|
Technical Barriers To Trade
Technical barriers to trade (TBTs), a category of nontariff barriers to trade, are the widely divergent measures that countries use to regulate markets, protect their consumers, or preserve their natural resources (among other objectives), but they also can be used (or perceived by foreign countries as being used) to discriminate against imports in order to protect domestic industries. The 2012 classification of non-tariff measures (NTMs) developed by the Multi-Agency Support Team (MAST), a working group of eight international organisations, classifies TBTs as one of 16 non-tariff measures (NTMs) chapters. In this classification, TBTs are classified as chapter B and defined as "Measures referring to technical regulations, and procedures for assessment of conformity with technical regulations and standards, excluding measures covered by the WTO's SPS Agreement". Here, technical barriers to trade refer to measures such as labelling requirements, standards on technical specifications ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agreement On The Application Of Sanitary And Phytosanitary Measures
The Agreement on the Application of Sanitary and Phytosanitary Measures, also known as the SPS Agreement or just SPS, is an international treaty of the World Trade Organization (WTO). It was negotiated during the Uruguay Round of the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT), and entered into force with the establishment of the WTO at the beginning of 1995. Broadly, the sanitary and phytosanitary ("SPS") measures covered by the agreement are those aimed at the protection of human, animal or plant life or health from certain risks. Under the SPS agreement, the WTO sets constraints on member-states' policies relating to food safety (bacterial contaminants, pesticides, food inspection, inspection and food labelling, labelling) as well as animal health, animal and plant health (phytosanitation) with respect to imported pests and diseases. There are 3 standards organizations who set standards that WTO members should base their SPS methodologies on. As provided for in Article 3, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agreement On Technical Barriers To Trade
The Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade, commonly referred to as the TBT Agreement, is an international treaty administered by the World Trade Organization. It was last renegotiated during the Uruguay Round of the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade, with its present form entering into force with the establishment of the WTO at the beginning of 1995, binding on all WTO members. Purpose The TBT exists to ensure that technical regulations, standards, testing, and certification procedures do not create unnecessary obstacles to trade. The agreement prohibits technical requirements created in order to limit trade, as opposed to technical requirements created for legitimate purposes such as consumer or environmental protection. In fact, its purpose is to avoid unnecessary obstacles to international trade and to give recognition to all WTO members to protect legitimate interests according to own regulatory autonomy, although promoting the use of international standards. The l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OECD
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD; , OCDE) is an international organization, intergovernmental organization with 38 member countries, founded in 1961 to stimulate economic progress and international trade, world trade. It is a forum (legal), forum whose member countries describe themselves as committed to democracy and the market economy, providing a platform to compare policy experiences, seek answers to common problems, identify good practices, and coordinate domestic and international policies of its members. The majority of OECD members are generally regarded as developed country, developed countries, with High-income economy, high-income economies, and a very high Human Development Index. their collective population is 1.38 billion people with an average life expectancy of 80 years and a median age of 40, against a global average of 30. , OECD Member countries collectively comprised 62.2% of list of countries by GDP (nominal), global nom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
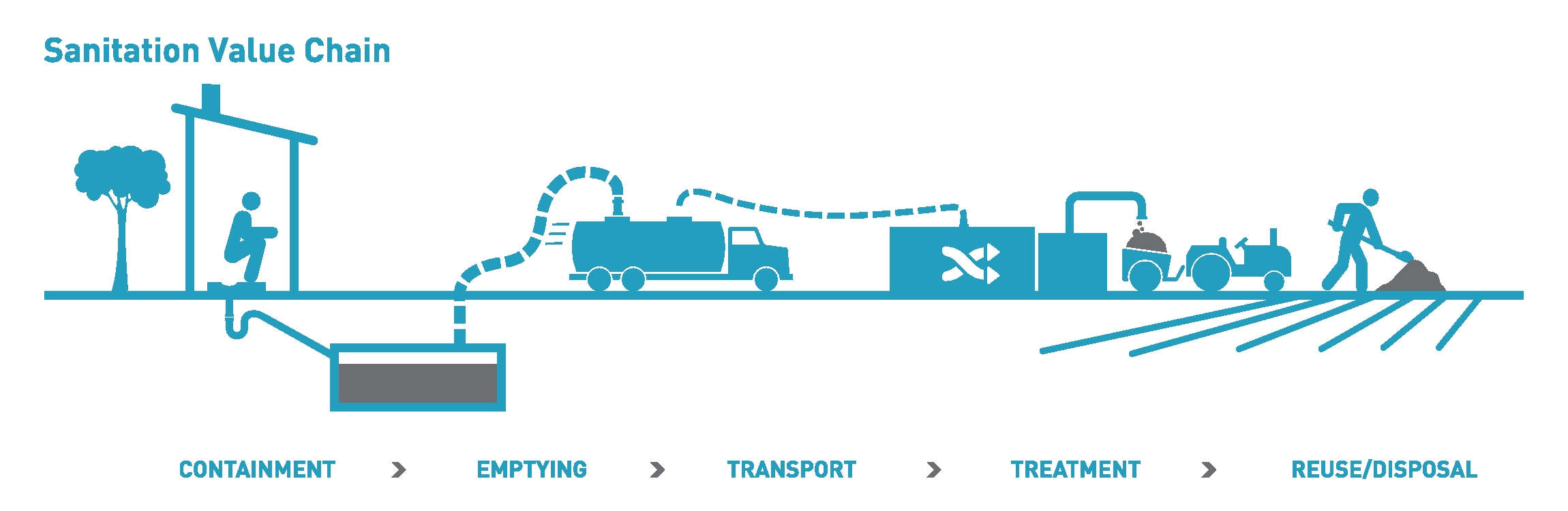
Sanitary And Phytosanitary Measures And Agreements
Sanitation refers to public health conditions related to clean drinking water and treatment and disposal of Human waste, human excreta and sewage. Risk management, Preventing human contact with feces is part of sanitation, as is hand washing with soap. Sanitation systems aim to protect human health by providing a clean environment that will stop the Transmission (medicine), transmission of disease, especially through the fecal–oral route.SuSanA (2008)Towards more sustainable sanitation solutions . Sustainable Sanitation Alliance (SuSanA) For example, diarrhea, a main cause of Undernutrition in children, malnutrition and stunted growth in children, can be reduced through adequate sanitation. There are many other diseases which are easily transmitted in communities that have low levels of sanitation, such as ascariasis (a type of intestinal worm infection or helminthiasis), cholera, hepatitis, polio, schistosomiasis, and trachoma, to name just a few. A range of sanitation techno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-tariff Barriers To Trade
Non-tariff barriers to trade (NTBs; also called non-tariff measures, NTMs) are trade barriers that restrict imports or exports of goods or services through measures other than the imposition of tariffs. Such barriers are subject to controversy and debate, as they may comply with international rules on trade yet serve protectionist purposes. Sometimes, uniformly applied rules of trade may be more burdensome to some countries than others, e.g. for countries with developing economies. The Southern African Development Community (SADC) defines a non-tariff barrier as "''any obstacle to international trade that is not an import or export duty. They may take the form of import quotas, subsidies, customs delays, technical barriers, or other systems preventing or impeding trade''". According to the World Trade Organization, non-tariff barriers to trade include import licensing, rules for valuation of goods at customs, pre-shipment inspections, rules of origin ('made in'), and trade prepa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |