|
Tashkent State Technical University
Tashkent State Technical University (TSTU) ( Uzbek: ''Toshkent Davlat Texnika Universiteti'') is one of the oldest universities of Uzbekistan. Currently, the university consists of 6 faculties, and prepares highly skilled professionals in technical and engineering fields. For this year, it is estimated to run 56 departments with over 10 746 students, who are taught by 6 academicians of the Academy of Sciences of Uzbekistan, 74 doctors of sciences and 314 candidates of sciences. History The history of "Tashkent State Technical University," named after Abu Rayhan Beruni ('’’TSTU'’’), goes back to the Soviet Union times. TSTU is currently one of the oldest educational places in Uzbekistan. Its first establishment date refers to the April 21, 1918. Firstly, the university was established as the small technical faculty of "Turkistan National University", and it worked for the whole Central Asia. That technical faculty saw many changes in its history, but it is the base of cur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tashkent
Tashkent (, uz, Toshkent, Тошкент/, ) (from russian: Ташкент), or Toshkent (; ), also historically known as Chach is the capital and largest city of Uzbekistan. It is the most populous city in Central Asia, with a population of 2,909,500 (2022). It is in northeastern Uzbekistan, near the border with Kazakhstan. Tashkent comes from the Turkic ''tash'' and ''kent'', literally translated as "Stone City" or "City of Stones". Before Islamic influence started in the mid-8th century AD, Tashkent was influenced by the Sogdian and Turkic cultures. After Genghis Khan destroyed it in 1219, it was rebuilt and profited from the Silk Road. From the 18th to the 19th century, the city became an independent city-state, before being re-conquered by the Khanate of Kokand. In 1865, Tashkent fell to the Russian Empire; it became the capital of Russian Turkestan. In Soviet times, it witnessed major growth and demographic changes due to forced deportations from throughout the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Namangan Engineering-Economic Institute
Namangan (; ) is a city in eastern Uzbekistan. It is the administrative, economic, and cultural center of Namangan Region. Administratively, it is a district-level city. Namangan is located in the northern edge of the Fergana Valley, less than 30 km from the Kyrgyzstan border. The city is served by Namangan Airport. Namangan has been an important craft and trade center in the Fergana Valley since the 17th century. Many factories were built in the city during Soviet times. During World War II, industrial production in Namangan increased fivefold compared with that of 1926–1927. Currently, Namangan is mainly a center for light industry, especially in food. The officially registered population of the city was 475,700 in 2014. Uzbeks are the largest ethnic group. History The city takes its name from the local salt mines (in Persian نمککان (''namak kan'') — "a salt mine"). Babur mentioned the village of Namangan in his memoirs ''Baburnama''. In his book ''A brief H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
News Of TSTU
News is information about current events. This may be provided through many different media: word of mouth, printing, postal systems, broadcasting, electronic communication, or through the testimony of observers and witnesses to events. News is sometimes called "hard news" to differentiate it from soft media. Common topics for news reports include war, government, politics, education, health, the environment, economy, business, fashion, entertainment, and sport, as well as quirky or unusual events. Government proclamations, concerning royal ceremonies, laws, taxes, public health, and criminals, have been dubbed news since ancient times. Technological and social developments, often driven by government communication and espionage networks, have increased the speed with which news can spread, as well as influenced its content. Throughout history, people have transported new information through oral means. Having developed in China over centuries, newspapers became establ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Technical Science And Innovation
Technical may refer to: * Technical (vehicle), an improvised fighting vehicle * Technical analysis, a discipline for forecasting the future direction of prices through the study of past market data * Technical drawing, showing how something is constructed or functions (also known as drafting) * Technical file, set of technical drawings * Technical death metal, a subgenre of death metal that focuses on complex rhythms, riffs, and song structures * Technical foul, an infraction of the rules in basketball usually concerning unsportsmanlike non-contact behavior * Technical rehearsal for a performance, often simply referred to as a technical * Technical support, a range of services providing assistance with technology products * Vocational education, often known as technical education * Legal technicality, an aspect of law See also * Lego Technic, a line of Lego toys * Tech (other) * Technicals (other) * Technics (other) * Technique (other) * Te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chirchik Technology College
Chirchiq, also spelled as Chirchik, ( uz, Chirchiq / Чирчиқ; russian: Чирчик) is a district-level city in Tashkent Region, Uzbekistan. It is about 32 km northeast of Tashkent, along the river Chirchiq. Chirchiq lies in the Chatkal Mountains. The population of Chirchiq as of 2021 is approximately 162,800. It is located at latitude 41° 28' 8N; longitude 69° 34' 56E, 582 meters above sea level. History The city was founded in 1935,''Chirchiq'' article on Encyclopædia Britannica,sewww.britannica.com/ref> when several local villages grew together as a consequence of the construction of a hydroelectric power station on the Chirchiq River. Economy Chirchiq is in the middle of an intensively cultivated area, producing mainly vegetables and fruits, including melons and grapes. A large electrochemical works produces fertilizer for the region's collective farms. Chirchiq's industries also include the production of ferroalloys and machinery for the agricultural ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Almalyk Technical College
Almalyk, ''Almalıq'', Almalik, or Almaliq is a Turkic adjective form of "apple". It may refer to: * Olmaliq, formerly "Almalyk", city in Tashkent Province, Uzbekistan * Almaliq, Xinjiang Almaliq ( ug, ئالمالىق; zh, t=, p=Ālìmálǐ),Previously transcribed into Chinese as , ''Ā'ěrmǎlì''; , ''Ālǐmǎchéng''; , ''Ālǐmá'' and , ''Ālìmǎlì''. also spelled Armalec, Almalik, Almalig, Almaligh and Almarikh, was a ..., a medieval city in the northwest of Xinjiang, China * Almalıq, a village in Kalbajar Rayon, Azerbaijan {{geodis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angren Technical College
Angren may refer to: * Angren, Uzbekistan, town near Tashkent, Uzbekistan * Angren River, river in Tashkent Province of Uzbekistan * River Isen In J. R. R. Tolkien's fantasy writings, Isengard () is a large fortress in Nan Curunír, the Wizard's Vale, in the western part of Middle-earth. In the fantasy world, the name of the fortress is described as a translation of Angrenost, a word ..., a fictional river in Middle-earth, also called Angren * Ngamring County, pinyin Angren, county in Tibet {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nukus Industrial-Pedagogical Institute
Nukus ( kaa, Nókis / ; uz, Nukus / ; kk, Нүкіс / ) is the sixth-largest city in Uzbekistan and the capital of the autonomous Republic of Karakalpakstan. The population of Nukus as of January 1, 2022 was 329,100. The Amu Darya river passes west of the town. Administratively, Nukus is a district-level city, that includes the urban-type settlement Karatau. The city is best known for its world-class Nukus Museum of Art. History The name Nukus comes from the old tribal name of the Karakalpaks, Nukus. Nukus developed from a small settlement in 1932 into a large, modern Soviet city with broad avenues and big public buildings by the 1950s. The city's isolation made it host to the Red Army's Chemical Research Institute, a major research and testing center for chemical weapons. In 2002 the United States Department of Defense dismantled the Chemical Research Institute, the major research and testing site for the Novichok agent, under a $6 million Cooperative Threat Reduction prog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tashkent State Institute Of Aviation
Tashkent (, uz, Toshkent, Тошкент/, ) (from russian: Ташкент), or Toshkent (; ), also historically known as Chach is the capital and largest city of Uzbekistan. It is the most populous city in Central Asia, with a population of 2,909,500 (2022). It is in northeastern Uzbekistan, near the border with Kazakhstan. Tashkent comes from the Turkic ''tash'' and ''kent'', literally translated as "Stone City" or "City of Stones". Before Islamic influence started in the mid-8th century AD, Tashkent was influenced by the Sogdian and Turkic cultures. After Genghis Khan destroyed it in 1219, it was rebuilt and profited from the Silk Road. From the 18th to the 19th century, the city became an independent city-state, before being re-conquered by the Khanate of Kokand. In 1865, Tashkent fell to the Russian Empire; it became the capital of Russian Turkestan. In Soviet times, it witnessed major growth and demographic changes due to forced deportations from throughout the Sov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
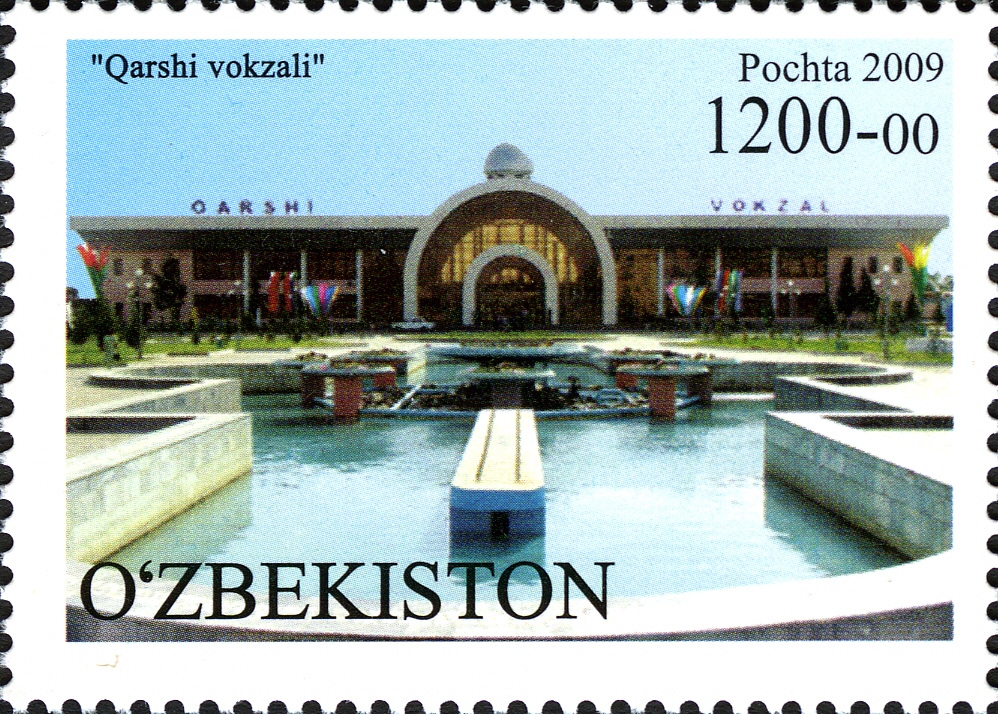
Karshi Engineering-economic Institute
Qarshi ( uz, Qarshi/Қарши, ; fa, نخشب ''Nakhshab'') is a city in southern Uzbekistan. It is the capital of Qashqadaryo Region. Administratively, Qarshi is a district-level city, that includes the urban-type settlement Qashqadaryo. It has a population of 278,300 (2021 estimate). It is about 520 km south-southwest of Tashkent, and about 335 km north of Uzbekistan's border with Afghanistan. It is located at latitude 38° 51' 48N; longitude 65° 47' 52E at an altitude of 374 meters. The city is important in natural gas production, but Qarshi is also famous for its production of woven flat carpets. History Originally the Sogdian city of Nakhshab (which could be possibly named Eucratideia during the rule of Greco-Bactrian Kingdom), and the Islamic Uzbek (Turkic) city of Nasaf, and the Mongol city of Qarshi (pronounced ''Kharsh''), Qarshi was the second city of the Emirate of Bukhara. It is in the center of a fertile oasis that produces wheat, cotton, and silk an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tashkent Architecture And Construction Institute
Tashkent (, uz, Toshkent, Тошкент/, ) (from russian: Ташкент), or Toshkent (; ), also historically known as Chach is the capital and largest city of Uzbekistan. It is the most populous city in Central Asia, with a population of 2,909,500 (2022). It is in northeastern Uzbekistan, near the border with Kazakhstan. Tashkent comes from the Turkic ''tash'' and ''kent'', literally translated as "Stone City" or "City of Stones". Before Islamic influence started in the mid-8th century AD, Tashkent was influenced by the Sogdian and Turkic cultures. After Genghis Khan destroyed it in 1219, it was rebuilt and profited from the Silk Road. From the 18th to the 19th century, the city became an independent city-state, before being re-conquered by the Khanate of Kokand. In 1865, Tashkent fell to the Russian Empire; it became the capital of Russian Turkestan. In Soviet times, it witnessed major growth and demographic changes due to forced deportations from throughout the Sov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)