|
Tel Tsaf
Tel Tsaf () is an archaeological site located in the central Jordan Valley, south-east of Beit She'an. Tel Tsaf is dated to the Middle Chalcolithic (ca. 5300/5200–4700/4500 BC) a little-known period in the archaeology of the Levant, post-dating the Pottery Neolithic B phase of the Wadi Rabah Culture and pre-dating the Ghassulian of the Late Chalcolithic. History Middle Chalcolithic The excavations unearthed four architectural complexes. Each consists of a closed courtyard with rounded or rectangular rooms and numerous rounded silos. Four burials were found within or adjacent to silos. Outside the settlement a well was cut into the water table, approximately 6.5 m in depth. Common finds included numerous flints, pottery and animal bones. The terms "Tel Tsaf Decoration" or "Tsafian" were derived from an assemblage of painted pottery, consisting mainly of relatively elaborate vessels bearing geometric decoration using red and black paint on a white slip background. The decoratio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tel Tsaf Courtyard Building
TEL or Tel may refer to: Businesses and organisations * Tokyo Electron, a semiconductor equipment manufacturer * TE Connectivity, a technology company, NYSE stock ticker TEL * The European Library, an Internet service Place names * Tel, Azerbaijan * Tel River, in Orissa, India Science and technology * Technology-Enhanced Learning * Tetraethyllead, a gasoline additive to make leaded gasoline * ETV6, previously known as TEL, a gene * Transporter erector launcher, a mobile missile launch platform * Tolman electronic parameter, a property of ligands * tel, List of URI schemes, a URI scheme for telephone numbers * .tel, an internet top-level domain * tel, a parameter in the hCard microformat Other uses * Tell (archaeology), or tel, a type of archaeological mound created by human occupation * Test of Economic Literacy, a standardized test of economics * Thomson–East Coast MRT line, a mass rapid transit line in Singapore * Telescopium, a minor constellation in the southern celestial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grave Goods
Grave goods, in archaeology and anthropology, are items buried along with a body. They are usually personal possessions, supplies to smooth the deceased's journey into an afterlife, or offerings to gods. Grave goods may be classed by researchers as a type of votive deposit. Most grave goods recovered by archaeologists consist of inorganic objects such as pottery and stone and metal tools, but organic objects that have since decayed were also placed in ancient tombs. If grave goods were to be useful to the deceased in the afterlife, then favorite foods or everyday objects were supplied. Oftentimes, social status played a role in what was left and how often it was left. Funerary art is a broad term but generally means artworks made specifically to decorate a burial place, such as miniature models of possessions - including slaves or servants - for "use" in an afterlife. (Ancient Egypt sometimes saw the burial of real servants with the deceased. Similar cases of human sacrifice of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeology In Israel
The archaeology of Israel is the study of the archaeology of the present-day Israel, stretching from prehistory through three millennia of documented history. The ancient Land of Israel was a geographical bridge between the political and cultural centers of Mesopotamia and Egypt. Despite the importance of the country to three major religions, serious archaeological research only began in the 15th century.''Encyclopedia of Zionism and Israel'', edited by Raphael Patai, Herzl Press and McGraw-Hill, New York, 1971, vol. I, pp. 66–71 Although he never travelled to the Levant, or even left the Netherlands, the first major work on the antiquities of Israel is considered to be Adriaan Reland's ''Antiquitates Sacrae veterum Hebraeorum,'' published in 1708. Edward Robinson, an American theologian who visited the country in 1838, published its first topographical studies. Lady Hester Stanhope performed the first modern excavation at Ashkelon in 1815. A Frenchman, Louis Felicien de Sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiocarbon Dating
Radiocarbon dating (also referred to as carbon dating or carbon-14 dating) is a method for Chronological dating, determining the age of an object containing organic material by using the properties of carbon-14, radiocarbon, a radioactive Isotopes of carbon, isotope of carbon. The method was developed in the late 1940s at the University of Chicago by Willard Libby. It is based on the fact that radiocarbon () is constantly being created in the Atmosphere of Earth, Earth's atmosphere by the interaction of cosmic rays with atmospheric nitrogen. The resulting combines with atmospheric oxygen to form radioactive carbon dioxide, which is incorporated into plants by photosynthesis; animals then acquire by eating the plants. When the animal or plant dies, it stops exchanging carbon with its environment, and thereafter the amount of it contains begins to decrease as the undergoes radioactive decay. Measuring the amount of in a sample from a dead plant or animal, such as a piece of w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
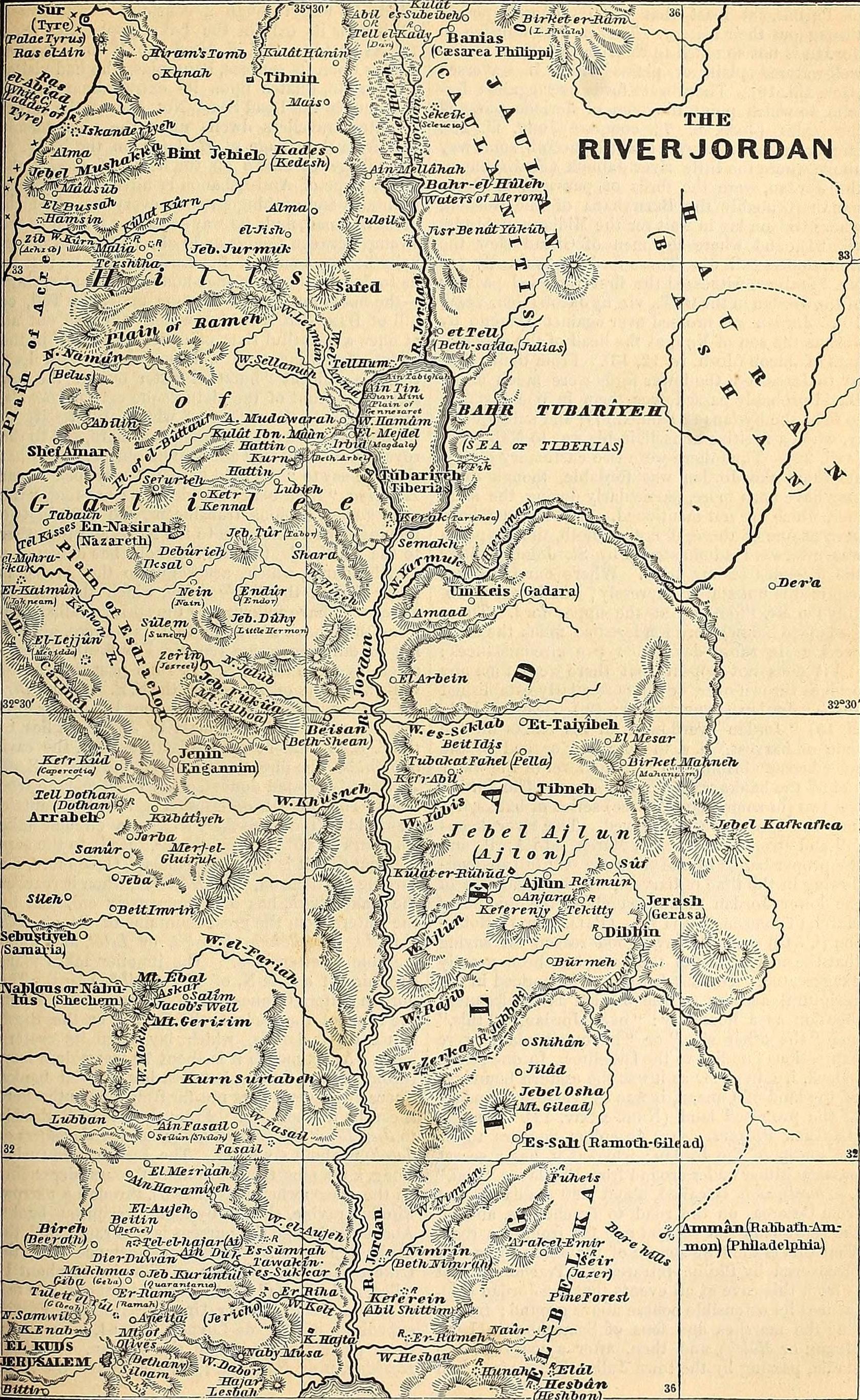
Jordan River
The Jordan River or River Jordan (, ''Nahr al-ʾUrdunn''; , ''Nəhar hayYardēn''), also known as ''Nahr Al-Sharieat'' (), is a endorheic river in the Levant that flows roughly north to south through the Sea of Galilee and drains to the Dead Sea. The river passes by or through Jordan, Syria, Israel, and the Palestinian territories. Jordan and the Israeli-occupied Golan Heights border the river to the east, while Israel and the Israeli-occupied West Bank lie to its west. Both Jordan and the West Bank derive their names in relation to the river. The river holds major significance in Judaism and Christianity. According to the Bible, the Israelites crossed it into the Promised Land and Jesus of Nazareth was baptized by John the Baptist in it. Etymology Several hypotheses for the origin of most of the river's names in modern languages (e.g., Jordan, Yarden, Urdunn), one is that it comes from Semitic 'Yard, on' 'flow down' <√ירד reflecting the river's declivity, possibly a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berlin
Berlin ( ; ) is the Capital of Germany, capital and largest city of Germany, by both area and List of cities in Germany by population, population. With 3.7 million inhabitants, it has the List of cities in the European Union by population within city limits, highest population within its city limits of any city in the European Union. The city is also one of the states of Germany, being the List of German states by area, third smallest state in the country by area. Berlin is surrounded by the state of Brandenburg, and Brandenburg's capital Potsdam is nearby. The urban area of Berlin has a population of over 4.6 million and is therefore the most populous urban area in Germany. The Berlin/Brandenburg Metropolitan Region, Berlin-Brandenburg capital region has around 6.2 million inhabitants and is Germany's second-largest metropolitan region after the Rhine-Ruhr region, as well as the List of EU metropolitan areas by GDP, fifth-biggest metropolitan region by GDP in the European Union. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Archaeological Institute
The German Archaeological Institute (, ''DAI'') is a research institute in the field of archaeology (and other related fields). The DAI is a "federal agency" under the Federal Foreign Office, Federal Foreign Office of Germany. Status, tasks and goals The Institute comes under the umbrella of the Federal Foreign Office of Germany. (PDF) It has a legal right to academic self-administration but is also an important component of Germany's cultural, artistic, and foreign policy programmes. The DAI has often laid the groundwork for the establishment of interstate relationships. It maintains relationships with many academic organisations around the world. Its members include German archaeologists, German representatives of affiliated disciplines, and several important foreign researchers. It is not possible to apply for membership; it can only be received by Co-option#First sense, co-option. Selection as a corresponding member, corresponding or ordinary member is accordingly a special ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zinman Institute Of Archaeology
The University of Haifa (, ) is a public research university located on Mount Carmel in Haifa, Israel. Founded in 1963 as a branch of the Hebrew University of Jerusalem, the University of Haifa received full academic accreditation as an independent university in 1972, becoming Israel's sixth academic institution and the fourth university. The university has the largest university library in Israel. As of 2019, approximately 18,000 students were enrolled at the University of Haifa. Among Israeli higher education institutions the University of Haifa has the largest percentage (41%) of Arab-Israeli students. Overview The University of Haifa was founded in 1963 by Haifa mayor Abba Hushi, to operate under the academic auspices of the Hebrew University of Jerusalem. Haifa University is located on Mount Carmel. In 1972, the University of Haifa declared its independence and became the sixth academic institution in Israel and the fourth university. About 18,100 undergraduate and gra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Haifa
The University of Haifa (, ) is a public research university located on Mount Carmel in Haifa, Israel. Founded in 1963 as a branch of the Hebrew University of Jerusalem, the University of Haifa received full academic accreditation as an independent university in 1972, becoming Israel's sixth academic institution and the fourth university. The university has the largest university library in Israel. As of 2019, approximately 18,000 students were enrolled at the University of Haifa. Among Israeli higher education institutions the University of Haifa has the largest percentage (41%) of Arab-Israeli students. Overview The University of Haifa was founded in 1963 by Haifa mayor Abba Hushi, to operate under the academic auspices of the Hebrew University of Jerusalem. Haifa University is located on Mount Carmel. In 1972, the University of Haifa declared its independence and became the sixth academic institution in Israel and the fourth university. About 18,100 undergraduate a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jerusalem
Jerusalem is a city in the Southern Levant, on a plateau in the Judaean Mountains between the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and the Dead Sea. It is one of the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest cities in the world, and is considered Holy city, holy to the three major Abrahamic religions—Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. Both Israel and Palestine claim Jerusalem as their capital city; Israel maintains its primary governmental institutions there, while Palestine ultimately foresees it as its seat of power. Neither claim is widely Status of Jerusalem, recognized internationally. Throughout History of Jerusalem, its long history, Jerusalem has been destroyed at least twice, Siege of Jerusalem (other), besieged 23 times, captured and recaptured 44 times, and attacked 52 times. According to Eric H. Cline's tally in Jerusalem Besieged. The part of Jerusalem called the City of David (historic), City of David shows first signs of settlement in the 4th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hebrew University
The Hebrew University of Jerusalem (HUJI; ) is an Israeli public research university based in Jerusalem. Co-founded by Albert Einstein and Chaim Weizmann in July 1918, the public university officially opened on 1 April 1925. It is the second-oldest Israeli university, having been founded 30 years before the establishment of the State of Israel but six years after the older Technion university. The HUJI has three campuses in Jerusalem: one in Rehovot, one in Rishon LeZion and one in Eilat. Until 2023, the world's largest library for Jewish studies—the National Library of Israel—was located on its Edmond J. Safra campus in the Givat Ram neighbourhood of Jerusalem. The university has five affiliated teaching hospitals (including the Hadassah Medical Center), seven faculties, more than 100 research centers, and 315 academic departments. , one-third of all the doctoral candidates in Israel were studying at the HUJI. Among its first board of governors were Sigmund Freud and M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |