|
Tanus (river)
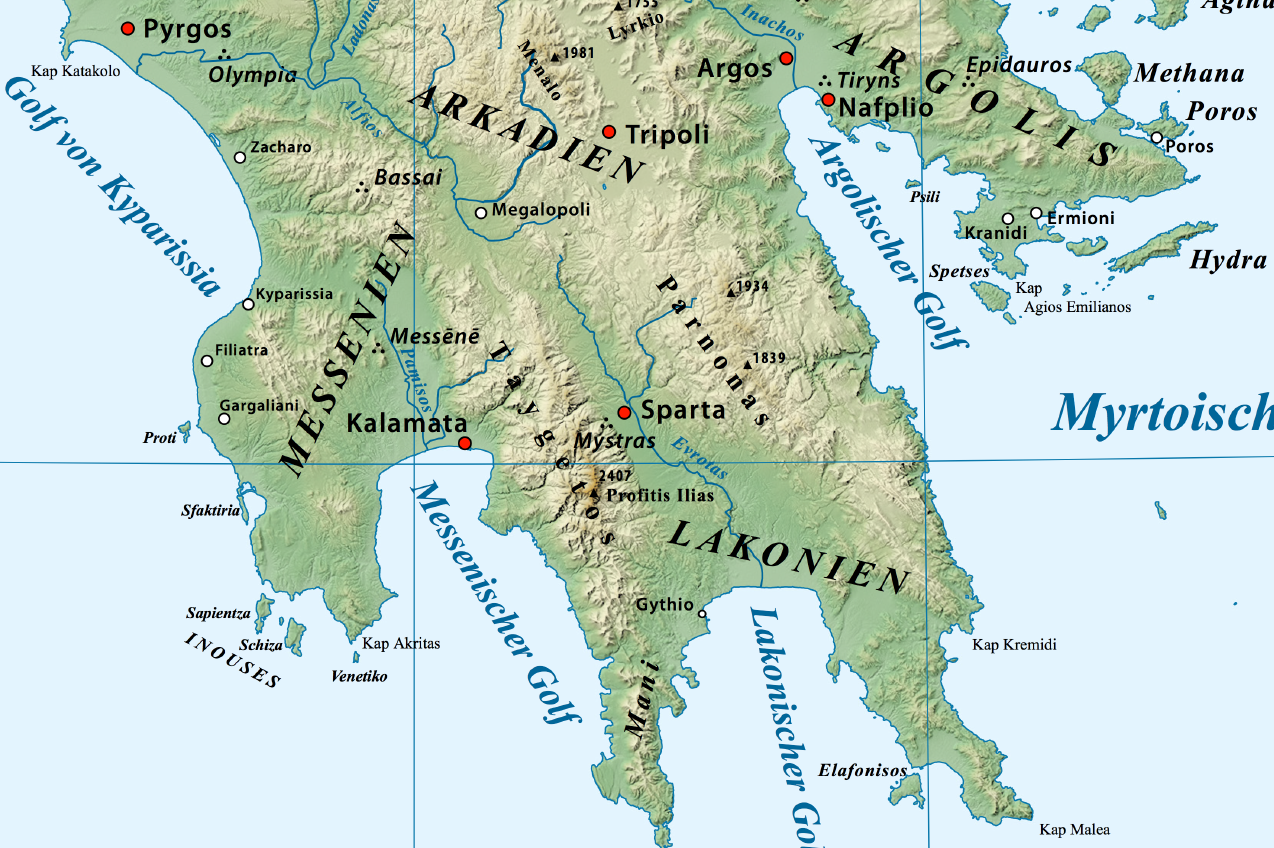
The Tanos or Tanus (Τάνος), also called the Tanaus or Tanaos (Τάναος)Euripides, ''Electr.'' 413. is a river of the Peloponnese, Greece. In antiquity it was the northern border of the Thyreatis, or territory of the city of Thyrea, in the ancient region of Cynuria. It waters one of the most fertile plains in the Peloponnesus. The river rises in the summits of Mount Parnon, and falls into the sea, at present north of Astros, but earlier south of the latter place. It formed the boundary between the Argeia and ancient Laconia in the time of Euripides Euripides () was a Greek tragedy, tragedian of classical Athens. Along with Aeschylus and Sophocles, he is one of the three ancient Greek tragedians for whom any plays have survived in full. Some ancient scholars attributed ninety-five plays to ..., who accordingly represents it as the boundary between the two states in the heroic age. References Rivers of Greece Geography of Peloponnese (region) {{Greece-ri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Tanos In North Kynouria, Arcadia, Greece
A river is a natural stream of fresh water that flows on land or inside Subterranean river, caves towards another body of water at a lower elevation, such as an ocean, lake, or another river. A river may run dry before reaching the end of its course if it runs out of water, or only flow during certain seasons. Rivers are regulated by the water cycle, the processes by which water moves around the Earth. Water first enters rivers through precipitation, whether from rainfall, the Runoff (hydrology), runoff of water down a slope, the melting of glaciers or snow, or seepage from aquifers beneath the surface of the Earth. Rivers flow in channeled watercourses and merge in confluences to form drainage basins, or catchments, areas where surface water eventually flows to a common outlet. Rivers have a great effect on the landscape around them. They may regularly overflow their Bank (geography), banks and flood the surrounding area, spreading nutrients to the surrounding area. Sedime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
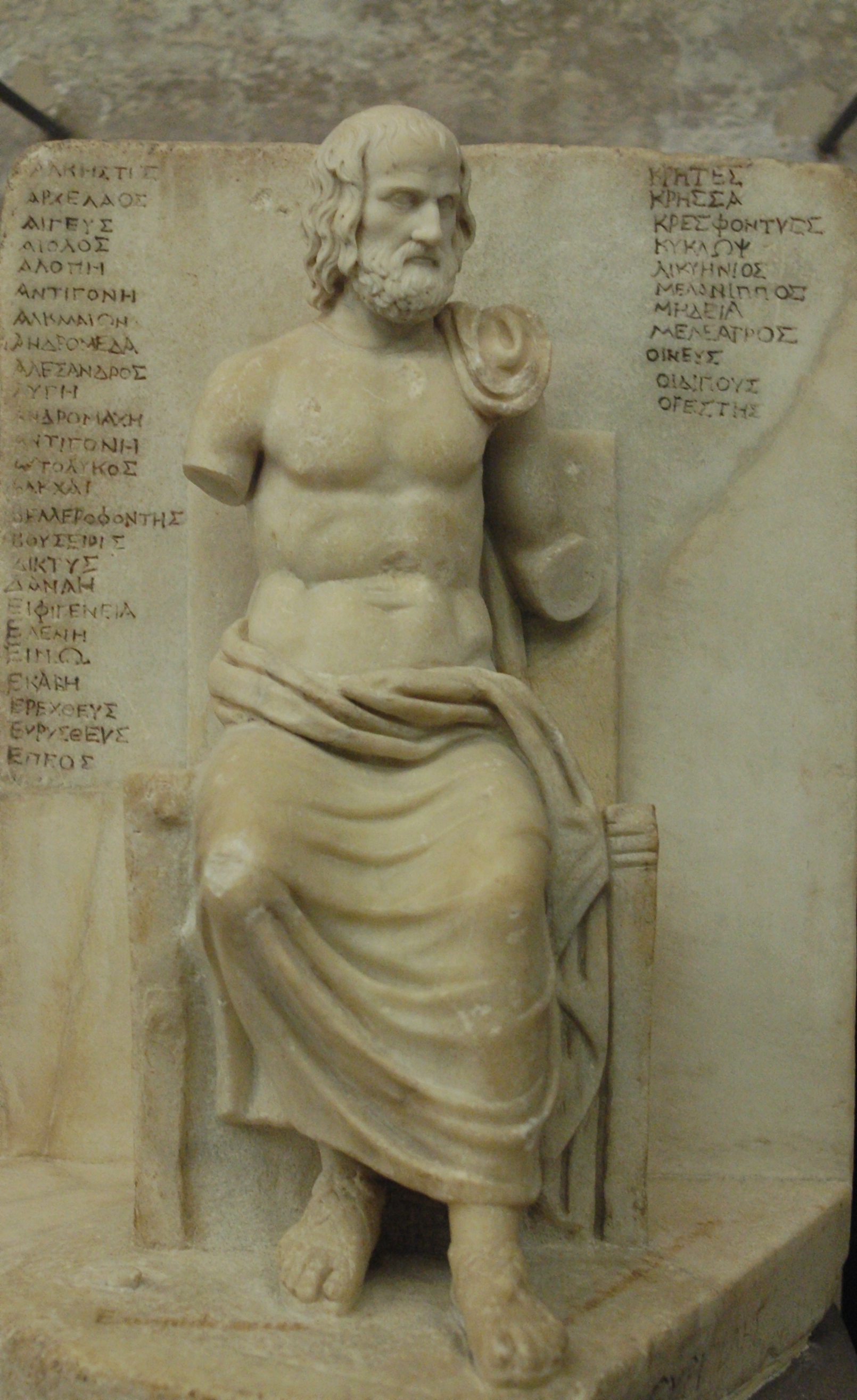
Euripides
Euripides () was a Greek tragedy, tragedian of classical Athens. Along with Aeschylus and Sophocles, he is one of the three ancient Greek tragedians for whom any plays have survived in full. Some ancient scholars attributed ninety-five plays to him, but the ''Suda'' says it was ninety-two at most. Of these, eighteen or nineteen have survived more or less complete (''Rhesus (play), Rhesus'' is suspect). There are many fragments (some substantial) of most of his other plays. More of his plays have survived intact than those of Aeschylus and Sophocles together, partly because his popularity grew as theirs declinedMoses Hadas, ''Ten Plays by Euripides'', Bantam Classic (2006), Introduction, p. ixhe became, in the Hellenistic Age, a cornerstone of ancient literary education, along with Homer, Demosthenes, and Menander.L.P.E.Parker, ''Euripides: Alcestis'', Oxford University Press (2007), Introduction p. lx Euripides is identified with theatrical innovations that have profoundly influ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
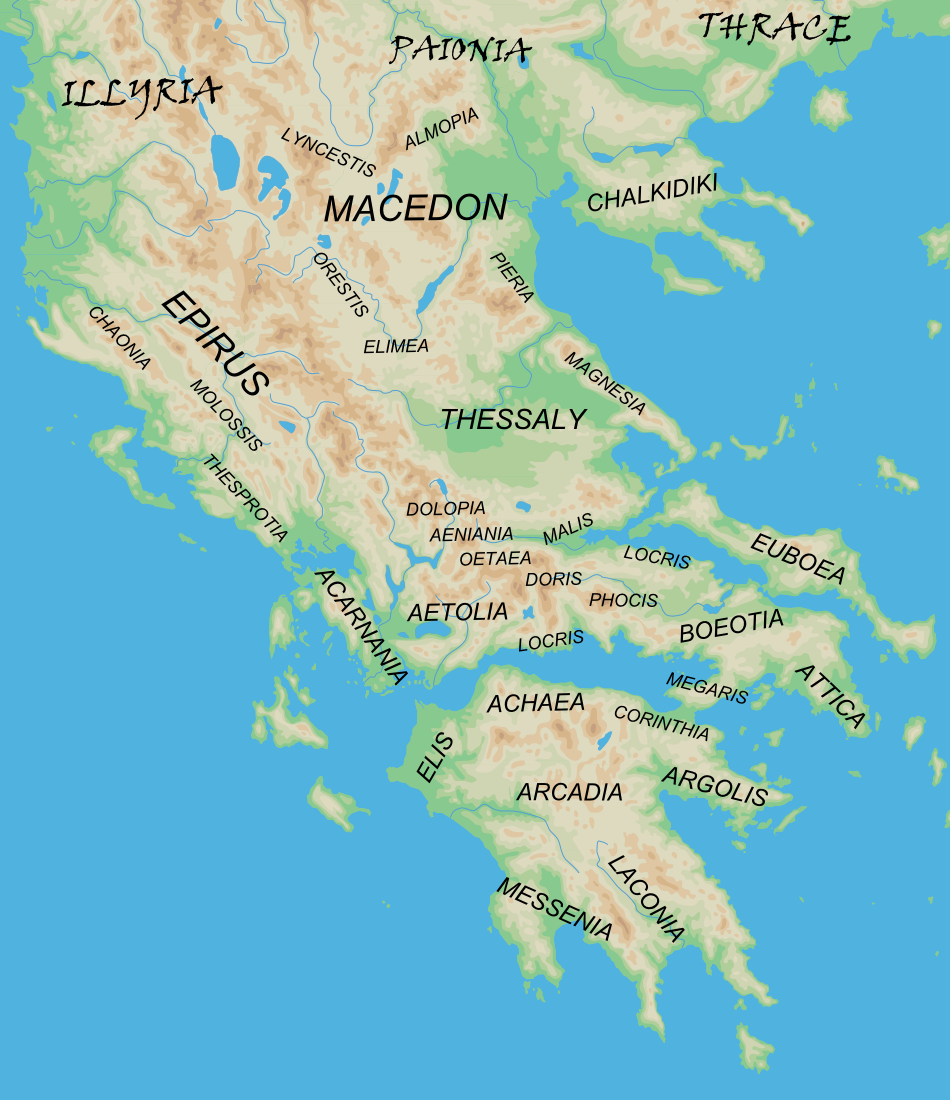
Peloponnese
The Peloponnese ( ), Peloponnesus ( ; , ) or Morea (; ) is a peninsula and geographic region in Southern Greece, and the southernmost region of the Balkans. It is connected to the central part of the country by the Isthmus of Corinth land bridge which separates the Gulf of Corinth from the Saronic Gulf. From the late Middle Ages until the 19th century, the peninsula was known as the Morea, a name still in colloquial use in its demotic form. The peninsula is divided among three administrative regions: most belongs to the Peloponnese region, with smaller parts belonging to the West Greece and Attica regions. Geography The Peloponnese is a peninsula located at the southern tip of the mainland, in area, and constitutes the southernmost part of mainland Greece. It is connected to the mainland by the Isthmus of Corinth, where the Corinth Canal was constructed in 1893. However, it is also connected to the mainland by several bridges across the canal, including two submers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greece
Greece, officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. Located on the southern tip of the Balkan peninsula, it shares land borders with Albania to the northwest, North Macedonia and Bulgaria to the north, and Turkey to the east. The Aegean Sea lies to the east of the Geography of Greece, mainland, the Ionian Sea to the west, and the Sea of Crete and the Mediterranean Sea to the south. Greece has the longest coastline on the Mediterranean Basin, spanning List of islands of Greece, thousands of islands and nine Geographic regions of Greece, traditional geographic regions. It has a population of over 10 million. Athens is the nation's capital and List of cities and towns in Greece, largest city, followed by Thessaloniki and Patras. Greece is considered the cradle of Western culture, Western civilisation and the birthplace of Athenian democracy, democracy, Western philosophy, Western literature, historiography, political science, major History of science in cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thyreatis
Thyrea (), also Thyraea, Thyreae or Thyreai (Θυρέαι), was a town of Cynuria, and was fought over between ancient Argolis and ancient Laconia. Its territory was called the Thyreatis (Θυρεᾶτις). According to Pausanias, Thyrea was named after a mythological figure: Thyraeos, the son of Lycaon. History Thyrea enters history as the location of the Battle of the Champions () between Argos and Sparta. According to Herodotus, Sparta had surrounded and captured the plain of Thyrea. When the Argives marched out to defend it, the two armies agreed to let 300 champions from each city fight, with the winner taking the territory. In 464 BCE when we hear of the Thyreans assisting the Spartans put down the helot uprising. When the Aeginetans were expelled from their own island by the Athenians, at the commencement of the Peloponnesian War (431 BCE), the Spartans allowed them to settle in the Thyreatis, which at that time contained two towns, Thyrea and Anthene or Ath ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cynuria
Cynuria ( – ''Kynouria'' or – ''Kynouriake'') is an ancient district on the eastern coast of the Peloponnese, between the Argolis and Laconia, so called from the Cynurians, one of the most ancient tribes in the peninsula. It was believed to have taken its name from the mythical Cynurus. Location and history Herodotus regarded the Cynurians as autochthones, but at the same time called them Ionians. There can be little doubt, however, that they were Pelasgians; but in consequence of their maritime position, they were regarded as a different race from the Arcadian Pelasgians, and came to be looked upon as Ionians, which was the case with the Pelasgians dwelling upon the coast of the Gulf of Corinth, in the district afterwards called Achaia. They were a semi-barbarous and predatory tribe, dwelling chiefly in the eastern slopes of Mount Parnon; but their exact boundaries cannot be defined, as they were only a tribe, and never formed a political body. At a later time they were a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Parnon
Parnon or Parnonas () or Malevos (Μαλεβός) is a mountain range, or massif, on the east of the Laconian plain and the Evrotas Valley. It is visible from Athens above the top of the Argive mountains. The western part is in the Laconia prefecture and the northeastern part is in the Arcadia prefecture. The Parnon range separates Laconia from Arcadia. Its summit offers panoramic views of southeastern Arcadia and South Kynouria and much of Laconia that includes the northern and the central portions and reaches as far as the Taygetos mountains. It also views a part of the central Arcadia and the southern Argolis prefectures. It views the Myrtoan and the Laconian Gulfs. Geography Physical The Parnon Massif is divided into three parts.Unless otherwise cited this section relies heavily on The northernmost, which is the highest, runs from just north of Ano Doliana in North Kynouria, eastern Arcadia, southeast to Platanaki Pass. Platanaki, ancient Glyppia, is on the anc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astros, Greece
Astros (Greek language, Greek: Άστρος ) is a town near the Argolic Gulf in the northeast Peloponnese in eastern Arcadia (regional unit), Arcadia. It is the seat of North Kynouria municipality (Greek: Βόρεια Κυνουρία) and is accessible by the road connecting Corinth and Argos, Greece, Argos to the south. Its port, Paralio Astros lies 4 km to the northeast of the inland town. History The name of the town, built during the Greek War of Independence, is supposed to be taken from the ancient settlement ''Astron'', mentioned in Geography (Ptolemy), Ptolemy's ''Geography''.William Smith (lexicographer), William Smith, ''Dictionary of Greek and Roman Geography'', p 727 Astros was the site of the Second National Assembly at Astros, Second National Assembly of the Hellenes during the Greek War of Independence, under the presidency of Petros Mavromichalis. This assembly produced the first constitution of Modern Greece. The town The town has an elementary school, a h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argeia (region)
The regions of ancient Greece were sub-divisions of the Hellenic world as conceived by the ancient Greeks, shown by their presence in the works of ancient historians and geographers or in surviving legends and myths. Conceptually, there is no clear theme to the structure of these regions. Some, particularly in the Peloponnese, can be seen primarily as distinct geo-physical units, defined by physical boundaries such as mountain ranges and rivers. Conversely, the division of central Greece between Boeotia, Phocis, Doris and the three parts of Locris, seems to be attributable to ancient tribal divisions and not major geographical features. Both types of regions retained their identity throughout the Greek Dark Ages and its tumultuous changes in the local population and culture, giving them a less political and more symbolic presence. Other geographical divisions not identified with the aforementioned areas did, however, change over time, suggesting a closer connection with tribal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Laconia
Laconia or Lakonia (, , ) is a historical and Administrative regions of Greece, administrative region of Greece located on the southeastern part of the Peloponnese peninsula. Its administrative capital is Sparti (municipality), Sparta. The word ''Laconic phrase, laconic''—to speak in a blunt, concise way—is derived from the name of this region, a reference to the ancient Spartans who were renowned for their verbal austerity and blunt, often pithy remarks. Geography Laconia is bordered by Messenia to the west and Arcadia (regional unit), Arcadia to the north and is surrounded by the Myrtoan Sea to the east and by the Laconian Gulf and the Mediterranean Sea to the south. It encompasses Cape Malea and Cape Tainaron and a large part of the Mani Peninsula. The Mani Peninsula is in the west region of Laconia. The islands of Kythira and Antikythera lie to the south, but they administratively belong to the Attica (region), Attica regional unit of Islands (regional unit), islands. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rivers Of Greece
This is a list of rivers that are at least partially in Greece. The rivers flowing into the sea are sorted along the coast. Rivers flowing into other rivers are listed by the rivers they flow into. The confluence is given in parentheses. For an alphabetical overview of rivers of Greece see :Rivers of Greece. Tributaries Adriatic Sea * Aoos/Vjosë (near Novoselë, Albania) ** Drino (in Tepelenë, Albania) ** Sarantaporos (near Çarshovë, Albania) ** Voidomatis (near Konitsa) Ionian Sea Rivers in this section are sorted north (Albanian border) to south (Cape Malea). Epirus & Central Greece * Pavla/Pavllë (near Vrinë, Albania) * Thyamis (near Igoumenitsa) ** Tyria (near Vrosina) *Acheron (near Parga) * Louros (near Preveza) * Arachthos (in Kommeno) * Acheloos (near Astakos) ** Megdovas (near Fragkista) ** Agrafiotis (near Fragkista) ** Granitsiotis (near Granitsa) * Evinos (near Missolonghi) * Mornos (near Nafpaktos) * Pleistos, near Kirra Peloponnese * E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |