|
Terminology Extraction
Terminology extraction (also known as term extraction, glossary extraction, term recognition, or terminology mining) is a subtask of information extraction. The goal of terminology extraction is to automatically extract relevant terms from a given corpus. In the semantic web era, a growing number of communities and networked enterprises started to access and interoperate through the internet. Modeling these communities and their information needs is important for several web applications, like topic-driven web crawlers, web services, recommender systems, etc. The development of terminology extraction is also essential to the language industry. One of the first steps to model a knowledge domain is to collect a vocabulary of domain-relevant terms, constituting the linguistic surface manifestation of domain concepts. Several methods to automatically extract technical terms from domain-specific document warehouses have been described in the literature. Typically, approaches ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Translation
Translation is the communication of the semantics, meaning of a #Source and target languages, source-language text by means of an Dynamic and formal equivalence, equivalent #Source and target languages, target-language text. The English language draws a terminological distinction (which does not exist in every language) between ''translating'' (a written text) and ''interpreting'' (oral or Sign language, signed communication between users of different languages); under this distinction, translation can begin only after the appearance of writing within a language community. A translator always risks inadvertently introducing source-language words, grammar, or syntax into the target-language rendering. On the other hand, such "spill-overs" have sometimes imported useful source-language calques and loanwords that have enriched target languages. Translators, including early translators of sacred texts, have helped shape the very languages into which they have translated. Becau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tasks Of Natural Language Processing
Task may refer to: * Task (computing), a unit of execution or homeworks * Task (language instruction) refers to a certain type of activity used in language instructional design * Task (project management), an activity that needs to be accomplished within a defined period of time * Task (teaching style) * TASK party, a series of improvisational participatory art-related events organized by artist Oliver Herring * Two-pore-domain potassium channel, a family of potassium ion channels See also * The Task (other) * Task force (other) * Task switching (other) * {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Text Simplification
Text simplification is an operation used in natural language processing to change, enhance, classify, or otherwise process an existing body of human-readable text so its grammar and structure is greatly simplified while the underlying meaning and information remain the same. Text simplification is an important area of research because of communication needs in an increasingly complex and interconnected world more dominated by science, technology, and new media. But natural human languages pose huge problems because they ordinarily contain large vocabularies and complex constructions that machines, no matter how fast and well-programmed, cannot easily process. However, researchers have discovered that, to reduce linguistic diversity, they can use methods of semantic compression to limit and simplify a set of words used in given texts. Example Text simplification is illustrated with an example used by Siddharthan (2006). The first sentence contains two relative clauses and one c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
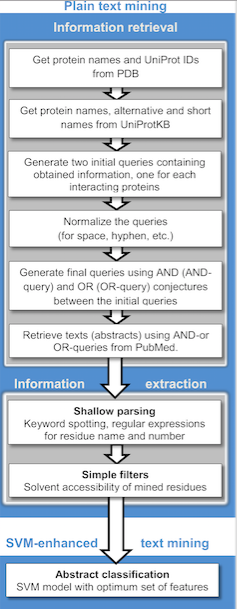
Text Mining
Text mining, text data mining (TDM) or text analytics is the process of deriving high-quality information from text. It involves "the discovery by computer of new, previously unknown information, by automatically extracting information from different written resources." Written resources may include websites, books, emails, reviews, and articles. High-quality information is typically obtained by devising patterns and trends by means such as statistical pattern learning. According to Hotho et al. (2005), there are three perspectives of text mining: information extraction, data mining, and knowledge discovery in databases (KDD). Text mining usually involves the process of structuring the input text (usually parsing, along with the addition of some derived linguistic features and the removal of others, and subsequent insertion into a database), deriving patterns within the structured data, and finally evaluation and interpretation of the output. 'High quality' in text mining usually ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terminology
Terminology is a group of specialized words and respective meanings in a particular field, and also the study of such terms and their use; the latter meaning is also known as terminology science. A ''term'' is a word, Compound (linguistics), compound word, or multi-word Expression (language), expression that in specific context (language use), contexts is given specific meanings—these may deviate from the meanings the same words have in other contexts and in everyday language. Terminology is a discipline that studies, among other things, the development of such terms and their interrelationships within a specialized domain. Terminology differs from lexicography, as it involves the study of concepts, conceptual systems and their labels (''terms''), whereas lexicography studies words and their meanings. Terminology is a discipline that systematically studies the "labelling or designating of concepts" particular to one or more subject fields or domains of human activity. It does t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxonomy (general)
280px, Generalized scheme of taxonomy Taxonomy is a practice and science concerned with classification or categorization. Typically, there are two parts to it: the development of an underlying scheme of classes (a taxonomy) and the allocation of things to the classes (classification). Originally, taxonomy referred only to the classification of organisms on the basis of shared characteristics. Today it also has a more general sense. It may refer to the classification of things or concepts, as well as to the principles underlying such work. Thus a taxonomy can be used to organize species, documents, videos or anything else. A taxonomy organizes taxonomic units known as "taxa" (singular "taxon"). Many are hierarchies. One function of a taxonomy is to help users more easily find what they are searching for. This may be effected in ways that include a library classification system and a search engine taxonomy. Etymology The word was coined in 1813 by the Swiss botanist A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subject Indexing
Subject indexing is the act of describing or classifying a document A document is a writing, written, drawing, drawn, presented, or memorialized representation of thought, often the manifestation of nonfiction, non-fictional, as well as fictional, content. The word originates from the Latin ', which denotes ... by index terms, keywords, or other symbols in order to indicate what different documents are '' about'', to summarize their contents or to increase findability. In other words, it is about identifying and describing the '' subject'' of documents. Indexes are constructed, separately, on three distinct levels: terms in a document such as a book; objects in a collection such as a library; and documents (such as books and articles) within a field of knowledge. Subject indexing is used in information retrieval especially to create bibliographic indexes to retrieve documents on a particular subject. Examples of academic indexing services are Zentralblatt MATH, Ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Domain Ontology
In information science, an ontology encompasses a representation, formal naming, and definitions of the categories, properties, and relations between the concepts, data, or entities that pertain to one, many, or all domains of discourse. More simply, an ontology is a way of showing the properties of a subject area and how they are related, by defining a set of terms and relational expressions that represent the entities in that subject area. The field which studies ontologies so conceived is sometimes referred to as ''applied ontology''. Every academic discipline or field, in creating its terminology, thereby lays the groundwork for an ontology. Each uses ontological assumptions to frame explicit theories, research and applications. Improved ontologies may improve problem solving within that domain, interoperability of data systems, and discoverability of data. Translating research papers within every field is a problem made easier when experts from different countries maintai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Language Processing
Natural language processing (NLP) is a subfield of computer science and especially artificial intelligence. It is primarily concerned with providing computers with the ability to process data encoded in natural language and is thus closely related to information retrieval, knowledge representation and computational linguistics, a subfield of linguistics. Major tasks in natural language processing are speech recognition, text classification, natural-language understanding, natural language understanding, and natural language generation. History Natural language processing has its roots in the 1950s. Already in 1950, Alan Turing published an article titled "Computing Machinery and Intelligence" which proposed what is now called the Turing test as a criterion of intelligence, though at the time that was not articulated as a problem separate from artificial intelligence. The proposed test includes a task that involves the automated interpretation and generation of natural language ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glossary
A glossary (from , ''glossa''; language, speech, wording), also known as a vocabulary or clavis, is an alphabetical list of Term (language), terms in a particular domain of knowledge with the definitions for those terms. Traditionally, a glossary appears at the end of a book and includes terms within that book that are either newly introduced, uncommon, or specialized. While glossaries are most commonly associated with non-fiction books, in some cases, fiction novels sometimes include a glossary for unfamiliar terms. A bilingual glossary is a list of terms in one language defined in a second language or Gloss (annotation), glossed by synonyms (or at least near-synonyms) in another language. In a general sense, a glossary contains explanations of concepts relevant to a certain field of study or action. In this sense, the term is related to the notion of ontology. Automatic methods have been also provided that transform a glossary into an ontology or a computational lexicon. C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computational Linguistics
Computational linguistics is an interdisciplinary field concerned with the computational modelling of natural language, as well as the study of appropriate computational approaches to linguistic questions. In general, computational linguistics draws upon linguistics, computer science, artificial intelligence, mathematics, logic, philosophy, cognitive science, cognitive psychology, psycholinguistics, anthropology and neuroscience, among others. Computational linguistics is closely related to mathematical linguistics. Origins The field overlapped with artificial intelligence since the efforts in the United States in the 1950s to use computers to automatically translate texts from foreign languages, particularly Russian scientific journals, into English. Since rule-based approaches were able to make arithmetic (systematic) calculations much faster and more accurately than humans, it was expected that lexicon, morphology, syntax and semantics can be learned using explicit rules, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |