works in rock and pop music. A self-described "non-musician", Eno has helped introduce unconventional concepts and approaches to contemporary music. He has been described as one of popular music's most influential and innovative figures. In 2019, he was inducted into the Rock and Roll Hall of Fame as a member of Roxy Music. Born in Suffolk, Eno studied painting and experimental music at the art school of Ipswich Civic College in the mid-1960s, and then at Winchester School of Art. He joined the glam rock group Roxy Music as its synthesiser player in 1971 and recorded two albums with them before departing in 1973. He then released solo albums, beginning with ''Here Come the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |