|
Tervingi
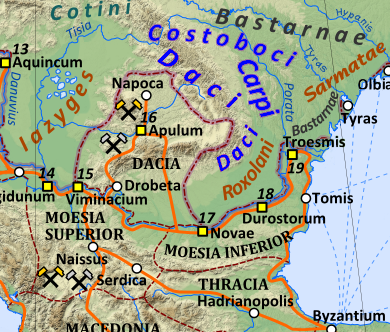
The Thervingi, Tervingi, or Teruingi (sometimes pluralised Tervings or Thervings) were a Gothic people of the plains north of the Lower Danube and west of the Dniester River in the 3rd and the 4th centuries. They had close contacts with the Greuthungi, another Gothic people from east of the Dniester, and they also had significant interactions with the Roman Empire. They were one of the main components of the large movement of Goths and other peoples over the Danube in 376, and they are seen as one of the most important ancestral groups of the Visigoths. Etymology According to a proposal made by Moritz Schönfeld in 1911, and still widely cited, the name ''Tervingi'' was probably related to the Gothic word "''triu''", equivalent to English "tree", and thus means "forest people".Wolfram, ''History of the Goths'', trans. T. J. Dunlop (Berkeley, University of California Press, 1988), p. 25. Herwig Wolfram agrees with the older position of Franz Altheim that such geographical nam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visigoths
The Visigoths (; ) were a Germanic people united under the rule of a king and living within the Roman Empire during late antiquity. The Visigoths first appeared in the Balkans, as a Roman-allied Barbarian kingdoms, barbarian military group united under the command of Alaric I. Their exact origins are believed to have been diverse but they probably included many descendants of the Thervingi who had moved into the Roman Empire beginning in 376 and had played a major role in defeating the Romans at the Battle of Adrianople in 378. Relations between the Romans and Alaric's Visigoths varied, with the two groups making treaties when convenient, and warring with one another when not. Under Alaric, the Visigoths invaded Italy and sack of Rome (410), sacked Rome in August 410. The Visigoths were subsequently settled in southern Gaul as ''foederati'' to the Romans, a relationship that was established in 418. This developed as an independent kingdom with its Capital city, capital at Toulou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greuthungi
The Greuthungi (also spelled Greutungi) were a Goths, Gothic people who lived on the Pontic–Caspian steppe, Pontic steppe between the Dniester River, Dniester and Don river, Don rivers in what is now Ukraine, in the 3rd and the 4th centuries. They had close contacts with the Tervingi, another Gothic people, who lived west of the Dniester River. To the east of the Greuthungi, living near the Don river, were the Alans. When the Huns arrived in the European Steppe region in the late 4th century, first the Alans were forced to join them, and then a part of the Greuthungi. Alans and Goths became an important part of Attila's forces, together with other eastern European peoples. Many Greuthungi, together with some Alans and Huns, crossed the Lower Danube to join a large group of Tervingi who had entered the Roman Empire in 376. These peoples defeated an imperial army in the Battle of Adrianople in 378, and came to a settlement agreement within the Roman empire by 382 AD. The original ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goths
The Goths were a Germanic people who played a major role in the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the emergence of medieval Europe. They were first reported by Graeco-Roman authors in the 3rd century AD, living north of the Danube in what is now Ukraine, Moldova, and Romania. From here they conducted raids into Roman territory, and large numbers of them joined the Roman military. These early Goths lived in the regions where archaeologists find the Chernyakhov culture, which flourished throughout this region during the 3rd and 4th centuries. In the late 4th century, the lands of the Goths in present-day Ukraine were overwhelmed by a significant westward movement of Alans and Huns from the east. Large numbers of Goths subsequently concentrated upon the Roman border at the Lower Danube, seeking refuge inside the Roman Empire. After they entered the Empire, violence broke out, and Goth-led forces inflicted a devastating defeat upon the Romans at the Battle of Adrianople in 378. Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Naissus
The Battle of Naissus in 268 or 269 was the defeat of a Gothic coalition by the Roman Empire under Emperor Gallienus (or Emperor Claudius II Gothicus) and the future Emperor Aurelian near Naissus (Niš). The events around the invasion and the battle are an important part of the history of the Crisis of the Third Century. The result was a great Roman victory which, combined with the effective pursuit of the invaders in the aftermath of the battle and the energetic efforts of the future Emperor Aurelian, largely removed the threat from Germanic tribes in the Balkan frontier for the following decades. Sources As is often the case in the history of the Roman Empire in the troubled third century, it is very difficult to reconstruct the course of events around the battle of Naissus. Surviving accounts of the period, including Zosimus' ''New History'', Zonaras' ''Epitome of the Histories'', George Syncellus' ''Selection of Chronography'', and the '' Augustan History'', rely princ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heruli
The Heruli (also Eluri, Eruli, Herules, Herulians) were one of the smaller Germanic peoples of Late Antiquity, known from records in the third to sixth centuries AD. The best recorded group of Heruli established a kingdom north of the Middle Danube, probably including the area north of present day Vienna. This kingdom was a neighbour to several other small and short-lived kingdoms in the late 5th century AD and early 6th century, including those of the Sciri, Rugii, Danubian Suebi, and Gepids. After the conquest of this Heruli kingdom by the Lombards in 508, splinter groups moved to Sweden, Ostrogothic Italy, and present-day Serbia, which was under Eastern Roman control. The Danubian Heruli are generally equated to the "Elouri" who lived near the Sea of Azov during the late 3rd or early 4th century, and are believed to have migrated westwards. In 267-270 these Elouri took part together with Goths and other eastern European peoples in two massive raids into Roman provinces in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peuci
The Bastarnae, Bastarni or Basternae, also known as the Peuci or Peucini, were an ancient people who are known from Greek and Roman records to have inhabited areas north and east of the Carpathian Mountains between about 300 BC and about 300 AD, stretching in an ark from the sources of the Vistula in present-day Poland and Slovakia, to the Lower Danube, and including all or most of present-day Moldava. The Peucini were sometimes described as a subtribe, who settled the Peuke Island in the Danube Delta, but apparently due to their importance their name was sometimes used for the Bastarnae as a whole. Near the sources of the Vistula another part of the Bastarnae were the Sidones, while the Atmoni, another tribe of the Bastarnae are only mentioned in one listing by Strabo. The earliest Graeco-Roman historians to refer to the Bastarnae imply that they were culturally Celtic. Also consistent with connections to the cultures to their west, later Roman-era sources state directly that t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Claudius II
Marcus Aurelius Claudius "Gothicus" (10 May 214 – August/September 270), also known as Claudius II, was Roman emperor from 268 to 270. During his reign he fought successfully against the Alemanni and decisively defeated the Goths at the Battle of Naissus. He died after succumbing to a "pestilence", possibly the Plague of Cyprian that had ravaged the provinces of the Empire. Early life and origin The most significant source for Claudius II (and the only one regarding his early life) is the collection of imperial biographies called the ''Historia Augusta''. However, his story, like the rest of the ''Historia Augusta'', is riddled with fabrications and obsequious praises. In 4th century, Claudius was declared a relative of Constantine the Great's father, Constantius Chlorus, and, consequently, of the ruling dynasty. The ''Historia Augusta'' should be used with extreme caution and supplemented with information from other sources: the works of Aurelius Victor, Pseudo-Aurelius ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
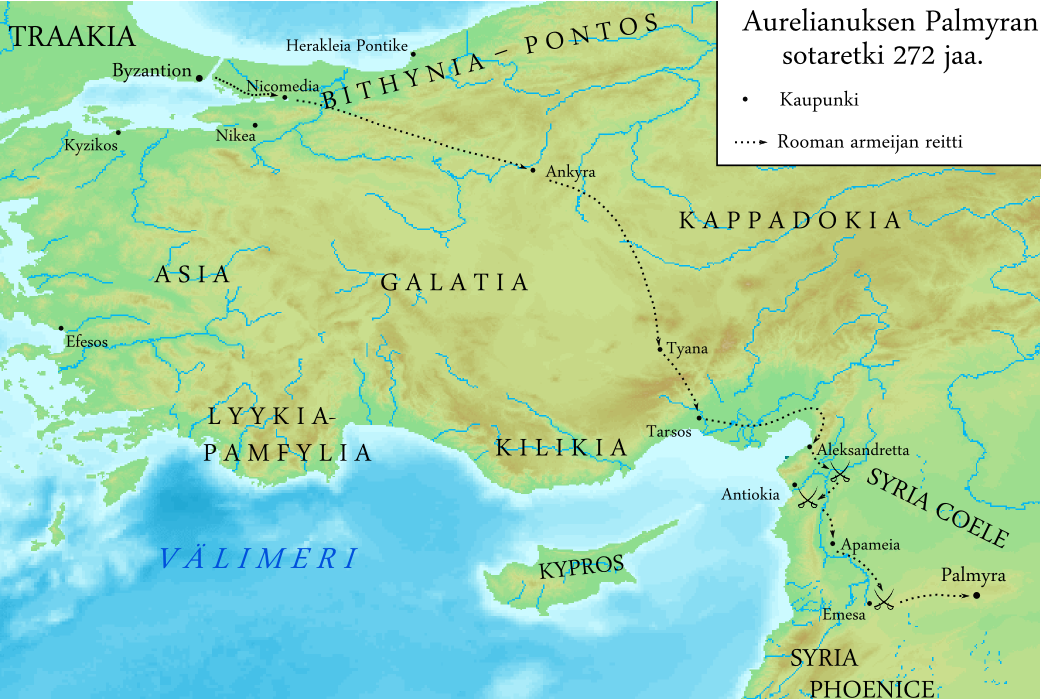
Aurelian
Aurelian (; ; 9 September ) was a Roman emperor who reigned from 270 to 275 AD during the Crisis of the Third Century. As emperor, he won an unprecedented series of military victories which reunited the Roman Empire after it had nearly disintegrated under the pressure of barbarian invasions and internal revolts. Born in modest circumstances, most likely in Moesia, Moesia Superior, he entered the Roman army in 235 and climbed up the ranks. He went on to lead the cavalry of the emperor Gallienus, until Gallienus' Gallienus#Assassination, assassination in 268. Following that, Claudius Gothicus became emperor until his own death in 270. Claudius' brother Quintillus then ruled for three months, before Aurelian took the empire for himself. Aurelian was chosen Roman emperor by the Illyrians, Illyriciani as one of themselves. During his reign, he defeated the Alamanni after a devastating war. He also defeated the Goths, Vandals, Juthungi, Sarmatians, and Carpi (people), Carpi. Aurelian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Historia Augusta
The ''Historia Augusta'' (English: ''Augustan History'') is a late Roman collection of biographies, written in Latin, of the Roman emperors, their junior colleagues, Caesar (title), designated heirs and Roman usurper, usurpers from 117 to 284. Supposedly modeled on the similar work of Suetonius, ''The Twelve Caesars'', it presents itself as a compilation of works by six different authors, collectively known as the ''Scriptores Historiae Augustae'', written during the reigns of Diocletian and Constantine I and addressed to those emperors or other important personages in Ancient Rome. The collection, as extant, comprises thirty biographies, most of which contain the life of a single emperor, but some include a group of two or more, grouped together merely because these emperors were either similar or contemporaneous. The true authorship of the work, its actual date, its reliability and its purpose have long been matters for controversy by historians and scholars ever since Hermann ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scythian
The Scythians ( or ) or Scyths (, but note Scytho- () in composition) and sometimes also referred to as the Pontic Scythians, were an ancient Eastern Iranian equestrian nomadic people who had migrated during the 9th to 8th centuries BC from Central Asia to the Pontic Steppe in modern-day Ukraine and Southern Russia, where they remained established from the 7th century BC until the 3rd century BC. Skilled in mounted warfare, the Scythians replaced the Agathyrsi and the Cimmerians as the dominant power on the western Eurasian Steppe in the 8th century BC. In the 7th century BC, the Scythians crossed the Caucasus Mountains and frequently raided West Asia along with the Cimmerians. After being expelled from West Asia by the Medes, the Scythians retreated back into the Pontic Steppe in the 6th century BC, and were later conquered by the Sarmatians in the 3rd to 2nd centuries BC. By the 3rd century AD, last remnants of the Scythians were overwhelmed by the Goths, and by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panegyric
A panegyric ( or ) is a formal public speech or written verse, delivered in high praise of a person or thing. The original panegyrics were speeches delivered at public events in ancient Athens. Etymology The word originated as a compound of - 'all' (the form taken by the word πᾶν, neuter of πᾶς 'all', when that is used as a prefix) and the word 'assembly' (an Aeolic dialect form, corresponding to the Attic or Ionic form ). Compounded, these gave 'general or national assembly, especially a festival in honour of a god' and the derived adjective 'of or for a public assembly or festival'. In Hellenistic Greek the noun came also to mean 'a festal oration, laudatory speech', and the adjective 'of or relating to a eulogy, flattering'. The noun had been borrowed into Classical Latin by around the second century CE, as ''panēgyris'' 'festival' (in post-Classical usage also 'general assembly'). Correspondingly, Classical Latin also included the adjective ''panēgyricus'', whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Celts
The Celts ( , see Names of the Celts#Pronunciation, pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples ( ) were a collection of Indo-European languages, Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancient Indo-European people, reached the apogee of their influence and territorial expansion during the 4th century BC, extending across the length of Europe from Britain to Asia Minor."; . "[T]he Celts, were Indo-Europeans, a fact that explains a certain compatibility between Celtic, Roman, and Germanic mythology."; . "The Celts and Germans were two Indo-European groups whose civilizations had some common characteristics."; . "Celts and Germans were of course derived from the same Indo-European stock."; . "Celt, also spelled Kelt, Latin Celta, plural Celtae, a member of an early Indo-European people who from the 2nd millennium bce to the 1st century bce spread over much of Europe." in Europe and Anatolia, identified by their use of Celtic languages and other cultural similarities.. "C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |