 |
Test Statistic
Test statistic is a quantity derived from the sample for statistical hypothesis testing.Berger, R. L.; Casella, G. (2001). ''Statistical Inference'', Duxbury Press, Second Edition (p.374) A hypothesis test is typically specified in terms of a test statistic, considered as a numerical summary of a data-set that reduces the data to one value that can be used to perform the hypothesis test. In general, a test statistic is selected or defined in such a way as to quantify, within observed data, behaviours that would distinguish the null from the alternative hypothesis, where such an alternative is prescribed, or that would characterize the null hypothesis if there is no explicitly stated alternative hypothesis. An important property of a test statistic is that its sampling distribution under the null hypothesis must be calculable, either exactly or approximately, which allows ''p''-values to be calculated. A ''test statistic'' shares some of the same qualities of a descriptive stat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Statistical Hypothesis Testing
A statistical hypothesis test is a method of statistical inference used to decide whether the data provide sufficient evidence to reject a particular hypothesis. A statistical hypothesis test typically involves a calculation of a test statistic. Then a decision is made, either by comparing the test statistic to a Critical value (statistics), critical value or equivalently by evaluating a p-value, ''p''-value computed from the test statistic. Roughly 100 list of statistical tests, specialized statistical tests are in use and noteworthy. History While hypothesis testing was popularized early in the 20th century, early forms were used in the 1700s. The first use is credited to John Arbuthnot (1710), followed by Pierre-Simon Laplace (1770s), in analyzing the human sex ratio at birth; see . Choice of null hypothesis Paul Meehl has argued that the epistemological importance of the choice of null hypothesis has gone largely unacknowledged. When the null hypothesis is predicted by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
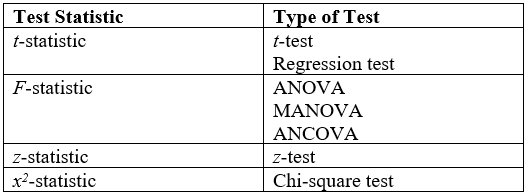
Common Test Statistics Chart
Common may refer to: As an Irish surname, it is anglicised from Irish language, Irish Gaelic surname Ó Comáin. Places * Common, a townland in County Tyrone, Northern Ireland * Boston Common, a central public park in Boston, Massachusetts * Cambridge Common, common land area in Cambridge, Massachusetts * Clapham Common, originally common land, now a park in London, UK * Common Moss, a townland in County Tyrone, Northern Ireland * Lexington Battle Green, Lexington Common, a common land area in Lexington, Massachusetts * Salem Common Historic District (Salem, Massachusetts), Salem Common Historic District, a common land area in Salem, Massachusetts People * Common (rapper) (born 1972), American hip hop artist, actor, and poet * Andrew Ainslie Common (1841–1903), English amateur astronomer * Andrew Common (1889–1953), British shipping director * John Common, American songwriter, musician and singer * Thomas Common (1850–1919), Scottish translator and literary critic Arts, e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Z-test
A ''Z''-test is any statistical test for which the distribution of the test statistic under the null hypothesis can be approximated by a normal distribution. ''Z''-test tests the mean of a distribution. For each statistical significance, significance level in the Confidence intervals, confidence interval, the ''Z''-test has a single critical value (for example, 1.96 for 5% two-tailed), which makes it more convenient than the Student's t-test, Student's ''t''-test whose critical values are defined by the sample size (through the corresponding degrees of freedom (statistics), degrees of freedom). Both the ''Z''-test and Student's ''t''-test have similarities in that they both help determine the significance of a set of data. However, the ''Z''-test is rarely used in practice because the population deviation is difficult to determine. Applicability Because of the central limit theorem, many test statistics are approximately normally distributed for large samples. Therefore, many s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Null Distribution
Null may refer to: Science, technology, and mathematics Astronomy *Nuller, an optical tool using interferometry to block certain sources of light Computing *Null (SQL) (or NULL), a special marker and keyword in SQL indicating that a data value does not exist, is not known, or is missing. *Null character, the zero-valued ASCII character, also designated by , often used as a terminator, separator or filler. This symbol has no visual representation. * Null device, a virtual file that discards data written to it, on Unix systems /dev/null *Null pointer or reference (sometimes written NULL, nil, or None), an object pointer (or reference) not currently set to point (or refer) to a valid object Mathematics * Null (mathematics), a zero value in several branches of mathematics Physics *Null (physics), a point in a field where the field quantity is zero * Null (radio), a concept in electromagnetism Arts and media *The Null Corporation, an imprint of the band Nine Inch Nails * ''Null'' (In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
McGraw Hill
McGraw Hill is an American education science company that provides educational content, software, and services for students and educators across various levels—from K-12 to higher education and professional settings. They produce textbooks, digital learning tools, and adaptive technology to enhance learning experiences and outcomes. It is one of the "big three" educational publishers along with Houghton Mifflin Harcourt and Pearson Education. McGraw Hill also publishes reference and trade publications for the medical, business, and engineering professions. Formerly a division of The McGraw Hill Companies (later renamed McGraw Hill Financial, now S&P Global), McGraw Hill Education was divested and acquired by Apollo Global Management in March 2013 for $2.4 billion in cash. McGraw Hill was sold in 2021 to Platinum Equity for $4.5 billion. History McGraw Hill was founded in 1888, when James H. McGraw, co-founder of McGraw Hill, purchased the ''American Journal of Railwa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Binomial Distribution
In probability theory and statistics, the binomial distribution with parameters and is the discrete probability distribution of the number of successes in a sequence of statistical independence, independent experiment (probability theory), experiments, each asking a yes–no question, and each with its own Boolean-valued function, Boolean-valued outcome (probability), outcome: ''success'' (with probability ) or ''failure'' (with probability ). A single success/failure experiment is also called a Bernoulli trial or Bernoulli experiment, and a sequence of outcomes is called a Bernoulli process; for a single trial, i.e., , the binomial distribution is a Bernoulli distribution. The binomial distribution is the basis for the binomial test of statistical significance. The binomial distribution is frequently used to model the number of successes in a sample of size drawn with replacement from a population of size . If the sampling is carried out without replacement, the draws ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Welch's T Test
In statistics, Welch's ''t''-test, or unequal variances ''t''-test, is a two-sample location test which is used to test the (null) hypothesis that two populations have equal means. It is named for its creator, Bernard Lewis Welch, and is an adaptation of Student's ''t''-test, and is more reliable when the two samples have unequal variances and possibly unequal sample sizes. These tests are often referred to as "unpaired" or "independent samples" ''t''-tests, as they are typically applied when the statistical units underlying the two samples being compared are non-overlapping. Given that Welch's ''t''-test has been less popular than Student's ''t''-test and may be less familiar to readers, a more informative name is "Welch's unequal variances ''t''-test" — or "unequal variances ''t''-test" for brevity. Sometimes, it is referred as Satterthwaite or Welch–Satterthwaite test. Assumptions Student's ''t''-test assumes that the sample means being compared for two populations are no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Chebyshev's Inequality
In probability theory, Chebyshev's inequality (also called the Bienaymé–Chebyshev inequality) provides an upper bound on the probability of deviation of a random variable (with finite variance) from its mean. More specifically, the probability that a random variable deviates from its mean by more than k\sigma is at most 1/k^2, where k is any positive constant and \sigma is the standard deviation (the square root of the variance). The rule is often called Chebyshev's theorem, about the range of standard deviations around the mean, in statistics. The inequality has great utility because it can be applied to any probability distribution in which the mean and variance are defined. For example, it can be used to prove the weak law of large numbers. Its practical usage is similar to the 68–95–99.7 rule, which applies only to normal distributions. Chebyshev's inequality is more general, stating that a minimum of just 75% of values must lie within two standard deviations of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Standard Error
The standard error (SE) of a statistic (usually an estimator of a parameter, like the average or mean) is the standard deviation of its sampling distribution or an estimate of that standard deviation. In other words, it is the standard deviation of statistic values (each value is per sample that is a set of observations made per sampling on the same population). If the statistic is the sample mean, it is called the standard error of the mean (SEM). The standard error is a key ingredient in producing confidence intervals. The sampling distribution of a mean is generated by repeated sampling from the same population and recording the sample mean per sample. This forms a distribution of different means, and this distribution has its own mean and variance. Mathematically, the variance of the sampling mean distribution obtained is equal to the variance of the population divided by the sample size. This is because as the sample size increases, sample means cluster more closely arou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Z-test
A ''Z''-test is any statistical test for which the distribution of the test statistic under the null hypothesis can be approximated by a normal distribution. ''Z''-test tests the mean of a distribution. For each statistical significance, significance level in the Confidence intervals, confidence interval, the ''Z''-test has a single critical value (for example, 1.96 for 5% two-tailed), which makes it more convenient than the Student's t-test, Student's ''t''-test whose critical values are defined by the sample size (through the corresponding degrees of freedom (statistics), degrees of freedom). Both the ''Z''-test and Student's ''t''-test have similarities in that they both help determine the significance of a set of data. However, the ''Z''-test is rarely used in practice because the population deviation is difficult to determine. Applicability Because of the central limit theorem, many test statistics are approximately normally distributed for large samples. Therefore, many s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
:Category:Statistical Tests
{{CatAutoTOC ...
Statistical hypothesis testing Tests Test(s), testing, or TEST may refer to: * Test (assessment), an educational assessment intended to measure the respondents' knowledge or other abilities Arts and entertainment * ''Test'' (2013 film), an American film * ''Test'' (2014 film) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |