|
Telemachy
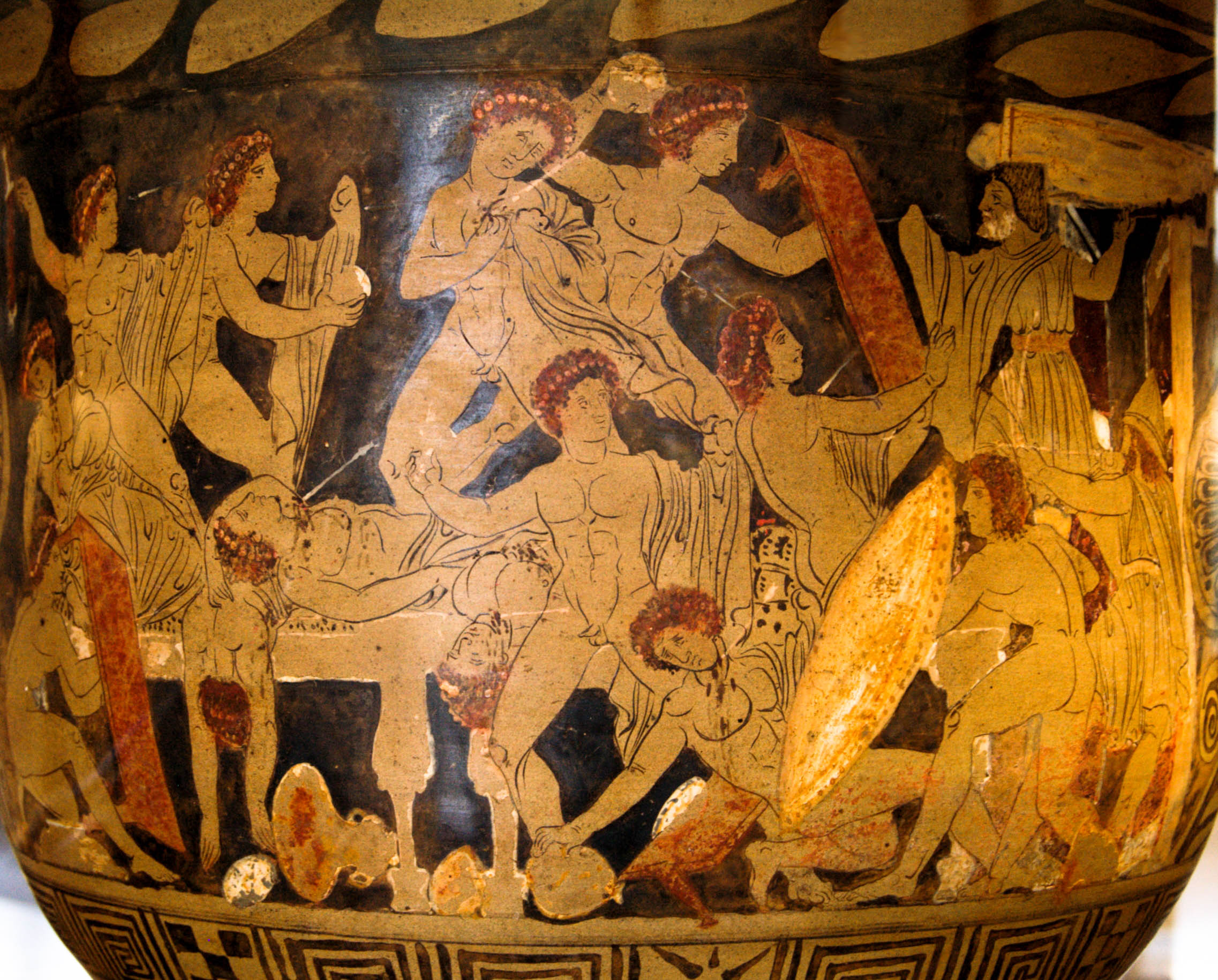
The ''Telemachy'' (from Greek language, Greek Τηλεμάχεια, ''Tēlemacheia'') is a term traditionally applied to the first four books of Homer's epic poem the ''Odyssey''. They are named so because, just as the ''Odyssey'' tells the story of Odysseus, they tell the story of Odysseus's son Telemachus as he journeys from home for the first time in search of news about his missing father. The ''Telemachy'' as an introduction to the ''Odyssey'' The ''Odyssey'' is a ''nostos'' that recalls the story of Odysseus' journey home to Homer's Ithaca, Ithaca, finally completed twenty years after the Trojan War began. Odysseus, however, does not directly appear in the narrative until Book 5. Instead, the ''Telemachy''s subject is the effect of Odysseus' absence on his family, Telemachus in particular. The first four books of the ''Odyssey'' give the reader a glimpse of the goings-on at the palace in Ithaca. There are a multitude of suitors vying for Penelope's hand in marriage, consu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
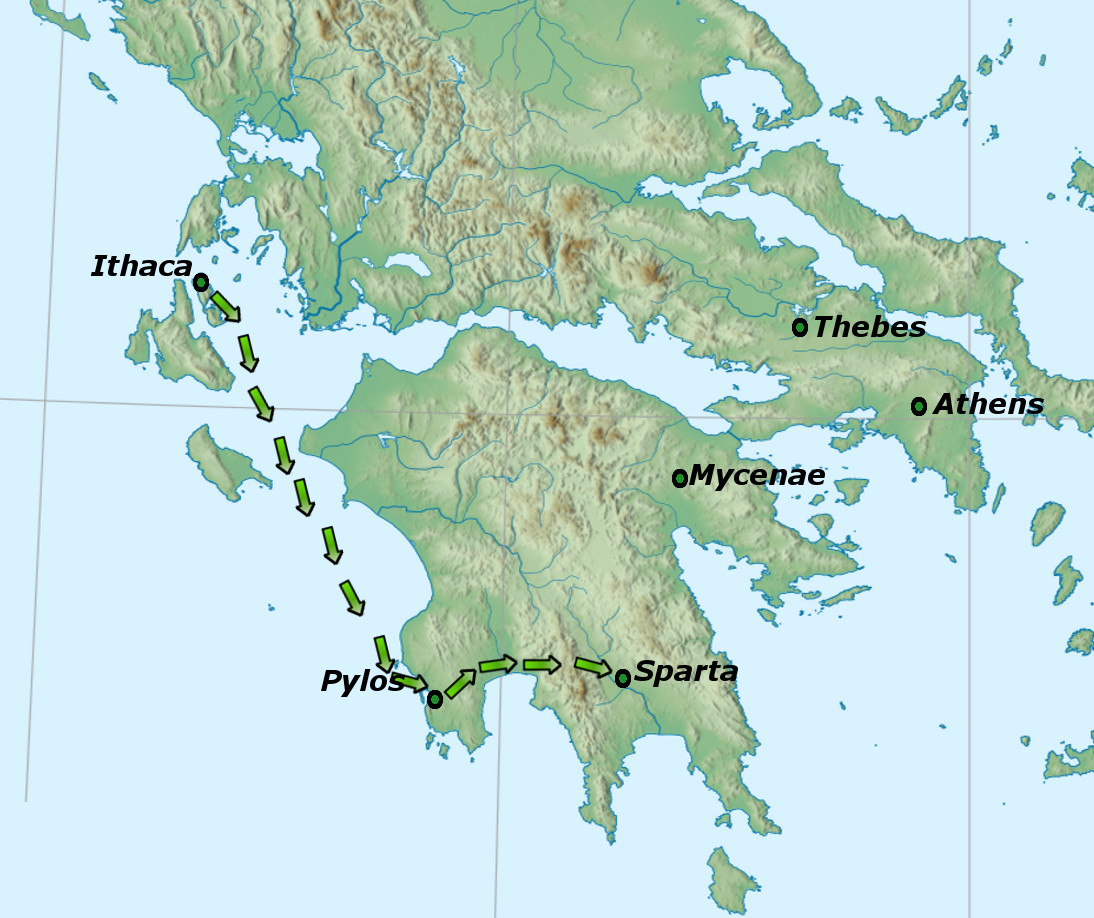
Telemachus Map
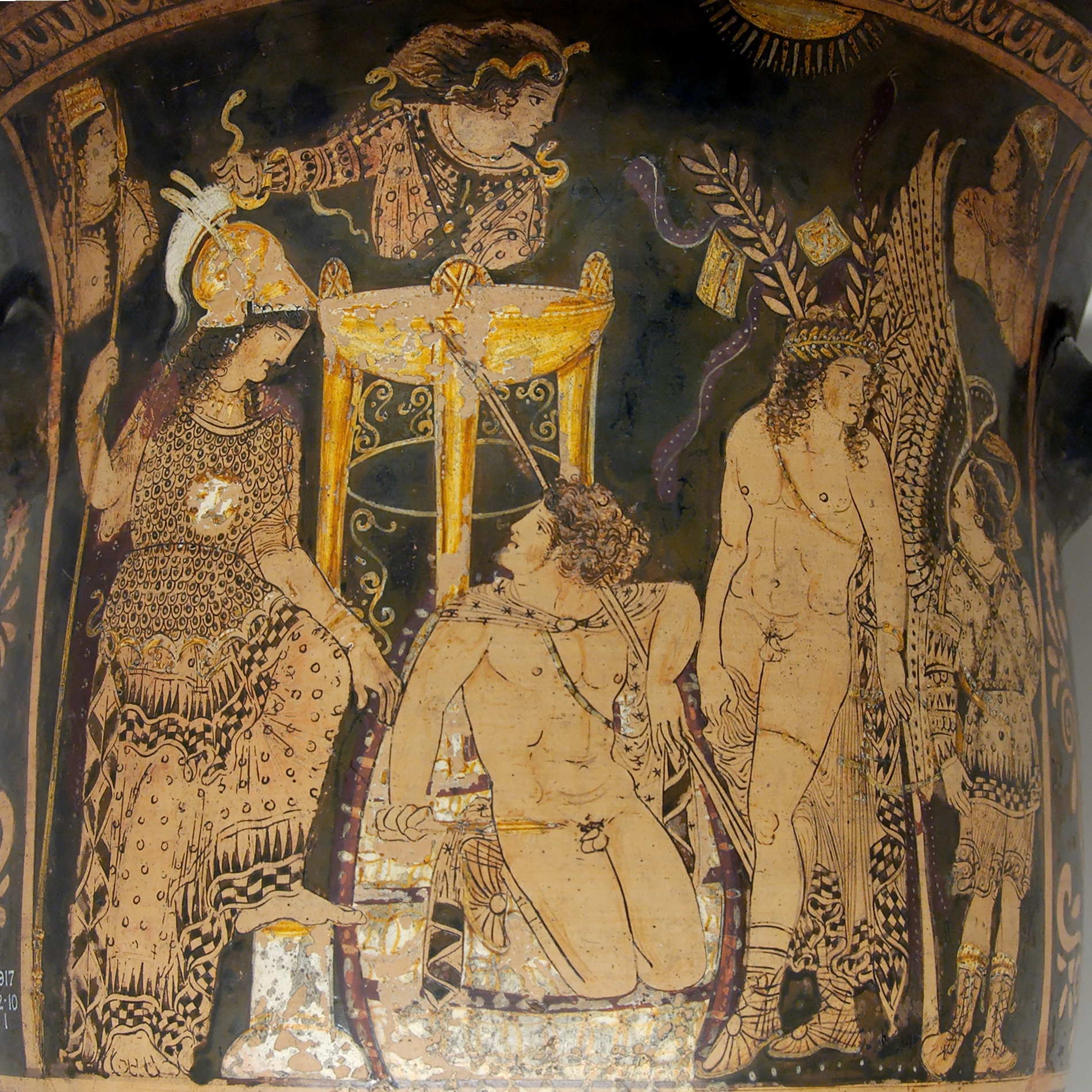
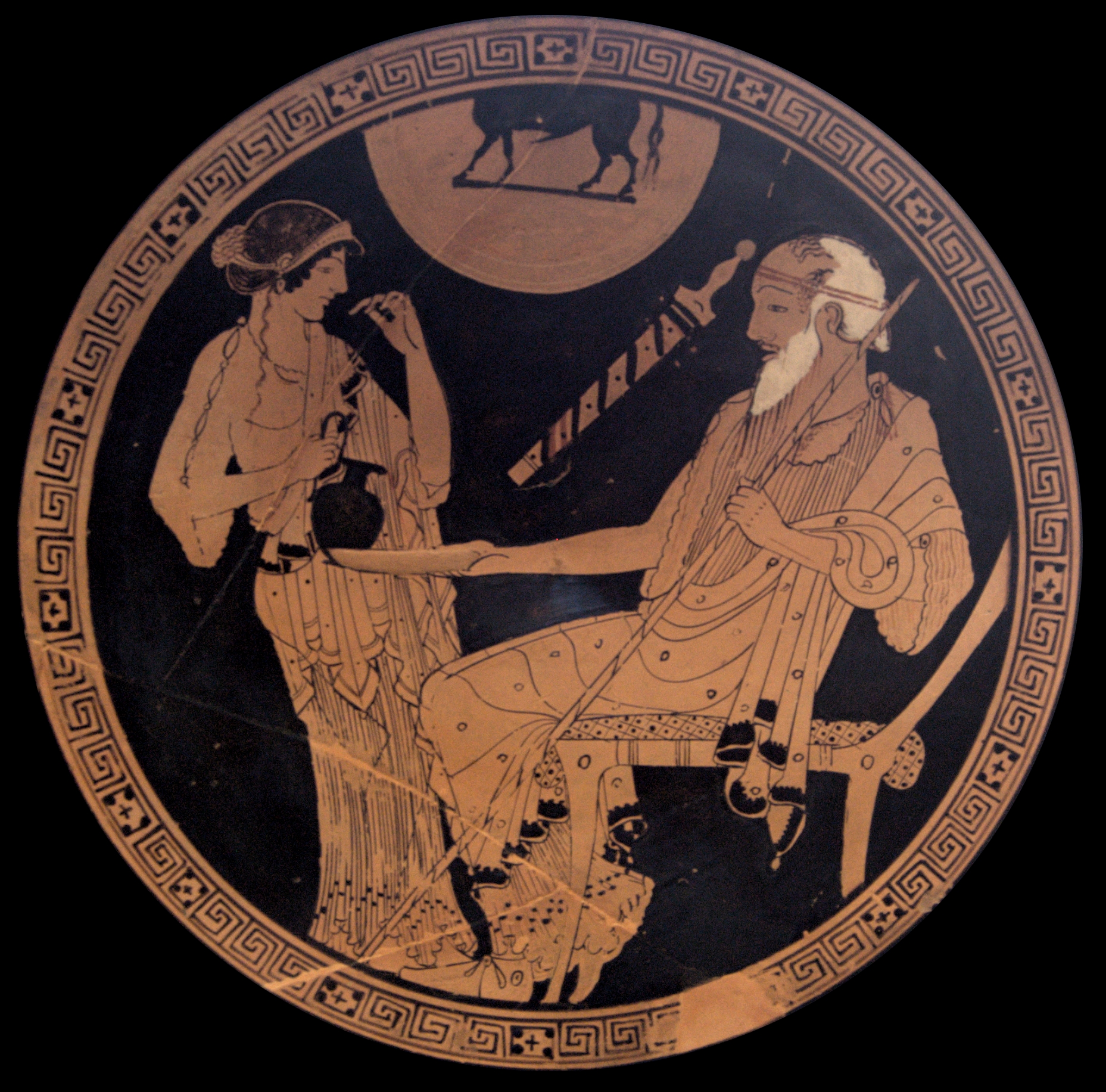
In Greek mythology, Telemachus ( ; ) is the son of Odysseus and Penelope, who are central characters in Homer's ''Odyssey''. When Telemachus reached manhood, he visited Pylos and Sparta in search of his wandering father. On his return to Homer's Ithaca, Ithaca, he found that Odysseus had reached home before him. Then father and son slew the Suitors of Penelope, suitors who had gathered around Penelope. According to later tradition, Telemachus married Circe after Odysseus's death. The first four books of the ''Odyssey'' focus on Telemachus's journeys in search of news about his father, who has yet to return home from the Trojan War, and are traditionally given the title ''Telemachy''. Etymology Telemachus's name in Greek language, Greek means "far from battle", or perhaps "fighting from afar", as a bowman does. ''Odyssey'' In Homer's ''Odyssey'', Telemachus, under the instructions of Athena (who accompanies him during the quest), spends the first four books trying to gain know ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homer
Homer (; , ; possibly born ) was an Ancient Greece, Ancient Greek poet who is credited as the author of the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Despite doubts about his authorship, Homer is considered one of the most revered and influential authors in history. The ''Iliad'' centers on a quarrel between King Agamemnon and the warrior Achilles during the last year of the Trojan War. The ''Odyssey'' chronicles the ten-year journey of Odysseus, king of Homer's Ithaca, Ithaca, back to his home after the fall of Troy. The epics depict man's struggle, the ''Odyssey'' especially so, as Odysseus perseveres through the punishment of the gods. The poems are in Homeric Greek, also known as Epic Greek, a literary language that shows a mixture of features of the Ionic Greek, Ionic and Aeolic Greek, Aeolic dialects from different centuries; the predominant influence is Eastern Ionic. Most researchers believe that the poems w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Odyssey
The ''Odyssey'' (; ) is one of two major epics of ancient Greek literature attributed to Homer. It is one of the oldest surviving works of literature and remains popular with modern audiences. Like the ''Iliad'', the ''Odyssey'' is divided into 24 books. It follows the heroic king of Ithaca, Odysseus, also known by the Latin variant Ulysses, and his homecoming journey after the ten-year long Trojan War. His journey from Troy to Ithaca lasts an additional ten years, during which time he encounters many perils and all of his crewmates are killed. In Odysseus's long absence, he is presumed dead, leaving his wife Penelope and son Telemachus to contend with a group of unruly suitors competing for Penelope's hand in marriage. The ''Odyssey'' was first written down in Homeric Greek around the 8th or 7th century BC; by the mid-6th century BC, it had become part of the Greek literary canon. In antiquity, Homer's authorship was taken as true, but contemporary sch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telemachus
In Greek mythology, Telemachus ( ; ) is the son of Odysseus and Penelope, who are central characters in Homer's ''Odyssey''. When Telemachus reached manhood, he visited Pylos and Sparta in search of his wandering father. On his return to Ithaca, he found that Odysseus had reached home before him. Then father and son slew the suitors who had gathered around Penelope. According to later tradition, Telemachus married Circe after Odysseus's death. The first four books of the ''Odyssey'' focus on Telemachus's journeys in search of news about his father, who has yet to return home from the Trojan War, and are traditionally given the title '' Telemachy''. Etymology Telemachus's name in Greek means "far from battle", or perhaps "fighting from afar", as a bowman does. ''Odyssey'' In Homer's ''Odyssey'', Telemachus, under the instructions of Athena (who accompanies him during the quest), spends the first four books trying to gain knowledge of his father, Odysseus, who left for Troy w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xenia (Greek)
Xenia ( ) is an Ancient Greeks, ancient Greek concept of hospitality. It is almost always translated as 'guest-friendship' or 'ritualized friendship'. It is an institutionalized relationship rooted in generosity, gift exchange, and reciprocity. Historically, hospitality towards foreigners and guests (Hellenes not from your polis) was understood as a moral obligation, as well as a political imperative. Hospitality towards foreign Hellenes honored Zeus, Zeus ''Xenios'' (and Athena, Athene ''Xenia''), patrons of foreigners. The rituals of hospitality created and expressed a reciprocal relationship between guest and host expressed in both material benefits (e.g. gifts, protection, shelter) as well as non-material ones (e.g. favors, certain normative rights). The word is derived from ''Xenos (Greek), xenos'' . Overview Xenia consists of two basic rules: # The respect from hosts to guests. Hosts must be hospitable to guests and provide them with a bath, food, drink, gifts, and safe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Athena
Athena or Athene, often given the epithet Pallas, is an ancient Greek religion, ancient Greek goddess associated with wisdom, warfare, and handicraft who was later syncretism, syncretized with the Roman goddess Minerva. Athena was regarded as the patron and protectress of various cities across Greece, particularly the city of Athens, from which she most likely received her name. The Parthenon on the Acropolis of Athens is dedicated to her. Her major symbols include Owl of Athena, owls, olive trees, snakes, and the Gorgoneion. In art, she is generally depicted wearing a helmet and holding a spear. From her origin as an Aegean tutelary deity, palace goddess, Athena was closely associated with the city. She was known as ''Polias'' and ''Poliouchos'' (both derived from ''polis'', meaning "city-state"), and her temples were usually located atop the fortified acropolis in the central part of the city. The Parthenon on the Athenian Acropolis is dedicated to her, along with numero ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cliffhanger
A cliffhanger or cliffhanger ending is a plot device in fiction which features a main character in a precarious situation, facing a difficult dilemma or confronted with a shocking revelation at the end of an episode of serialized fiction or before a commercial break in a television programme. A cliffhanger is intended to incentivize the audience to return to see how the characters resolve the dilemma. Some serials end with the caveat, "To Be Continued" or "The End?" In serial films and Television show, television series, the following episode sometimes begins with a recap sequence. Cliffhangers were used as literary devices in several works of the Middle Ages with ''One Thousand and One Nights'' ending on a cliffhanger each night. Cliffhangers appeared as an element of the Victorian era serial novel that emerged in the 1840s, with many associating the form with Charles Dickens, a pioneer of the serial publication of narrative fiction.Grossman, Jonathan H. (2012). ''Charles Dick ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orestes
In Greek mythology, Orestes or Orestis (; ) was the son of Agamemnon and Clytemnestra, and the brother of Electra and Iphigenia. He was also known by the patronymic Agamemnonides (), meaning "son of Agamemnon." He is the subject of several Ancient Greek plays and of various myths connected with his madness, revenge, and purification, which retain obscure threads of much older works. In particular Orestes plays a main role in Aeschylus' '' Oresteia.'' Etymology The Greek name Ὀρέστης, having become "Orestēs" in Latin and its descendants, is derived from Greek ὄρος (óros, "mountain") and ἵστημι (hístēmi, "to stand"), and so can be thought to have the meaning "stands on a mountain". Greek literature Homer In the Homeric telling of the story, Orestes is a member of the doomed house of Atreus, which is descended from Tantalus and Niobe. He is absent from Mycenae when his father, Agamemnon, returns from the Trojan War with the Trojan princess Cass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nestor (mythology)
In Greek mythology, Nestor of Gerenia (, ''Nestōr Gerēnios'') was a legendary king of Pylos. He is a prominent secondary character in Homer's ''Iliad'' and ''Odyssey'', where he appears as an elderly warrior who frequently offers advice to the other characters. The Mycenaean Greece, Mycenaean-era palace at Pylos is known as the ''Palace of Nestor'', though there is no evidence that he was an actual person. Description In the account of Dares Phrygius, Dares the Phrygian, Nestor was illustrated as "... large, broad and fair. His nose was long and hooked. He was a wise adviser." Family Nestor was the son of King Neleus of Pylos and Chloris of Pylos, Chloris, daughter of King AmphionBibliotheca (Pseudo-Apollodorus), Apollodorus, 1.9.9; Scholia on Homer, ''Odyssey'' 11.281 citing Pherecydes of Athens, Pherecydes of Orchomenus (Boeotia), Orchomenus. Otherwise, Nestor's mother was called Polymede. His wife was either Eurydice of Pylos, Eurydice or Anaxibia; their children inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sparta
Sparta was a prominent city-state in Laconia in ancient Greece. In antiquity, the city-state was known as Lacedaemon (), while the name Sparta referred to its main settlement in the Evrotas Valley, valley of Evrotas (river), Evrotas river in Laconia, in southeastern Peloponnese. Around 650 BC, it rose to become the dominant military land-power in ancient Greece. Sparta was recognized as the leading force of the unified Greek military during the Greco-Persian Wars, in rivalry with the rising naval power of Classical Athens, Athens. Sparta was the principal enemy of History of Athens, Athens during the Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC), from which it emerged victorious after the Battle of Aegospotami. The decisive Battle of Leuctra against Thebes, Greece, Thebes in 371 BC ended the Spartan hegemony, although the city-state maintained its Independence, political independence until its forced integration into the Achaean League in 192 BC. The city nevertheless recovered m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |