|
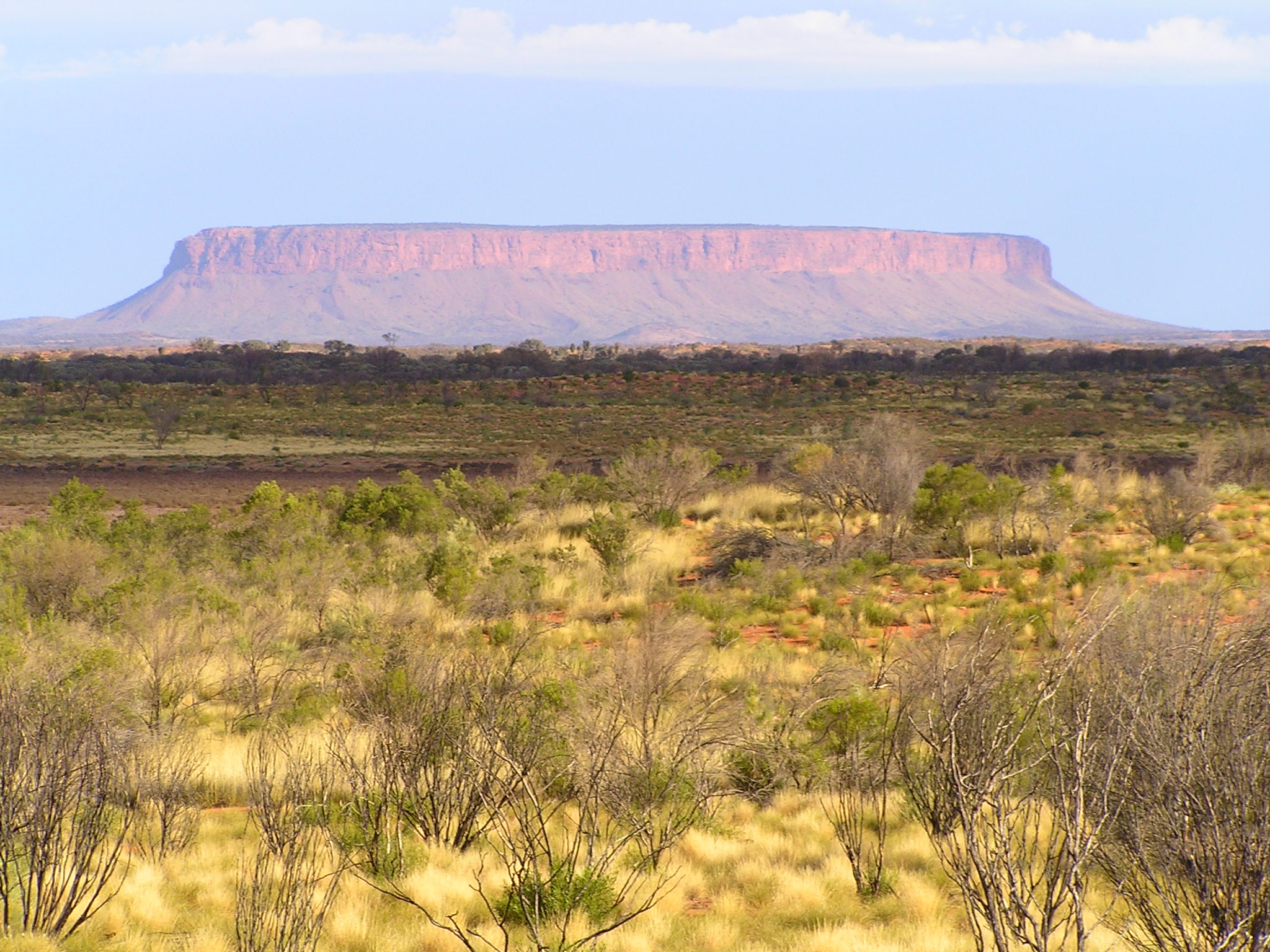
Tepe-Kermen
Tepe-Kermen (; Ukrainian and Russian: ) is a butte and an early medieval settlement in the Bakhchysarai Raion of Crimea. It is located 7 km southeast of Bakhchysarai, and 2 km northeast of the settlement Kyz-Kermen. Its height is 544 meters. The easiest way to climb the mountain is from the northern slope. There are 2 paths leading to the top. Settlement The name Tepe-Kermen is of Turkic origin: in Crimean Tatar it means "hill-fortress" or "fortress on the top" ( - hill, peak, - fortress). The same name is given to the remains of the medieval city-fortress (according to other sources - a monastery) Tepe-Kermen, which covers the upper part of the mountain in several levels. Its area is about 1 hectare. In fact, it was not a settlement but a fortified castle, where the local population used to hide from enemy forces. This explains the lack of water sources. According to some available sources, the unfortified settlement appeared in the 5th-6th century, and the constructio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bakhchysarai
Bakhchysarai is a city in the Autonomous Republic of Crimea, Ukraine. It is the administrative center of the Bakhchysarai Raion (district), as well as the former capital of the Crimean Khanate. Its main landmark is Hansaray, the only extant palace of the Crimean Khans, currently open to tourists as a museum. Population: Since the beginning of the Russo-Ukrainian War in 2014, it has been occupied by the Russian Federation. Geography Bakhchysarai lies in a narrow valley of the river, about 30 Kilometers south-west of Simferopol. History The earliest known man-made objects found in the valley date from the Mesolithic period. Settlements have existed in the valley since Late Antiquity. Before the founding of Bakhchysarai the Qırq Yer fortress (modern Çufut Qale), Salaçıq, and Eski Yurt were built. These have since become incorporated into the urban area of modern Bakhchysarai. Bakhchysarai first appears in historical documents in 1502. In 1532 Sahib I Giray, Kh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bakhchysarai Raion
Bakhchysarai Raion (; ; ) is one of the 25 regions of Crimea, an internationally recognized territory of Ukraine occupied and annexed by Russia in 2014. Population: The Bakhchysarai Raion is situated in the southwestern part of the peninsula. Two thirds of the raion's area is mountainous, while the northwestern part of the region is occupied by the coastal plain. Places of interest The raion contains a great number of historical landmarks of the ancient history and the Middle Ages history of Crimea, among which are so called cave cities Chufut-Kale, Mangup, and others. The administrative centre of the raion, Bakhchysarai, in the past was a capital of the Crimean Khanate. In addition, the Crimean Astrophysical Observatory is located in the town of Nauchnyi. A few other important attractions located within the raion: * Bakhchysarai Palace * The "cave city" of Çufut Qale * The "cave city" of Eski Kermen * Mangup * The "cave city" of Tepe-Kermen * Uspenskyi Cave Monastery 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beylerbey
''Beylerbey'' (, meaning the 'commander of commanders' or 'lord of lords’, sometimes rendered governor-general) was a high rank in the western Islamic world in the late Middle Ages and early modern period, from the Anatolian Seljuks and the Ilkhanids to Safavid Iran and the Ottoman Empire. Initially designating a commander-in-chief, it eventually came to be held by senior provincial governors. In Ottoman usage, where the rank survived the longest, it designated the governors-general of some of the largest and most important provinces, although in later centuries it became devalued into a mere honorific title. The title is originally Turkic and its equivalents in Arabic were ''amir al-umara'', and in Persian, ''mir-i miran''. Early use The title originated with the Seljuks, and was used in the Sultanate of Rum initially as an alternative for the Arabic title of ''malik al-umara'' ("chief of the commanders"), designating the army's commander-in-chief. Among the Mongol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountains Under 1000 Metres
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually higher than a hill, typically rising at least above the surrounding land. A few mountains are isolated summits, but most occur in mountain ranges. Mountains are formed through tectonic forces, erosion, or volcanism, which act on time scales of up to tens of millions of years. Once mountain building ceases, mountains are slowly leveled through the action of weathering, through slumping and other forms of mass wasting, as well as through erosion by rivers and glaciers. High elevations on mountains produce colder climates than at sea level at similar latitude. These colder climates strongly affect the ecosystems of mountains: different elevations have different plants and animals. Because of the less hospitable terrain and climate, mountains ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesa
A mesa is an isolated, flat-topped elevation, ridge, or hill, bounded from all sides by steep escarpments and standing distinctly above a surrounding plain. Mesas consist of flat-lying soft sedimentary rocks, such as shales, capped by a resistant layer of harder rock, like sandstone or limestone, forming a caprock that protects the flat summit. The caprock may also include dissected lava flows or eroded duricrust. Unlike a ''plateau'', which is a broader, elevated region that may not have horizontal bedrock (e.g., Tibetan Plateau), a mesa is defined by flat-lying strata and steep-sided isolation. Large, flat-topped plateaus with horizontal strata, less isolated and often part of extensive plateau systems, are called '' tablelands''. A ''butte'' is a smaller, eroded mesa with a limited summit, while a '' cuesta'' has a gentle dip slope and one steep escarpment due to tilted strata.Duszyński, F., Migoń, P. and Strzelecki, M.C., 2019. ''Escarpment retreat in sedim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nave
The nave () is the central part of a church, stretching from the (normally western) main entrance or rear wall, to the transepts, or in a church without transepts, to the chancel. When a church contains side aisles, as in a basilica-type building, the strict definition of the term "nave" is restricted to the central aisle. In a broader, more colloquial sense, the nave includes all areas available for the lay worshippers, including the side-aisles and transepts.Cram, Ralph Adams Nave The Catholic Encyclopedia. Vol. 10. New York: Robert Appleton Company, 1911. Accessed 13 July 2018 Either way, the nave is distinct from the area reserved for the choir and clergy. Description The nave extends from the entry—which may have a separate vestibule (the narthex)—to the chancel and may be flanked by lower side-aisles separated from the nave by an arcade. If the aisles are high and of a width comparable to the central nave, the structure is sometimes said to have three nave ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cella
In Classical architecture, a or naos () is the inner chamber of an ancient Greek or Roman temple. Its enclosure within walls has given rise to extended meanings: of a hermit's or monk's cell, and (since the 17th century) of a biological cell in plants or animals. Greek and Roman temples In ancient Greek and Roman temples, the ''cella'' was a room at the center of the building, usually containing a cult image or statue representing the particular deity venerated in the temple. In addition, the ''cella'' might contain a table to receive supplementary votive offerings, such as votive statues of associated deities, precious and semi-precious stones, helmets, spear and arrow heads, swords, and war trophies. No gatherings or sacrifices took place in the ''cella'', as the altar for sacrifices was always located outside the building along the axis and temporary altars for other deities were built next to it. The accumulated offerings made Greek and Roman temples virtual treasuri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1299
Year 1299 ( MCCXCIX) was a common year starting on Thursday of the Julian calendar. Events By place Europe * July 4 – Battle of Cape Orlando: An Aragonese-Angevin fleet (some 60 galleys) led by Admiral Roger of Lauria defeats a Sicilian fleet near Sicily. During the battle, the larger Aragonese fleet is trapped on a lee shore, but can exploit the situation with the intervention of its 6 reserve galleys. The Sicilians flee when the flagship, with King Frederick III of Sicily on board, pulls back after he collapses from heat exhaustion. Lauria captures 18 Sicilian ships, and orders the massacre of their crews to avenge the death of his nephew at the hands of Frederick. * July 31 – Pisa and Genoa agree to a thirty-year truce. Part of the treaty includes the end of the Pisan military support to Genoa's enemies in Corsica. * November 10 – John I, count of Holland, dies and is succeeded by his uncle John II. He establishes a personal union with the Cou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nogai Khan
Nogai, or Noğay ( Kypchak and Turki: نوغای; also spelled Nogay, Nogaj, Nohai, Nokhai, Noqai, Ngoche, Noche, Kara Nokhai, and Isa Nogai; died 1299/1300) was a general and kingmaker of the Golden Horde. His great grandfather was Jochi, son of Genghis Khan. Though he never formally ruled the Golden Horde himself, he was effectively the co-ruler of the state alongside whatever khan was in power at the time and had unrestricted control over the portions west of the Dnieper. At his height, Nogai was one of the most powerful men in Europe and widely thought of as the Horde's true head. The Russian chroniclers gave him the title of tsar, and the Franciscan missionaries in the Crimea spoke of him as a co-emperor. Nogai was also a notable convert to Islam. Name French historian Paul Pelliot wrote that Nokhai meant "dog". Although in the Mongolian language, "nokhoi" (in Mongolian script: , ''nokhai'') literally means a "dog", it does not necessarily mean a particularly negative and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chersonesus
Chersonesus, contracted in medieval Greek to Cherson (), was an Greeks in pre-Roman Crimea, ancient Greek Greek colonization, colony founded approximately 2,500 years ago in the southwestern part of the Crimean Peninsula. Settlers from Heraclea Pontica in Bithynia established the colony in the 6th century BC. The ancient city was located on the shore of the Black Sea on the outskirts of present-day Sevastopol on the Crimean Peninsula, where it is referred to as ''Khersones''. The site is part of the ''National Preserve of Tauric Chersonesos''. The name ''Chersonesos'' in Greek means "peninsula" and aptly describes the site on which the colony was established. It should not be confused with the ''Tauric Chersonese'', a name often applied to the whole of the southern Crimea. During much of the classical period, Chersonesus operated as a democracy ruled by a group of elected archons and a council called the ''Damiorgi''. As time passed, the government grew more oligarchic, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Golden Horde
The Golden Horde, self-designated as ''Ulug Ulus'' ( in Turkic) was originally a Mongols, Mongol and later Turkicized khanate established in the 13th century and originating as the northwestern sector of the Mongol Empire. With the division of the Mongol Empire after 1259, it became a functionally separate khanate. It is also known as the Kipchak Khanate or the Ulus of Jochi, and replaced the earlier, less organized Cuman–Kipchak confederation. After the death of Batu Khan (the founder of the Blue Horde) in 1255, his dynasty flourished for a full century, until 1359, though the intrigues of Nogai Khan, Nogai instigated a partial civil war in the late 1290s. The Horde's military power peaked during the reign of Özbeg Khan (1312–1341), who adopted Islam. The territory of the Golden Horde at its peak extended from Siberia and Central Asia to parts of Eastern Europe from the Ural Mountains, Urals to the Danube in the west, and from the Black Sea to the Caspian Sea in the south ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |