|
Tetrallantos
''Tetrallantos'' is a genus of green algae in the Scenedesmaceae family. It is a component of the phytoplankton or metaphyton of freshwater habitats such as ponds and lakes It has been found worldwide, but appears to be somewhat rare. ''Tetrallantos'' consists of colonies (called coenobia) of four or eight cells. Each cell is crescent-shaped with rounded ends. In the center of the colony, two cells lie in one plane with their ends touching each other; the other cells are attached to those ends and are curved away in a different plane. Fragments of the parent cell wall persist as faint threads connecting the cells together. Each cell contains a single chloroplast filling the cell with a pyrenoid in its center. ''Tetrallantos'' reproduces asexually by the formation of autospores. In each cell, four (sometimes two or eight) spores are formed per sporangium, and are organized into the shape of coenobia. These are released from the mother cell via a tear in its cell wall A cell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scenedesmaceae
Scenedesmaceae is a family of green algae in the order Sphaeropleales. ''Scenedesmus'' algae are commonly found in freshwater plankton. The former family Coelastraceae is considered a synonym of Scenedesmaceae. Genera Genera in this family include: * '' Acutodesmus'' * '' Asterarcys'' * '' Astrocladium'' * '' Chodatodesmus'' * '' Closteriococcus'' * ''Coelastrella'' * '' Coelastropsis'' * '' Coelastrum'' * '' Comasiella'' * '' Crucigeniopsis'' * ''Danubia'' * ''Desmodesmus'' * ''Dimorphococcus'' * ''Enallax'' * '' Flechtneria'' * ''Gilbertsmithia'' * '' Hariotina'' * '' Hofmania'' * '' Hylodesmus'' * '' Komarekia'' * '' Lauterborniella'' * '' Neodesmus'' * '' Pectinodesmus'' * '' Pseudodidymocystis'' * '' Pseudotetrastrum'' * '' Scenedesmus'' * '' Schistochilium'' * '' Schmidledesmus'' * '' Schroederiella'' * '' Scotiellopsis'' * '' Soropediastrum'' * '' Staurogenia'' * '' Steinedesmus'' * ''Tetradesmus'' * '' Tetrallantos'' * '' Tetranephris'' * '' Tetrastrum'' * '' Trunca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. '' Panthera leo'' (lion) and '' Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus ''Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants of an ancestral taxon are grouped together (i.e. phylogenetic analysis should c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Green Algae
The green algae (singular: green alga) are a group consisting of the Prasinodermophyta and its unnamed sister which contains the Chlorophyta and Charophyta/ Streptophyta. The land plants ( Embryophytes) have emerged deep in the Charophyte alga as sister of the Zygnematophyceae. Since the realization that the Embryophytes emerged within the green algae, some authors are starting to properly include them. The completed clade that includes both green algae and embryophytes is monophyletic and is referred to as the clade Viridiplantae and as the kingdom Plantae. The green algae include unicellular and colonial flagellates, most with two flagella per cell, as well as various colonial, coccoid and filamentous forms, and macroscopic, multicellular seaweeds. There are about 22,000 species of green algae. Many species live most of their lives as single cells, while other species form coenobia (colonies), long filaments, or highly differentiated macroscopic seaweeds. A few oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phytoplankton
Phytoplankton () are the autotrophic (self-feeding) components of the plankton community and a key part of ocean and freshwater ecosystems. The name comes from the Greek words (), meaning 'plant', and (), meaning 'wanderer' or 'drifter'. Phytoplankton obtain their energy through photosynthesis, as do trees and other plants on land. This means phytoplankton must have light from the sun, so they live in the well-lit surface layers ( euphotic zone) of oceans and lakes. In comparison with terrestrial plants, phytoplankton are distributed over a larger surface area, are exposed to less seasonal variation and have markedly faster turnover rates than trees (days versus decades). As a result, phytoplankton respond rapidly on a global scale to climate variations. Phytoplankton form the base of marine and freshwater food webs and are key players in the global carbon cycle. They account for about half of global photosynthetic activity and at least half of the oxygen production, despi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coenobium (morphology)
Coenobium or coenobia may refer to : * Cenobitic monasticism Cenobitic (or coenobitic) monasticism is a monastic tradition that stresses community life. Often in the West the community belongs to a religious order, and the life of the cenobitic monk is regulated by a religious rule, a collection of prec ... (Cenobium, Cenobite), a monastic community in a tradition stressing communal life, as opposite to eremitism * Coenobium (morphology), a colony of cells, notably in algae * ''Coenobia'' (moth) {{dab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Wall
A cell wall is a structural layer surrounding some types of cells, just outside the cell membrane. It can be tough, flexible, and sometimes rigid. It provides the cell with both structural support and protection, and also acts as a filtering mechanism. Cell walls are absent in many eukaryotes, including animals, but are present in some other ones like fungi, algae and plants, and in most prokaryotes (except mollicute bacteria). A major function is to act as pressure vessels, preventing over-expansion of the cell when water enters. The composition of cell walls varies between taxonomic group and species and may depend on cell type and developmental stage. The primary cell wall of land plants is composed of the polysaccharides cellulose, hemicelluloses and pectin. Often, other polymers such as lignin, suberin or cutin are anchored to or embedded in plant cell walls. Algae possess cell walls made of glycoproteins and polysaccharides such as carrageenan and agar that are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
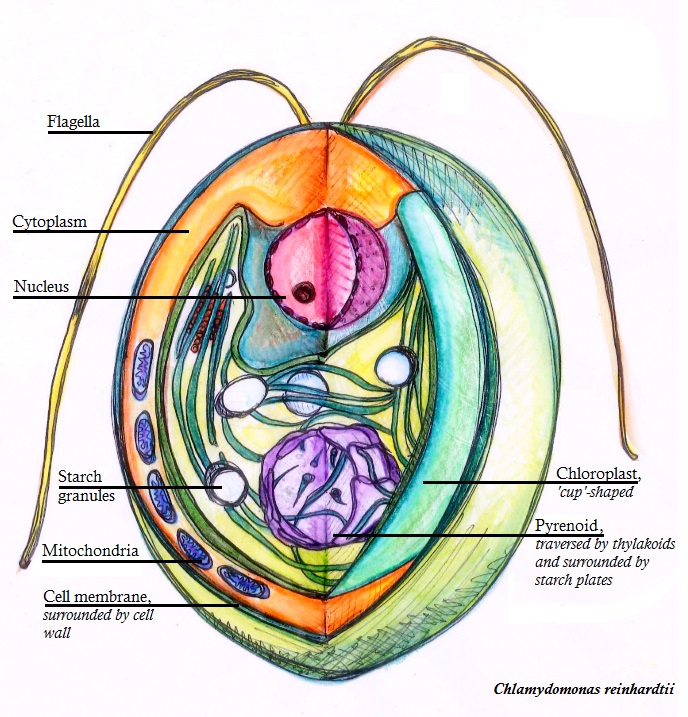
Chloroplast
A chloroplast () is a type of membrane-bound organelle known as a plastid that conducts photosynthesis mostly in plant and algal cells. The photosynthetic pigment chlorophyll captures the energy from sunlight, converts it, and stores it in the energy-storage molecules ATP and NADPH while freeing oxygen from water in the cells. The ATP and NADPH is then used to make organic molecules from carbon dioxide in a process known as the Calvin cycle. Chloroplasts carry out a number of other functions, including fatty acid synthesis, amino acid synthesis, and the immune response in plants. The number of chloroplasts per cell varies from one, in unicellular algae, up to 100 in plants like '' Arabidopsis'' and wheat. A chloroplast is characterized by its two membranes and a high concentration of chlorophyll. Other plastid types, such as the leucoplast and the chromoplast, contain little chlorophyll and do not carry out photosynthesis. Chloroplasts are highly dynamic—they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrenoid
Pyrenoids are sub-cellular micro-compartments found in chloroplasts of many algae,Giordano, M., Beardall, J., & Raven, J. A. (2005). CO2 concentrating mechanisms in algae: mechanisms, environmental modulation, and evolution. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol., 56, 99-131. and in a single group of land plants, the hornworts.Villarreal, J. C., & Renner, S. S. (2012) Hornwort pyrenoids, carbon-concentrating structures, evolved and were lost at least five times during the last 100 million years. ''Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences'',109(46), 1873-1887. Pyrenoids are associated with the operation of a carbon-concentrating mechanism (CCM). Their main function is to act as centres of carbon dioxide (CO2) fixation, by generating and maintaining a CO2 rich environment around the photosynthetic enzyme ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (RuBisCO). Pyrenoids therefore seem to have a role analogous to that of carboxysomes in cyanobacteria. Algae are restricted to aqueous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asexual Reproduction
Asexual reproduction is a type of reproduction that does not involve the fusion of gametes or change in the number of chromosomes. The offspring that arise by asexual reproduction from either unicellular or multicellular organisms inherit the full set of genes of their single parent and thus the newly created individual is genetically and physically similar to the parent or an exact clone of the parent. Asexual reproduction is the primary form of reproduction for single-celled organisms such as archaea and bacteria. Many eukaryotic organisms including plants, animals, and fungi can also reproduce asexually. In vertebrates, the most common form of asexual reproduction is parthenogenesis, which is typically used as an alternative to sexual reproduction in times when reproductive opportunities are limited. Komodo dragons and some monitor lizards can also reproduce asexually. While all prokaryotes reproduce without the formation and fusion of gametes, mechanisms for lateral g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autospore
An autospore is a non-motile (non-flagellated) aplanospore that is produced within a parent cell, and has the same shape as the parent cell, before release. Autospores, in addition to zoospore and aplanospore, are one of the three types of spores that algae use to reproduce and spread asexually. Autospores occur in several groups of algae, including Eustigmatophyceae, Dinoflagellates and green algae. For example, the colonial alga '' Dichotomococcus'' produces two autospores per reproducing cell; the autospores escape through a slit in the cell wall A cell wall is a structural layer surrounding some types of cells, just outside the cell membrane. It can be tough, flexible, and sometimes rigid. It provides the cell with both structural support and protection, and also acts as a filtering mech ... and remain attached to the mother cell. Autospore Formation An autospore is defined one of the daughter cells formed by the internal division of a single cell. Autospores are formed a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |