|
Temple Of The Winged Lions
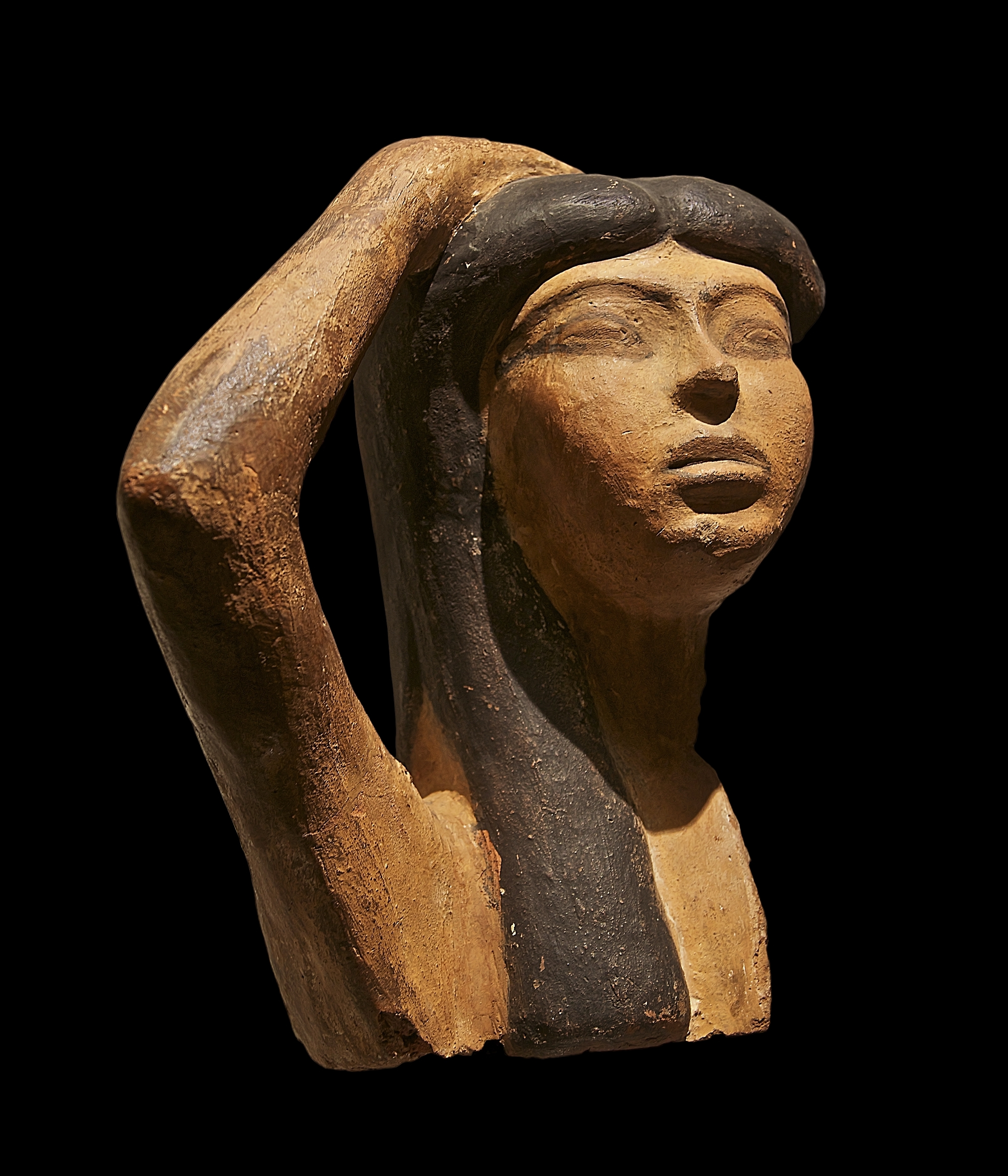
The Temple of the Winged Lions is a large Nabatean temple complex located in Petra, Jordan, and dated to the reign of King Aretas IV (9 BCE–40 CE). The temple is located in Petra's so-called Sacred Quarter, an area situated at the end of Petra's main Colonnaded Street consisting of two majestic temples, the Qasr al-Bint and, opposite, the Temple of the Winged Lions on the northern bank of Wadi Musa. The temple is likely dedicated to the supreme goddess figure of the Nabateans, but the exact identity of this goddess is uncertain. The temple could be dedicated to Dedun the Nubian god of luck, which is symbolized with lions. Because Altranelsa promoted Osiris-Dedun 300 years later in the area of Jebel Barkal by constructing Temples with similar symbols. Temple of Winged Lions was ultimately destroyed in the massive earthquake of 363 CE. Analyses of the architecture, goods, and practices associated with the Temple of the Winged Lions afford valuable insights into Nabataean religio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temple Of Winged Lions, Petra 01
A temple (from the Latin ) is a building reserved for spiritual rituals and activities such as prayer and sacrifice. Religions which erect temples include Christianity (whose temples are typically called churches), Hinduism (whose temples are called Mandir), Buddhism, Sikhism (whose temples are called gurudwara), Jainism (whose temples are sometimes called derasar), Islam (whose temples are called mosques), Judaism (whose temples are called synagogues), Zoroastrianism (whose temples are sometimes called Agiary), the Baha'i Faith (which are often simply referred to as Baha'i House of Worship), Taoism (which are sometimes called Daoguan), Shinto (which are sometimes called Jinja), Confucianism (which are sometimes called the Temple of Confucius), and ancient religions such as the Ancient Egyptian religion and the Ancient Greek religion. The form and function of temples are thus very variable, though they are often considered by believers to be, in some sense, the "house ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Uzza
Al-ʻUzzā ( ar, العزى or Old Arabic l ʕuzzeː was one of the three chief goddesses of Arabian religion in pre-Islamic times and she was worshiped by the pre-Islamic Arabs along with al-Lāt and Manāt. A stone cube at Nakhla (near Mecca) was held sacred as part of her cult. She is mentioned in Qur'an 53:19 as being one of the goddesses who people worshiped. Al-ʻUzzā, like Hubal, was called upon for protection by the pre-Islamic Quraysh. "In 624 at the ' battle called Uhud', the war cry of the Qurayshites was, "O people of Uzzā, people of Hubal!". Al-‘Uzzá also later appears in Ibn Ishaq's account of the alleged Satanic Verses. The temple dedicated to al-ʻUzzā and the statue was destroyed by Khalid ibn al Walid in Nakhla in 630 AD."He sent Khali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manar Al-Athar
Manar al-Athar is a photo archive based at the Faculty of Classics at the University of Oxford which aims to provide high-quality open-access images of archaeological sites and buildings. The archive's collection focuses on areas of the Roman Empire which later came under Islamic rule, namely the Levant, North Africa, Turkey, Georgia and Armenia. As of June 2022, the archive holds more than 83,000 unique images. Particular strengths include Late antiquity, as well as the transition from paganism to Christianity and later to Islam. The archive licenses its images under a Creative Commons CC BY-NC-SA 2.0 license; the images can be used for any non-commercial purpose, including in academic publications, and are jointly labelled in English and Arabic to encourage usage by academics and students around the world. History Manar al-Athar was founded in 2012 by Judith McKenzie, archaeologist and Associate Professor of Late Antique Egypt and the Holy Land at the University of Oxf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bedouin
The Bedouin, Beduin, or Bedu (; , singular ) are nomadic Arabs, Arab tribes who have historically inhabited the desert regions in the Arabian Peninsula, North Africa, the Levant, and Mesopotamia. The Bedouin originated in the Syrian Desert and Arabian Desert but spread across the rest of the Arab world in Western Asia, West Asia and North Africa after the spread of Islam. The English word ''bedouin'' comes from the Arabic ''badawī'', which means "desert dweller", and is traditionally contrasted with ''ḥāḍir'', the term for Sedentism, sedentary people. Bedouin territory stretches from the vast deserts of North Africa to the rocky sands of the Middle East. They are traditionally divided into tribes, or clans (known in Arabic as ''ʿašāʾir''; or ''qabāʾil'' ), and historically share a common culture of herding camels and goats. The vast majority of Bedouins adhere to Islam, although there are some fewer numbers of Arab Christians, Christian Bedouins present in the Fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dushara
Dushara, ( Nabataean Arabic: 𐢅𐢈𐢝𐢛𐢀 ''dwšrʾ'') also transliterated as Dusares, is a pre-Islamic Arabian god worshipped by the Nabataeans at Petra and Madain Saleh (of which city he was the patron). Safaitic inscriptions imply he was the son of Al-Lat, and that he assembled in the heavens with other gods. He is called "Dushara from Petra" in one inscription. Dushara was expected to bring justice if called by the correct ritual. Etymology Dushara is known first from epigraphic Nabataean sources who invariably spell the name ''dwsrʾ'', the Nabataean script denoting only consonants. He appears in Classical Greek sources Δουσάρης (''Dousárēs'') and in Latin as ''Dusares''. The original meaning is disputed, but early Muslim historian Ibn al-Kalbi in his " Book of Idols" explains the name as ''Dhū l-Šarā'' ( ar, ذو الشرى), meaning likely "The One from Shara", Shara being a mountain range south-east of the Dead Sea. If this interpretation is co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greenschist
Greenschists are metamorphic rocks that formed under the lowest temperatures and pressures usually produced by regional metamorphism, typically and 2–10 kilobars (). Greenschists commonly have an abundance of green minerals such as chlorite, serpentine, and epidote, and platy minerals such as muscovite and platy serpentine. The platiness gives the rock schistosity (a tendency to split into layers.) Other common minerals include quartz, orthoclase, talc, carbonate minerals and amphibole (actinolite). Greenschist is a general field petrologic term for metamorphic or altered mafic volcanic rock. In Europe, the term ''prasinite'' is sometimes used. A ''greenstone'' is sometimes a greenschist but can also be rock types without any schistosity, especially metabasalt ( spilite). However, basalts may remain quite black if primary pyroxene does not revert to chlorite or actinolite. To qualify for the name a rock must also exhibit schistosity or some foliation or layering. The ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osiris
Osiris (, from Egyptian ''wsjr'', cop, ⲟⲩⲥⲓⲣⲉ , ; Phoenician: 𐤀𐤎𐤓, romanized: ʾsr) is the god of fertility, agriculture, the afterlife, the dead, resurrection, life, and vegetation in ancient Egyptian religion. He was classically depicted as a green-skinned deity with a pharaoh's beard, partially mummy-wrapped at the legs, wearing a distinctive atef crown, and holding a symbolic crook and flail. He was one of the first to be associated with the mummy wrap. When his brother, Set cut him up into pieces after killing him, Osiris' wife Isis found all the pieces and wrapped his body up, enabling him to return to life. Osiris was widely worshipped until the decline of ancient Egyptian religion during the rise of Christianity in the Roman Empire. Osiris was at times considered the eldest son of the earth god Geb and the sky goddess Nut, as well as being brother and husband of Isis, and brother of Set, Nephthys, and Horus the Elder, with Horus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isis
Isis (; ''Ēse''; ; Meroitic language, Meroitic: ''Wos''[''a''] or ''Wusa''; Phoenician language, Phoenician: 𐤀𐤎, romanized: ʾs) was a major ancient Egyptian deities, goddess in ancient Egyptian religion whose worship spread throughout the Greco-Roman world. Isis was first mentioned in the Old Kingdom () as one of the main characters of the Osiris myth, in which she resurrects her slain brother and husband, the divine king Osiris, and produces and protects his heir, Horus. She was believed to help the dead enter the ancient Egyptian afterlife beliefs, afterlife as she had helped Osiris, and she was considered the divine mother of the pharaoh, who was likened to Horus. Her maternal aid was invoked in healing Spell (paranormal), spells to benefit ordinary people. Originally, she played a limited role in royal rituals and Egyptian temple, temple rites, although she was more prominent in ancient Egyptian burial customs, funerary practices and magical texts. She was usually ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aphrodite
Aphrodite ( ; grc-gre, Ἀφροδίτη, Aphrodítē; , , ) is an ancient Greek religion, ancient Greek goddess associated with love, lust, beauty, pleasure, passion (emotion), passion, and procreation. She was syncretized with the Roman goddess . Aphrodite's major symbols include Myrtle (common), myrtles, roses, doves, Old World sparrow, sparrows, and swans. The cult of Aphrodite was largely derived from that of the Ancient Canaanite religion, Phoenician goddess Astarte, a cognate of the East Semitic goddess Ishtar, whose cult was based on the Sumerian religion, Sumerian cult of Inanna. Aphrodite's main cult centers were Kythira, Cythera, Cyprus, Corinth, and Athens. Her main festival was the Aphrodisia, which was celebrated annually in midsummer. In Laconia, Aphrodite was worshipped as a warrior goddess. She was also the patron goddess of Prostitution in ancient Greece, prostitutes, an association which led early scholars to propose the concept of "sacred prostitution" in Gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atargatis
Atargatis (; grc, Ἀτάργατις, translit=Atárgatis or arc, , translit=ʿtrʿth; syc, ܬܪܥܬܐ, translit=Tarʿaṯā) was the chief goddess of northern Syria in Classical antiquity. Ctesias also used the name Derketo ( grc-koi, Δερκετὼ) for her, and the Romans called her Dea Syria, or in one word Deasura. Primarily she was a fertility goddess, but, as the ''baalat'' ("mistress") of her city and people she was also responsible for their protection and well-being. Her chief sanctuary was at Hierapolis, modern Manbij, northeast of Aleppo, Syria. Michael Rostovtzeff called her "the great mistress of the North Syrian lands".M. Rostovtseff, "Hadad and Atargatis at Palmyra", ''American Journal of Archaeology'' 37 (January 1933), pp 58-63, examining Palmyrene stamped tesserae. Her consort is usually Hadad. As Ataratheh, doves and fish were considered sacred to her: doves as an emblem of the love goddess, Love-Goddess, and fish as symbolic of the fertility and life of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Lat
Al-Lat ( ar, اللات, translit=Al-Lāt, ), also spelled Allat, Allatu and Alilat, is a pre-Islamic Arabian goddess worshipped under various associations throughout the entire Arabian Peninsula, including Mecca where she was worshipped alongside Manat and al-'Uzza as one of the daughters of Allah. The word ''Allat'' or Elat has been used to refer to various goddesses in the ancient Near East, including the goddess Asherah-Athirat. Al-Lat is attested in south Arabian inscriptions as Lat and Latan, but she had more prominence in north Arabia and the Hejaz, and her cult reached as far as Syria. The writers of the Safaitic script frequently invoked al-Lat in their inscriptions. She was also worshipped by the Nabataeans and was associated with al-'Uzza. The presence of her cult was attested in both Palmyra and Hatra. Under Greco-Roman influence, her iconography began to show the attributes of Athena, the Greek goddess of war, as well as her Roman equivalent Minerva. Ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
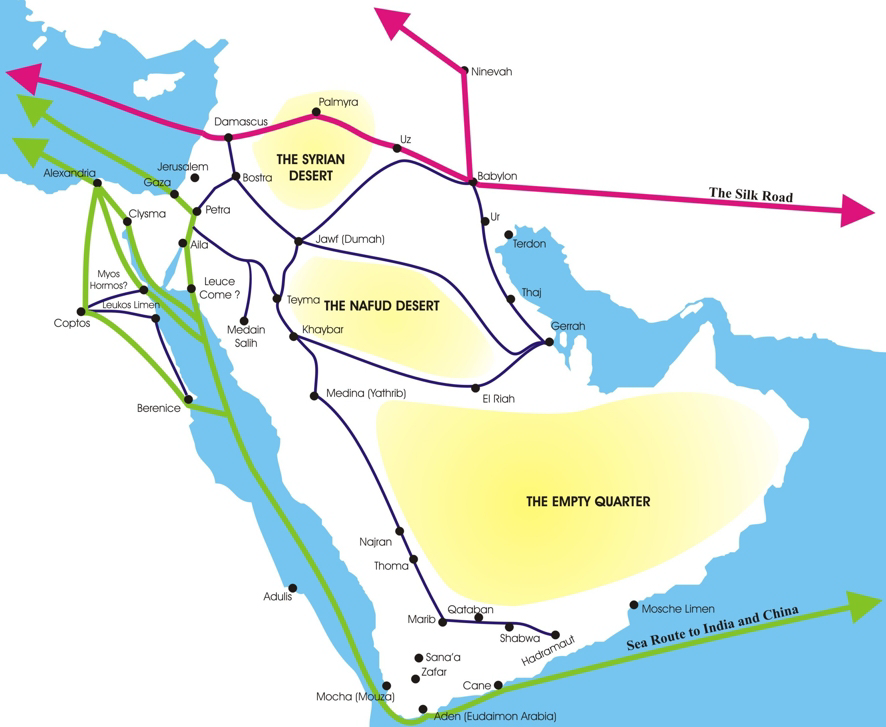
Nabataean Kingdom
The Nabataean Kingdom ( Nabataean Aramaic: 𐢕𐢃𐢋𐢈 ''Nabāṭū''), also named Nabatea (), was a political state of the Arab Nabataeans during classical antiquity. The Nabataean Kingdom controlled many of the trade routes of the region, amassing large wealth and drawing the envy of its neighbors. It stretched south along the Red Sea coast into the Hejaz, up as far north as Damascus, which it controlled for a short period (85–71 BC). Nabataea remained an independent political entity from the mid-3rd century BC until it was annexed in AD 106 by the Roman Empire, which renamed it Arabia Petraea. History Nabataeans The Nabataeans were one among several nomadic Bedouin tribes that roamed the Arabian Desert and moved with their herds to wherever they could find pasture and water. They became familiar with their area as seasons passed, and they struggled to survive during bad years when seasonal rainfall diminished. Although the Nabataeans were initially embedded in Ara ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |