|
Teodor III Muzaka
Theodor Corona Musachi () or Teodor III Korona Muzaka, was an Albanian nobleman who led the 1437–38 revolt against the Ottomans and was one of the founders of the League of Lezhë in 1444. Life Theodor Corona Musachi was а prominent member of the Muzaka family. They were rulers of the Principality of Muzaka, whose domains extended from Myzeqe till Kastoria, (modern-day Greece). According to John Muzaka's memoir, Theodor was the youngest son of Andrea III and his wife Chiranna Zenevisi, Lady of Grabossa. The couple had another son Lord Ginno II, who would become Lord John's father, as well as two daughters, Lady Maria and Lady Helena. Through his sister Maria, Theodor III was an in-law of Skanderbeg, who married his niece, Andronika Arianiti. In the chronicle, John Muzaka explained that Theodor inherited control over Berat from his father. However, the exact period of when the Muzaka family began to control the city, still remains unknown. Byzantine Eastern Roman source ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teodor II Muzaka
Teodor II Muzaka (), was an Albanian Prince from the House of Muzaka, he was the Lord of Berat and Lord of Myzeqe. Life Teodor II Muzaka was born into the House of Muzaka as the second son of Andrea II Muzaka and Euphemia Mataranga, who was from the Mataranga family. Upon the death of his father Andrea II, his lands were divided among his three sons, Gjin I, Teodor II and Stoya. Gjin inherited the majority of his father’s holdings, except for Berat, Myzeqe, and Kastoria. Teodor received Berat and Myzeqe, while Stoya inherited Kastoria along with its associated villages and estates. Between 1383 and 1384, Theodor II, together with his brother Stoya and the monk Dionysius, had a Greek Orthodox church ( Church of St. Athanasius of Mouzaki) built in Kastoria, which was dedicated to Athanasius the Great. Succession He died fighting during the Battle of Kosovo in 1389 on the side of the anti-Ottoman coalition led by Lazar of Serbia. After his death the rule ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skanderbeg
Gjergj Kastrioti (17 January 1468), commonly known as Skanderbeg, was an Albanians, Albanian Albanian nobility, feudal lord and military commander who led Skanderbeg's rebellion, a rebellion against the Ottoman Empire in what is today Albania, North Macedonia, Greece, Kosovo, Montenegro, and Serbia. A member of the noble House of Kastrioti, Kastrioti family, Skanderbeg was sent as a hostage to the Ottoman court. He graduated from the Enderun School and entered the service of the Ottoman sultan Murad II () for the next twenty years. His rise through the ranks culminated in his appointment as of the Sanjak of Dibra in 1440. During the Battle of Nish (1443), Battle of Nish in 1443, he deserted the Ottomans and Liberation of Kruja (1443), became the ruler of Krujë and nearby areas extending from Petrelë to Modrič, Struga, Modrič. In March 1444, he established the League of Lezhë, with support from Albanian nobility, local noblemen, and unified the Albanian principalities. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albanian Revolt Of 1432–36
Albanian may refer to: *Pertaining to Albania in Southeast Europe; in particular: **Albanians, an ethnic group native to the Balkans **Albanian language **Albanian culture **Demographics of Albania, includes other ethnic groups within the country *Pertaining to other places: **Albania (other) **Albany (other) **St Albans (other) *Albanian cattle *Albanian horse *''The Albanian'', a 2010 German-Albanian film See also * *Olbanian language *Albani people *Albaniana (other) *Alba (other) {{Disambiguation Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanjak Of Albania
The Sanjak of Albania (, or ; or ) was a second-level administrative unit of the Ottoman Empire between 1415 and 1444. Its mandate included territories of modern central and southern Albania between Krujë to the Kalamas River in northwestern Greece. Background During the 14th century, Ottoman rule began to extend over the Eastern Mediterranean and the Balkans. The divided nature of the Albania consisting of small, quarreling fiefdoms ruled by independent feudal lords and tribal chiefs meant that an Ottoman invasion was difficult to defend against. In 1385, the ruler of Durrës, Karl Thopia, appealed to the sultan for support against his rivals, the Balšić family. An Ottoman force quickly marched into Albania along the Via Egnatia and routed Balša II in the Battle of Savra. The principal Albanian clans soon swore fealty to the Ottoman Empire. The Ottomans allowed conquered Albanian clan chiefs to maintain their positions and property, but they had to pay tribute, send ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shkumbin
The Shkumbin (; ), also known as Shkembi, is a river in Albania. It is long and its drainage basin is . Its average discharge is . Etymology It derives from Latin ''Scampinus'' (recorded alternatively as ), which replaced the Illyrian name of the river: ''Genusus'' (recorded in , also , and in ). A Slavic intermediation has been rejected. Its inclusion in Latin loanwords into Proto-Albanian and phonetic evolution coincides with the historical existence of a large Roman town (near present-day Elbasan), which gave the river its new name. Overview The river originates in the eastern Valamara Mountains between ''Maja e Valamarës'' () and ''Gur i Topit'' () in Southeastern Albania. After descending from the Valamaras, it flows northwards through Proptisht and Qukës with many deep gorges and canyons and passes the Gora Mountains. A significant inflow comes from ''Gur i Kamjës'' () southwest of Pogradec. Over the course, it flows inside a syncline between the Mokra and She ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
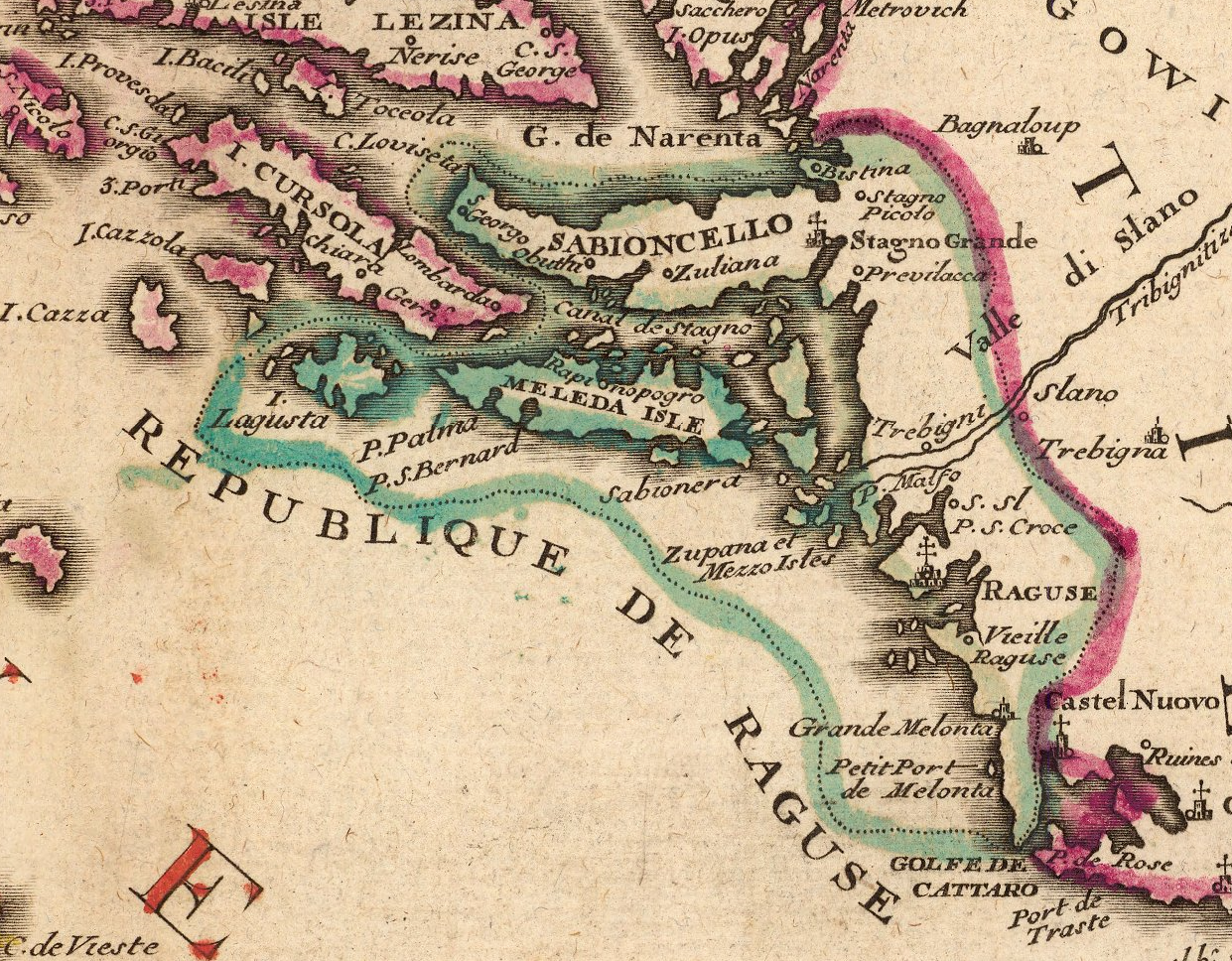
Ragusan Republic
The Republic of Ragusa, or the Republic of Dubrovnik, was an aristocratic maritime republic centered on the city of Dubrovnik (''Ragusa'' in Italian and Latin; ''Raguxa'' in Venetian) in South Dalmatia (today in southernmost Croatia) that carried that name from 1358 until 1808. It reached its commercial peak in the 15th and the 16th centuries, before being conquered by Napoleon's French Empire and formally annexed by the Napoleonic Kingdom of Italy in 1808. It had a population of about 30,000 people, of whom 5,000 lived within the city walls. Its motto was "'", a Latin phrase which can be translated as "Liberty is not well sold for all the gold". Names Originally named ' (Latin for "Ragusan municipality" or "community"), in the 14th century it was renamed ' (Latin for ''Ragusan Republic''), first mentioned in 1385. It was nevertheless a Republic under its previous name, although its Rector was appointed by Venice rather than by Ragusa's own Major Council. In Italian it is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Niketa Thopia
Niketa Thopia (, ; 1388 – d. 1415), also known as Nikola was the Lord of Krujë between 1392—1394 and 1403–1415. He was a member of the Albanians, Albanian Thopia family and an illegitimate son of Karl Thopia, the Prince of Albania (r. 1368–1388). Life Niketa Thopia was an illegitimate son of Albanians, Albanian prince Karl Thopia born to an unknown mother. Together with his sister Maria Thopia, they are Karl's only recognized illegitimate children. After his father’s death in 1388, Helena Thopia his older sister inherited control of Krujë. After her marriage to Marco Barbarigo di Croia, Marco Barbarigo a Republic of Venice, Venetian nobleman, he became the actual ruler of her lands. Moreover, his older brother Gjergj Thopia succeeded their father as Principality of Albania (medieval), Prince of Albania. Niketa, on the other hand inherited a territory south of Durazzo. Mark Barbarigo briefly held his and Helen’s possessions under Venetian suzerainty. However, facing n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Korun Aramija
Korun Aramija or Korun Haramija or Korun Kesedžija is a popular legendary hero of Serbian epic poetry and Bulgarian and Macedonian folklore. He is known as a rival of either Prince Marko or Nenad Jugović, other heroes of South Slavic folklore. The epic hero Korun Aramija is based on actual historical person, Theodor Corona Musachi from Muzaka family that was in conflict with Prince Marko over the town of Kastoria. Historical background The Muzaka family was in conflict with Prince Marko before his death in 1396 which is probably why Theodor Corona Musachi is commemorated in Serbian and south Slavic epic poetry as Korun, Marko's enemy. The term Aramija is derived from Turkish word for bandit (). Epic poems Songs about Korun and Nenad Jugović (three different versions) were collected by Vuk Karadžić and published posthumously in 1899 in chapter titled "The earliest songs about heroes" (). Narratives involving Korun as an adversary of Nenad explore the popular theme of b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serbian Epic Poetry
Serbian epic poetry () is a form of epic poetry created by Serbs originating in today's Serbia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, Montenegro and North Macedonia. The main cycles were composed by unknown Serb authors between the 14th and 19th centuries. They are largely concerned with historical events and personages. The instrument accompanying the epic poetry is the ''gusle''. Serbian epic poetry helped in developing the Serbian national consciousness. The cycles of Prince Marko, the Hajduks and Uskoks inspired the Serbs to restore freedom and their heroic past. The Hajduks in particular, are seen as an integral part of national identity; in stories, the hajduks were heroes: they had played the role of the Serbian elite during Ottoman rule, they had defended the Serbs against Ottoman oppression, and prepared for the national liberation and contributed to it in the Serbian Revolution. History The earliest surviving record of an epic poem related to Serbian epic poetry is a ten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prince Marko
Marko Mrnjavčević ( sr-Cyrl, Марко Мрњавчевић, ; – 17 May 1395) was the ''de jure'' Serbia in the Middle Ages, Serbian king from 1371 to 1395, while he was the ''de facto'' ruler of territory in western Macedonia (region), Macedonia centered on the town of Prilep. He is known as Prince Marko (; sr-Cyrl, Краљевић Марко, ''Kraljević Marko'', ) and King Marko (; sr-Cyrl, Краљ Марко; ) in South Slavs, South Slavic oral tradition, in which he has become a major character during the period of Ottoman Empire, Ottoman rule over the Balkans. Marko's father, King Vukašin Mrnjavčević, Vukašin, was co-ruler with Serbian Tsar Stefan Uroš V, whose reign was characterised by weakening central authority and the gradual disintegration of the Serbian Empire. Vukašin's holdings included lands in north-western Macedonia and Kosovo. In 1370 or 1371, he crowned Marko "young king"; this title included the possibility that Marko would succeed the chi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epirus
Epirus () is a Region#Geographical regions, geographical and historical region, historical region in southeastern Europe, now shared between Greece and Albania. It lies between the Pindus Mountains and the Ionian Sea, stretching from the Bay of Vlorë and the Ceraunian Mountains, Acroceraunian Mountains in the north to the Ambracian Gulf and the ruined Roman Empire, Roman city of Nicopolis in the south.. It is currently divided between the Modern regions of Greece, region of Epirus (region), Epirus in northwestern Greece and the counties of Gjirokastër County, Gjirokastër and Vlorë County, Vlorë in southern Albania. The largest city in Epirus is Ioannina, seat of the Greek region of Epirus, with Gjirokastër the largest city in the Albanian part of Epirus. A rugged and mountainous region, Epirus was the north-west area of ancient Greece. It was inhabited by the Greek tribes of the Chaonians, Molossians, and Thesprotians. It was home to the sanctuary of Dodona, the oldest o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |