|
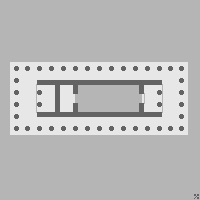
Temple Of Portunus
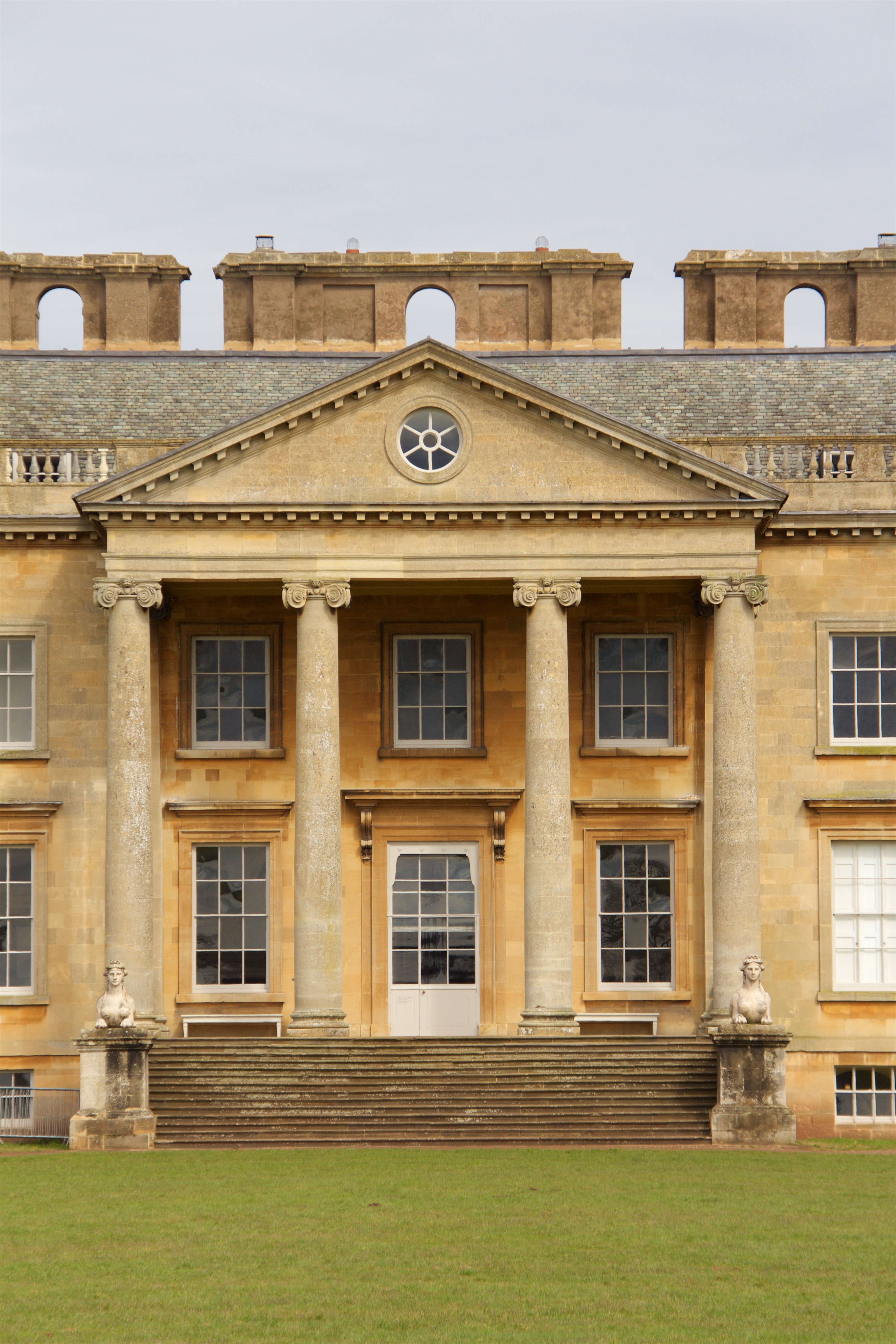
The Temple of Portunus () is an ancient Roman temple in Rome, Italy. It was built beside the Forum Boarium, the Roman cattle market associated with Hercules, which was adjacent to Rome's oldest river port () and the oldest stone bridge across the Tiber River, the Pons Aemilius. It was probably dedicated to the gateway god Portunus although the precise dedication remains unclear as there were several other temples in the area besides his. It was misidentified as the Temple of Fortuna Virilis (Latin for "Manly Luck") from the Renaissance and remains better known by this name. The temple is one of the best preserved of all Roman temples. It is dedicated to Portunus, the god of keys, doors and livestock, and so granaries, it is the main temple dedicated to the god in the city. During the Medieval period, the temple was converted to a Christian church dedicated to Santa Maria Egyziaca ("St Mary of Egypt"). It remained a church up until the early 20th century, when it was deconsecrated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forum Boarium
The Forum Boarium (, ) was the cattle market or '' forum venalium'' of ancient Rome. It was located on a level piece of land near the Tiber between the Capitoline, the Palatine and Aventine hills. As the site of the original docks of Rome () and adjacent to the Pons Aemilius, the earliest stone bridge across the Tiber, the Forum Boarium experienced intense commercial activity. History The site was a religious centre housing the Temple of Hercules Victor, the Temple of Portunus (Temple of Fortuna Virilis), and the massive 6th or 5th century BC Ara Maxima. According to legend, when Hercules arrived in this area with Geryon’s oxen, he was robbed of these by the giant Cacus, who lived in a cave at the foot of the Aventine hill. After slaying the giant, Hercules was honoured as a god by the ancient dwellers of the Palatine hill, who are said to have dedicated an altar to him. The tufa stone core of this altar is housed inside the church of Santa Maria in Cosmedin. The F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tiber
The Tiber ( ; ; ) is the List of rivers of Italy, third-longest river in Italy and the longest in Central Italy, rising in the Apennine Mountains in Emilia-Romagna and flowing through Tuscany, Umbria, and Lazio, where it is joined by the River Aniene, to the Tyrrhenian Sea, between Ostia (Rome), Ostia and Fiumicino. It Drainage basin, drains a basin estimated at . The river has achieved lasting fame as the main watercourse of the city of Rome, which was founded on its eastern banks. The river rises at Mount Fumaiolo in Central Italy and flows in a generally southerly direction past Perugia and Rome to meet the sea at Ostia (town), Ostia. The Tiber has advanced significantly at its mouth, by about , since Roman times, leaving the ancient port of Ostia Antica (archaeological site), Ostia Antica inland."Tiber River". ''Encyclopædia Britannica''. 2006 However, it does not form a proportional river delta, delta, owing to a strong north-flowing sea current close to the shore, d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peripteral
In Classical architecture, a ''peripteros'' (; see ) is a type of ancient Greek or Roman temple surrounded by a portico with columns. It is surrounded by a colonnade ('' pteron'') on all four sides of the ''cella'' (''naos''), creating a four-sided arcade, or peristyle ('' peristasis''). By extension, it also means simply the perimeter of a building (typically a classical temple), when that perimeter is made up of columns. The term is frequently used of buildings in the Doric order. Definition The ''peripteros'' can be a portico, a kiosk, or a chapel. If it is made up of four columns, it is a tetrastyle; of six, hexastyle; of eight, octastyle; of ten, decastyle; and of twelve, dodecastyle. If the columns are fitted into the wall instead of standing alone, the building is a pseudoperipteros A pseudoperipteros (, meaning "falsely peripteral") is a building with engaged columns embedded in the outer walls, except the front of the building. The form is found in classical archi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudoperipteral
A pseudoperipteros (, meaning "falsely peripteral") is a building with engaged columns embedded in the outer walls, except the front of the building. The form is found in classical architecture in ancient Greek temples, especially in the Hellenistic period. In Roman temples, the pseudoperipteral form became usual, where there were columns behind the portico as well. Typically the front has a portico with free-standing columns, but columns on the other three sides of the walls are engaged. If free-standing columns surround the entire building, it is a ''peripteros''. Unlike a ''peripteros'', a ''pseudoperipteros'' has no space ('' peristasis'') between the ''cella'' (''naos'', inner chamber) and the outer walls on the sides and rear, so the engaged columns can also be considered to be embedded directly into those walls of the ''cella''. The Temple of Olympian Zeus at Agrigento was a famous Greek example of this style. Its facade also has engaged columns. A pseudoperipteral bui ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Engaged Column
An engaged column is an architectural element in which a column is embedded in a wall and partly projecting from the surface of the wall, which may or may not carry a partial structural load. Sometimes defined as semi- or three-quarter detached, engaged columns are rarely found in classical Greek architecture, and then only in exceptional cases, but in Roman architecture they exist in abundance, most commonly embedded in the cella walls of pseudoperipteral Roman temples and other buildings. In the temples it is attached to the cella walls, repeating the columns of the peristyle, and in the theatres and amphitheatres, where they subdivided the arched openings: in all these cases engaged columns are utilized as a decorative feature, and as a rule the same proportions are maintained as if they had been isolated columns. In Romanesque work the classic proportions were no longer adhered to; the engaged column, attached to the piers, has always a special function to perform, e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ionic Column
The Ionic order is one of the three canonic orders of classical architecture, the other two being the Doric and the Corinthian. There are two lesser orders: the Tuscan (a plainer Doric), and the rich variant of Corinthian called the composite order. Of the three classical canonic orders, the Corinthian order has the narrowest columns, followed by the Ionic order, with the Doric order having the widest columns. The Ionic capital is characterized by the use of volutes. Ionic columns normally stand on a base which separates the shaft of the column from the stylobate or platform while the cap is usually enriched with egg-and-dart. The ancient architect and architectural historian Vitruvius associates the Ionic with feminine proportions (the Doric representing the masculine). Description Capital The major features of the Ionic order are the volutes of its capital, which have been the subject of much theoretical and practical discourse, based on a brief and obscure passage in Vit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pronaos
A portico is a porch leading to the entrance of a building, or extended as a colonnade, with a roof structure over a walkway, supported by columns or enclosed by walls. This idea was widely used in ancient Greece and has influenced many cultures, including most Western cultures. Porticos are sometimes topped with pediments. Palladio was a pioneer of using temple-fronts for secular buildings. In the UK, the temple-front applied to The Vyne, Hampshire, was the first portico applied to an English country house. A pronaos ( or ) is the inner area of the portico of a Greek or Roman temple, situated between the portico's colonnade or walls and the entrance to the ''cella'', or shrine. Roman temples commonly had an open pronaos, usually with only columns and no walls, and the pronaos could be as long as the ''cella''. The word ''pronaos'' () is Greek for "before a temple". In Latin, a pronaos is also referred to as an ''anticum'' or ''prodomus''. The pronaos of a Greek and Roman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nîmes
Nîmes ( , ; ; Latin: ''Nemausus'') is the Prefectures in France, prefecture of the Gard Departments of France, department in the Occitania (administrative region), Occitanie Regions of France, region of Southern France. Located between the Mediterranean Sea and the Cévennes, the Communes of France, commune of Nîmes had an estimated population of 148,561 in 2019. Dubbed the most Roman city outside Italy, Nîmes has a rich history dating back to the Roman Empire when the city had a population of 50,000–60,000 and was the regional capital. Several famous monuments are in Nîmes, such as the Arena of Nîmes and the Maison Carrée. Because of this, Nîmes is often referred to as the "French Rome". Origins Nimes is situated where the alluvial plain of the Vistrenque River abuts the hills of Mont Duplan to the northeast, Montaury to the southwest, and to the west Mt. Cavalier and the knoll of Canteduc. Its name appears in inscriptions in Gaulish as ''dede matrebo Namausikabo'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maison Carrée
Maison (French for "house") may refer to: People * Edna Maison (1892–1946), American silent-film actress * Jérémy Maison (born 1993), French cyclist * Leonard Maison, New York state senator 1834–1837 * Nicolas Joseph Maison (1771–1840), Marshal of France and Minister of War * René Maison (1895–1962), Belgian operatic tenor * Rudolf Maison (1854–1904), German sculptor Places in France * Maison-des-Champs, a commune in the Aube department, Grand Est * Maison-Feyne, a commune in the Creuse department, Nouvelle-Aquitaine * Maison-Maugis Maison-Maugis () is a former commune in the Orne department in north-western France. On 1 January 2016, it was merged into the new commune of Cour-Maugis sur Huisne. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Podium
A podium (: podiums or podia) is a platform used to raise something to a short distance above its surroundings. In architecture a building can rest on a large podium. Podiums can also be used to raise people, for instance the conductor of an orchestra stands on a podium as do many public speakers. Common parlance has shown an increasing use of ''podium'' in North American English to describe a lectern. In sports, a type of podium can be used to honor the top three competitors in events. In the modern Olympics a tri-level podium is used. Traditionally, the highest platform is in the center for the gold medalist. To their right is a lower platform for the silver medalist, and to the left of the gold medalist is a lower platform for the bronze medalist. At the 2016 Rio Summer Olympics, the Silver and Bronze podium places were of equal elevation. In many sports, results in the top three of a competition are often referred to as podiums or podium finishes. In some individual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cella
In Classical architecture, a or naos () is the inner chamber of an ancient Greek or Roman temple. Its enclosure within walls has given rise to extended meanings: of a hermit's or monk's cell, and (since the 17th century) of a biological cell in plants or animals. Greek and Roman temples In ancient Greek and Roman temples, the ''cella'' was a room at the center of the building, usually containing a cult image or statue representing the particular deity venerated in the temple. In addition, the ''cella'' might contain a table to receive supplementary votive offerings, such as votive statues of associated deities, precious and semi-precious stones, helmets, spear and arrow heads, swords, and war trophies. No gatherings or sacrifices took place in the ''cella'', as the altar for sacrifices was always located outside the building along the axis and temporary altars for other deities were built next to it. The accumulated offerings made Greek and Roman temples virtual treasuri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portico
A portico is a porch leading to the entrance of a building, or extended as a colonnade, with a roof structure over a walkway, supported by columns or enclosed by walls. This idea was widely used in ancient Greece and has influenced many cultures, including most Western cultures. Porticos are sometimes topped with pediments. Palladio was a pioneer of using temple-fronts for secular buildings. In the UK, the temple-front applied to The Vyne, Hampshire, was the first portico applied to an English country house. A pronaos ( or ) is the inner area of the portico of a Greek or Roman temple, situated between the portico's colonnade or walls and the entrance to the '' cella'', or shrine. Roman temples commonly had an open pronaos, usually with only columns and no walls, and the pronaos could be as long as the ''cella''. The word ''pronaos'' () is Greek for "before a temple". In Latin, a pronaos is also referred to as an ''anticum'' or ''prodomus''. The pronaos of a Greek a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |