|
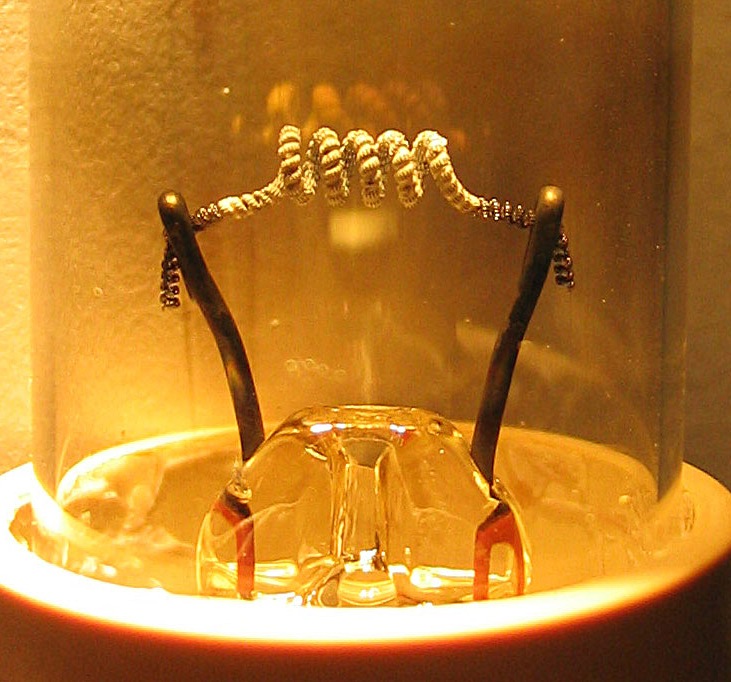
Teltron Tube
A teltron tube (named for Teltron Inc., which is now owned by 3B Scientific Ltd.) is a type of cathode-ray tube used to demonstrate the properties of electrons. There were several different types made by Teltron including a diode, a triode, a Maltese Cross tube, a simple deflection tube with a fluorescent screen, and one which could be used to measure the charge-to-mass ratio of an electron. The latter two contained an electron gun with deflecting plates. The beams can be bent by applying voltages to various electrodes in the tube or by holding a magnet close by. The electron beams are visible as fine bluish lines. This is accomplished by filling the tube with low-pressure helium (He) or Hydrogen (H2) gas. A few of the electrons in the beam collide with the helium atoms, causing them to fluoresce and emit light. They are usually used to teach electromagnetic effects because they show how an electron beam is affected by electric fields and by magnetic fields such as the Lorent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
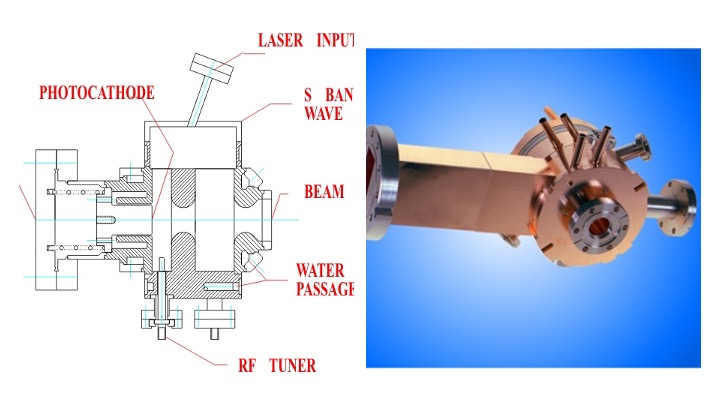
Electron Gun
file:Egun.jpg, Electron gun from a cathode-ray tube file:Vidicon Electron Gun.jpg, The electron gun from an RCA Vidicon video camera tube An electron gun (also called electron emitter) is an electrical component in some vacuum tubes that produces a narrow, collimation, collimated electron beam that has a precise kinetic energy. The largest use is in cathode-ray tubes (CRTs), used in older television sets, computer displays and oscilloscopes, before the advent of flat-panel displays. Electron guns are also used in field-emission display, field-emission displays (FEDs), which are essentially flat-panel displays made out of rows of extremely small cathode-ray tubes. They are also used in microwave linear beam vacuum tubes such as klystrons, inductive output tubes, travelling-wave tubes, and gyrotrons, as well as in scientific instruments such as electron microscopes and particle accelerators. Electron guns may be classified by the type of electric field generation (DC or RF), by e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mass Spectrometry
Mass spectrometry (MS) is an analytical technique that is used to measure the mass-to-charge ratio of ions. The results are presented as a ''mass spectrum'', a plot of intensity as a function of the mass-to-charge ratio. Mass spectrometry is used in many different fields and is applied to pure samples as well as complex mixtures. A mass spectrum is a type of plot of the ion signal as a function of the mass-to-charge ratio. These spectra are used to determine the elemental or isotopic signature of a sample, the masses of particles and of molecules, and to elucidate the chemical identity or structure of molecules and other chemical compounds. In a typical MS procedure, a sample, which may be solid, liquid, or gaseous, is ionization, ionized, for example by bombarding it with a Electron ionization, beam of electrons. This may cause some of the sample's molecules to break up into positively charged fragments or simply become positively charged without fragmenting. These ions (fragmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mass
Mass is an Intrinsic and extrinsic properties, intrinsic property of a physical body, body. It was traditionally believed to be related to the physical quantity, quantity of matter in a body, until the discovery of the atom and particle physics. It was found that different atoms and different elementary particle, elementary particles, theoretically with the same amount of matter, have nonetheless different masses. Mass in modern physics has multiple Mass in special relativity, definitions which are conceptually distinct, but physically equivalent. Mass can be experimentally defined as a measure (mathematics), measure of the body's inertia, meaning the resistance to acceleration (change of velocity) when a net force is applied. The object's mass also determines the Force, strength of its gravitational attraction to other bodies. The SI base unit of mass is the kilogram (kg). In physics, mass is Mass versus weight, not the same as weight, even though mass is often determined by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oil Drop Experiment
The oil drop experiment was performed by Robert Andrews Millikan, Robert A. Millikan and Harvey Fletcher in 1909 to measure the Elementary charge, elementary electric charge (the charge of the electron). The experiment took place in the Ryerson Physical Laboratory at the University of Chicago. Millikan received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1923. The experiment observed tiny electrically charged droplets of oil located between two parallel metal surfaces, forming the plates of a capacitor. The plates were oriented horizontally, with one plate above the other. A mist of atomizer nozzle, atomized oil drops was introduced through a small hole in the top plate; some would be ionization, ionized naturally. First, with zero applied electric field, the velocity of a falling droplet was measured. At terminal velocity, the drag (physics), drag force equals the gravity, gravitational force. As both forces depend on the radius in different ways, the radius of the droplet, and therefore the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elementary Charge
The elementary charge, usually denoted by , is a fundamental physical constant, defined as the electric charge carried by a single proton (+1 ''e'') or, equivalently, the magnitude of the negative electric charge carried by a single electron, which has charge −1 . In SI units, the coulomb is defined such that the value of the elementary charge is exactly or 160.2176634 zeptocoulombs (zC). Since the 2019 revision of the SI, the seven SI base units are defined in terms of seven fundamental physical constants, of which the elementary charge is one. In the centimetre–gram–second system of units (CGS), the corresponding quantity is . Robert A. Millikan and Harvey Fletcher's oil drop experiment first directly measured the magnitude of the elementary charge in 1909, differing from the modern accepted value by just 0.6%. Under assumptions of the then-disputed atomic theory, the elementary charge had also been indirectly inferred to ~3% accuracy from blackb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conservation Of Energy
The law of conservation of energy states that the total energy of an isolated system remains constant; it is said to be Conservation law, ''conserved'' over time. In the case of a Closed system#In thermodynamics, closed system, the principle says that the total amount of energy within the system can only be changed through energy entering or leaving the system. Energy can neither be created nor destroyed; rather, it can only be transformed or transferred from one form to another. For instance, chemical energy is Energy conversion, converted to kinetic energy when a stick of dynamite explodes. If one adds up all forms of energy that were released in the explosion, such as the kinetic energy and potential energy of the pieces, as well as heat and sound, one will get the exact decrease of chemical energy in the combustion of the dynamite. Classically, the conservation of energy was distinct from the conservation of mass. However, special relativity shows that mass is related to en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electromagnetic Coil
An electromagnetic coil is an electrical Electrical conductivity, conductor such as a wire in the shape of a wiktionary:coil, coil (spiral or helix). Electromagnetic coils are used in electrical engineering, in applications where electric currents interact with magnetic fields, in devices such as electric motors, Electric generator, generators, inductors, electromagnets, transformers, sensor coils such as in medical Magnetic resonance imaging, MRI imaging machines. Either an electric current is passed through the wire of the coil to generate a magnetic field, or conversely, an external ''time-varying'' magnetic field through the interior of the coil generates an Electromotive force, EMF (voltage) in the conductor. A current through any conductor creates a circular magnetic field around the conductor due to Ampere's circuital law, Ampere's law. The advantage of using the coil shape is that it increases the strength of the magnetic field produced by a given current. The magnet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermionic Emission
Thermionic emission is the liberation of charged particles from a hot electrode whose thermal energy gives some particles enough kinetic energy to escape the material's surface. The particles, sometimes called ''thermions'' in early literature, are now known to be ions or electrons. Thermal electron emission specifically refers to emission of electrons and occurs when thermal energy overcomes the material's work function. After emission, an opposite charge of equal magnitude to the emitted charge is initially left behind in the emitting region. But if the emitter is connected to a battery, that remaining charge is neutralized by charge supplied by the battery as particles are emitted, so the emitter will have the same charge it had before emission. This facilitates additional emission to sustain an electric current. Thomas Edison in 1880 while inventing his light bulb noticed this current, so subsequent scientists referred to the current as the Edison effect, though it wasn't un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclotron Motion Wider View
A cyclotron is a type of particle accelerator invented by Ernest Lawrence in 1929–1930 at the University of California, Berkeley, and patented in 1932. Lawrence, Ernest O. ''Method and apparatus for the acceleration of ions'', filed: January 26, 1932, granted: February 20, 1934 A cyclotron accelerates charged particles outwards from the center of a flat cylindrical vacuum chamber along a spiral path. The particles are held to a spiral trajectory by a static magnetic field and accelerated by a rapidly varying electric field. Lawrence was awarded the 1939 Nobel Prize in Physics for this invention. The cyclotron was the first "cyclical" accelerator. The primary accelerators before the development of the cyclotron were electrostatic accelerators, such as the Cockcroft–Walton generator and the Van de Graaff generator. In these accelerators, particles would cross an accelerating electric field only once. Thus, the energy gained by the particles was limited by the maximum electr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |