|
Tarkhun
Tarkhun ( Chinese: 突昏 ''tū-hūn'', died 710) was a Sogdian ruler ( Sogdian: '' əxšēδ'') of Samarkand from somewhere 705–707 to 710. After receiving the news of the capture of Bukhara by the Umayyad general Qutayba ibn Muslim in 709, Tarkhun sent envoys to the latter and acknowledged the authority of the Umayyad Caliphate. His two sons had to be kept at the Umayyad court as hostages. However, one year later, Tarkhun was overthrown by a local rebellion because of his pro-Muslim policy, and was succeeded by another Sogdian prince named Gurak, who had Tarkhun imprisoned. Tarkhun shortly after committed suicide. His two sons, however, managed to flee to the court of another Sogdian ruler named Divashtich at Panjikant, where they were treated honorably. The accession of Tarkhun is reported in the Chinese chronicles of the '' Tang Huiyao'': "During the years of Shenlong (705-707), Ninieshishi astich-Unash (698-700)died. And his son Tarkhun was put on the throne".'' Tang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Divashtich
Divashtich (also spelled Devashtich, Dewashtich, and Divasti), was a medieval Sogdian ruler in Transoxiana during the period of the Muslim conquest of Transoxiana. He was the ruler of Panjikant and its surroundings from ca. 706 until his downfall and execution in the autumn of 722. Origin Divashtich was the son of a certain Yodkhsetak, who belonged to a noble Sogdian dehqan family from Samarkand, which could trace its descent back to the Sasanian king Bahram V Gur (r. 420–438). The family bore the title of ''sur'' and began ruling parts of Sogdia during the 6th century. There were five members of the family bearing the title of ''sur'', Divashtich being the last of them. Dispute with Samarkand and the Arabs In ca. 706, Divashtich was elected as king of Panjikant, succeeding the Turkic prince Chukin Chur Bilga as the ruler of city. However, Divashtich did not hold absolute power, and shared his power with other princes. Although Divashtich only ruled Panjikant, he claimed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qutayba Ibn Muslim
Abū Ḥafṣ Qutayba ibn Abī Ṣāliḥ Muslim ibn ʿAmr al-Bāhilī (; 669–715/6) was an Arab commander of the Umayyad Caliphate who became governor of Khurasan and distinguished himself in the conquest of Transoxiana during the reign of al-Walid I (705–715). A capable soldier and administrator, he consolidated Muslim rule in the area and expanded the Caliphate's border to include most of Transoxiana. From 705 to , he consolidated Muslim control over the native principalities of Tokharistan and conquered the principality of Bukhara, while in 710–712 he conquered Khwarizm and completed the conquest of Sogdiana with the capture of Samarkand. The latter opened the road to the Jaxartes valley, and during the last years of his life Qutayba led annual campaigns there, extending Muslim control up to the Fergana Valley and parts of Chinese Turkestan. To increase his strained manpower, Qutayba initiated the wide-scale levy of native Khurasani and Transoxianian sol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
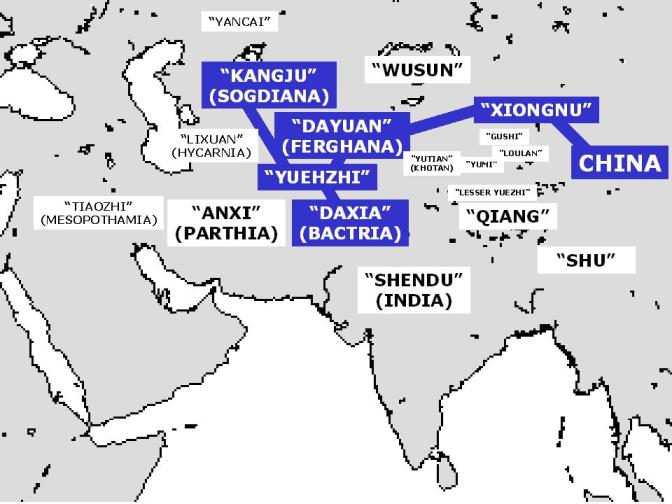
Sogdia
Sogdia () or Sogdiana was an ancient Iranian peoples, Iranian civilization between the Amu Darya and the Syr Darya, and in present-day Uzbekistan, Turkmenistan, Tajikistan, Kazakhstan, and Kyrgyzstan. Sogdiana was also a province of the Achaemenid Empire, and listed on the Behistun Inscription of Darius the Great. Sogdiana was first conquered by Cyrus the Great, the founder of the Achaemenid Empire, and then was annexed by the Macedonian ruler Alexander the Great in 328 BC. It would continue to change hands under the Seleucid Empire, the Greco-Bactrian Kingdom, the Kushan Empire, the Sasanian Empire, the Hephthalite Empire, the Western Turkic Khaganate, and the Muslim conquest of Transoxiana. The Sogdian city-states, although never politically united, were centered on the city of Samarkand. Sogdian language, Sogdian, an Eastern Iranian language, is no longer spoken. However, a descendant of one of its dialects, Yaghnobi language, Yaghnobi, is still spoken by the Yaghnobis of Taji ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gurak
Gurak or Ghurak () was a medieval Sogdian ruler in Central Asia during the period of the Muslim conquest of Transoxiana. In 710, he was installed as king ( Sogdian: ''ikhshid'') of Samarkand after the populace overthrew his predecessor, Tarkhun, due to his pro-Muslim stance. The Umayyad governor, Qutayba ibn Muslim, campaigned against Samarkand but in the end confirmed Gurak as its ruler. Gurak was a cautious and intelligent ruler, and managed, through shifting alliance between the Muslims and the Turgesh, to remain on his throne. Some time after the Muslim Pyrrhic victory Battle of the Defile The Battle of the Defile or Battle of the Pass () was fought in the Takhtakaracha Pass (in modern Uzbekistan) between a large army of the Umayyad Caliphate and the Turkic Türgesh khaganate over three days in July 731 CE. The Türgesh had bee ... in 731, he managed to recover his capital, Samarkand, and achieve a quasi-independence which he maintained until his death in 737 or 738. His ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ikhshid
( Persian: اخشید; from , ) was the princely title of the Iranian rulers of Soghdia and the Ferghana Valley in Transoxiana during the pre-Islamic and early Islamic periods. The title is of Iranian origin; scholars have derived it variously from the Old Iranian root , , or from , 'ruler, king' (which is also the origin of the title 'shah'). The Ikhshids of Sogdia, with their capital at Samarkand, are well attested during and after the Muslim conquest of Transoxiana. The line survived into Abbasid times, although by then its seat was in Istikhan. Among the most notable and energetic of the Soghdian kings was Gurak, who in 710 overthrew his predecessor Tarkhun and for almost thirty years, through shifting alliances, managed to preserve a precarious autonomy between the expanding Umayyad Caliphate and the Türgesh khaganate. Also, The ruler of Kāš (Kashgar) in the late 8th century, according to the Middle Persian Manichean text Mahrnāmag (Müller, lines 75-76), was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ikhshids
(Persian: اخشید; from , ) was the princely title of the Iranian rulers of Soghdia and the Ferghana Valley in Transoxiana during the pre-Islamic and early Islamic periods. The title is of Iranian origin; scholars have derived it variously from the Old Iranian root , , or from , 'ruler, king' (which is also the origin of the title 'shah'). The Ikhshids of Sogdia, with their capital at Samarkand, are well attested during and after the Muslim conquest of Transoxiana. The line survived into Abbasid times, although by then its seat was in Istikhan. Among the most notable and energetic of the Soghdian kings was Gurak, who in 710 overthrew his predecessor Tarkhun and for almost thirty years, through shifting alliances, managed to preserve a precarious autonomy between the expanding Umayyad Caliphate and the Türgesh khaganate. Also, The ruler of Kāš (Kashgar) in the late 8th century, according to the Middle Persian Manichean text Mahrnāmag (Müller, lines 75-76), was call ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samarkand
Samarkand ( ; Uzbek language, Uzbek and Tajik language, Tajik: Самарқанд / Samarqand, ) is a city in southeastern Uzbekistan and among the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest continuously inhabited cities in Central Asia. Samarkand is the capital of the Samarkand Region and a district-level city, that includes the urban-type settlements Kimyogarlar, Farxod, Farhod and Xishrav, Khishrav. With 551,700 inhabitants (2021), it is the List of cities in Uzbekistan, third-largest city in Uzbekistan. There is evidence of human activity in the area of the city dating from the late Paleolithic Era. Though there is no direct evidence of when Samarkand was founded, several theories propose that it was founded between the 8th and 7th centuries BC. Prospering from its location on the Silk Road between East Asia, China, Persia and Europe, at times Samarkand was one of the largest cities in Central Asia,Guidebook of history of Samarkand", and was an important city of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kangju
Kangju (; Eastern Han Chinese: ''kʰɑŋ-kɨɑ'' standard Chinese ''Kāngjū''), proposes that it was an Iranian word meaning "stone", and compares it to Pashto ''kā́ṇay'' "stone". Joseph Marquart, Omeljan Pritsak and Peter B. Golden have noted phonetic similarities between Kangju and Kengeres mentioned in the Orkhon inscriptions, the Kangarâyê in Transcaucasia, the city of Kengü Tarban, and the three Pecheneg tribes collectively known as Kangar mentioned by Constantine VII Porphyrogenitus. Nevertheless, all those connections remain hypothetical. Archaeological evidence suggests that the Kangju spoke an Eastern Iranian language, which was probably identical to Sogdian, or derived from it. History According to 2nd century BCE Chinese sources, Kangju lay north of the Dayuan and west of the Wusun, bordering the Yuezhi in the south. Their territory covered the region of the Ferghana Valley and the area between the Amu Darya and Syr Darya rivers, with the co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Year Of Birth Unknown
A year is a unit of time based on how long it takes the Earth to orbit the Sun. In scientific use, the tropical year (approximately 365 solar days, 5 hours, 48 minutes, 45 seconds) and the sidereal year (about 20 minutes longer) are more exact. The modern calendar year, as reckoned according to the Gregorian calendar, approximates the tropical year by using a system of leap years. The term 'year' is also used to indicate other periods of roughly similar duration, such as the lunar year (a roughly 354-day cycle of twelve of the Moon's phasessee lunar calendar), as well as periods loosely associated with the calendar or astronomical year, such as the seasonal year, the fiscal year, the academic year, etc. Due to the Earth's axial tilt, the course of a year sees the passing of the seasons, marked by changes in weather, the hours of daylight, and, consequently, vegetation and soil fertility. In temperate and subpolar regions around the planet, four seasons ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sogdian Monarchs
Sogdian may refer to: * anything pertaining to Sogdia / Sogdiana * Sogdian language * Sogdian alphabet * Sogdian people * Sogdian (Unicode block) See also * Old Sogdian (Unicode block), a separate Unicode block * Sogdian Rock The Sogdian Rock or Rock of Ariamazes, a fortress located north of Bactria in Sogdiana (near Samarkand), ruled by Arimazes, was captured by the forces of Alexander the Great in the early spring of 327 BC as part of his conquest of the Achaeme ..., a fortress in Sogdia {{Disambiguation Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
710 Deaths
__NOTOC__ Year 710 (Roman numerals, DCCX) was a common year starting on Wednesday of the Julian calendar. The denomination 710 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Byzantine Empire * The Byzantine outpost of Chersonesus (Crimea), Cherson (Crimea) rebels (with Khazars, Khazar assistance) against Emperor Justinian II. He sends a fleet under the ''Patrician (ancient Rome)#Late Roman and Byzantine period, patrikios'' Stephen, which retakes the city and restores Byzantine control. The fleet, however, is struck by a storm on its way back and loses many ships, while the Chersonites, again with the aid of the Khazars, rebel anew. * The Byzantine general Leo III the Isaurian, Leo (future emperor Leo III) recovers the Kingdom of Abkhazia, Abkhazia (Caucasus) for the Byzantine Empire, from the Arabs. Europe * Roderick becomes king of the Visigoths, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |