|
Tanger
Tangier ( ; , , ) is a city in northwestern Morocco, on the coasts of the Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean. The city is the capital of the Tanger-Tetouan-Al Hoceima region, as well as the Tangier-Assilah Prefecture of Morocco. Many civilisations and cultures have influenced the history of Tangier, starting from before the 10th centuryBCE. Starting as a strategic Phoenician town and trading centre, Tangier has been a nexus for many cultures. In 1923, it became an international zone managed by colonial powers and became a destination for many European and American diplomats, spies, bohemians, writers and businessmen. That status came to an end with Moroccan independence, in phases between 1956 and 1960. By the early 21st century, Tangier was undergoing rapid development and modernisation. Projects include tourism projects along the bay, a modern business district called Tangier City Centre, an airport terminal, and a football stadium. Tangier's economy is set to benefit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tanger-Med
Tanger Med (in Arabic: طنجة المتوسط ) is a Moroccan industrial port complex, located 45 km northeast of Tangier and opposite Tarifa, Spain (15 km north) on the Strait of Gibraltar, with handling capacities of 9 million containers, one of the largest industrial ports in the world, and the largest port in Africa and the Mediterranean Sea. 7 million passengers, 700,000 trucks and the export of 1 million vehicles. Tanger Med also consists of an industrial platform for 1100 companies, representing an annual export business of €8Bn in 2020. operating in various sectors such as automotive, aeronautics, food processing, logistics and textiles. Overview The Tanger Med Project is the largest port in Africa. The project is a strategic priority of the Moroccan government for the economic and social development of the North Morocco region. It is part of the economic policy orienting Morocco towards exports, based on eight clearly identified export sectors, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tangier International Zone
The Tangier International Zone (; ; ) was a international zone centered on the city of Tangier, Morocco, which existed from 1925 until its reintegration into independent Morocco in 1956, with interruption during the Spanish occupation of Tangier (1940–1945), and special economic status extended until early 1960. Surrounded on the land side by the Spanish protectorate in Morocco, it was governed under a unique and complex system that involved several European nations, the United States (mainly after 1945), and the Sultan of Morocco, himself under a French protectorate in Morocco, French protectorate. Due to its status as an international zone, Tangier played a crucial role for Moroccan nationalists, who wanted independence, to establish international contacts and recruit allies as well as organising gatherings and events. Background: early international governance in Tangier For nearly a century after the end of English Tangier, English rule in 1684, Tangier was primarily ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
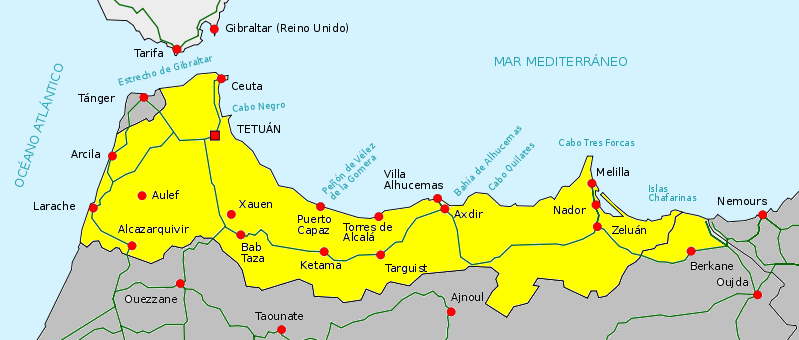
Tanger-Tetouan-Al Hoceima
Tangier-Tetouan-Al Hoceima () is the northernmost of the twelve regions of Morocco. It covers an area of 15,090 km2 and recorded a population of 4 030 222 in the 2024 Moroccan census. The capital of the region is Tangier. Geography Tanger-Tétouan-Al Hoceima is the northernmost of Morocco's twelve regions. In the north it faces the Strait of Gibraltar and the Mediterranean Sea and borders the Spanish exclave of Ceuta. It also borders the Moroccan regions of Rabat-Salé-Kénitra to the southwest, Fès-Meknès to the southeast and Oriental to the east. The Rif rises in the eastern part of the region and is the location of Al Hoceima National Park and Talassemtane National Park. The land near the Atlantic coast in the west is less rugged, and the fertile southwestern corner of the region is drained by the Loukkos River. History Tanger-Tetouan-Al Hoceima was formed in September 2015 by adding Al Hoceima Province, formerly part of Taza-Al Hoceima-Taounate region, to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Cities In Morocco
The basic unit of local government in Morocco is the commune. The following list includes all Moroccan municipalities with 50,000 or more inhabitants according to the 2024 census. In its 2024 census report, the High Commission for Planning also published a list of the legal populations of seven major Moroccan cities, some of which comprise more than one administrative unit. Those legal population figures are incorporated into the list, and the city definitions they are based upon are provided in the notes. List of cities with 50,000 or more inhabitants See also *List of cities in Western Sahara *List of metropolitan areas in Africa *List of largest cities in the Arab world Notes References {{DEFAULTSORT:List Of Cities In Morocco Lists of cities by country, Morocco, List of cities in Morocco geography-related lists, Cities Lists of cities in Africa, Morocco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morocco
Morocco, officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It has coastlines on the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to Algeria–Morocco border, the east, and the disputed territory of Western Sahara to Morocco–Western Sahara border, the south. Morocco also claims the Spain, Spanish Enclave and exclave, exclaves of Ceuta, Melilla and Peñón de Vélez de la Gomera, and several small Plazas de soberanía, Spanish-controlled islands off its coast. It has a population of approximately 37 million. Islam is both the official and predominant religion, while Arabic and Berber are the official languages. Additionally, French and the Moroccan dialect of Arabic are widely spoken. The culture of Morocco is a mix of Arab culture, Arab, Berbers, Berber, Culture of Africa, African and Culture of Europe, European cultures. Its capital is Rabat, while its largest city is Casablanca. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cape Spartel
Cape Spartel (; ; ) is a promontory in Morocco about above sea level at the entrance to the Strait of Gibraltar, 12 km west of Tangier. It is the northwesternmost point of the African continent. Below the cape are the Caves of Hercules. Description Cape Spartel is frequently but incorrectly referred to as the northernmost point of Africa, which is instead Ras ben Sakka, Tunisia; it is the most northwestern point. The cape rises to a height of 326 m at the top of Jebel Quebir, where a lighthouse built by Sultan Muhammad IV of Morocco, Muhammad IV in 1864 is situated at the end of a cliff. Below the cape are the Caves of Hercules, Tanger, Caves of Hercules. These are open to the public and they are accessible from Robinson Plage. The caves have shown evidence of Neolithic occupation. Before they were a tourist attraction they were brothels. Historically the rock was mined and this is one important cause of the caves' creation. Near Cape Spartel is Spartel, Spartel Bank, a su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petit Socco
The Petit Socco (), also known as the Place Souk Dakhel, or in Spanish as Zoco Chico, is a small square in the medina quarter of Tangier, Morocco. Name The words are a combination of the French word ''petit'', meaning 'little/small', and the Spanish word ''zoco'' (often spelled as ''socco'' in northern Morocco), meaning souk or marketplace. History The Petit Socco, intersected by rue Es-Siaghine and close to the Grand Mosque, has long been the focal point of the medina or old city of Tangier. Before the inception of the Tangier International Zone in 1923, many of the European nations' consulates in Tangier were in its immediate vicinity, as were the main banks. The head office of the State Bank of Morocco was established next to the Petit Socco at its creation in 1907, and stayed there until 1952 when it moved to a new building outside the medina. The Petit Socco was the hub of information in diplomatic-era Tanger, with the post offices (also offering telegraphy serv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mendoub's Residence
The Mendoub's Residence or Dar al-Mandub (, ), formerly known as the Forbes Museum of Tangier, is a cultural monument and property located on Mohammed Tazi Street in the Marshan neighborhood of Tangier, Morocco. History Residence of the ''Mendoub'' The governance of the Tangier International Zone was entrusted to an administrator appointed by the colonial powers and a personal representative of the Sultan of Morocco, who from 1923 was known as the Mendoub. The main office of the Mendoub was in the former German consulate, or Mendoubia. The Mendoub Palace was built as a residence in 1929 by Mendoub Mohammed Tazi. Forbes Museum The property was purchased in 1970 by Malcolm Forbes, the American publisher of ''Forbes magazine'', who converted it into a museum. The museum had a collection of a total of 115,000 models of toy soldiers. These figures re-enacted the major battles of history; from Waterloo to Dien Bien Phû, realistically recreated with lighting and sound effects ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regions Of Morocco
Regions are currently the highest administrative divisions in Morocco. Since 2015, Morocco officially administers 12 regions, including one (Dakhla-Oued Ed-Dahab) that lies completely within the disputed territory of Western Sahara and two (Laâyoune-Sakia El Hamra and Guelmim-Oued Noun) that lie partially within it. The regions are subdivided into a total of 75 second-level administrative divisions, which are Prefectures and provinces of Morocco, prefectures and provinces. A region is governed by a directly elections in Morocco, elected regional council. The president of the council is responsible for carrying out the council's decisions. Prior to the 2011 Moroccan constitutional referendum, 2011 constitutional reforms, this was the responsibility of the Wali (administrative title), Wali, the representative of the central government appointed by the King, who now plays a supporting role in the administration of the region. Regions since 2015 On 3 January 2010, the Moroccan g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moroccan Independence
The Revolution of the King and the People () was a Moroccan anti-colonial national liberation movement with the goal of ending the French and Spanish protectorates in Morocco in order to break free from colonial rule. The name refers to the coordination between the Moroccan monarch Sultan Mohammed V and the popular Moroccan Nationalist Movement in their efforts against colonialism and toward independence, particularly after the French authorities forced Sultan Mohammed V into exile on 20 August 1953 (Eid al-Adha). 20 August is considered a national holiday in Morocco, in remembrance of the Revolution of the King and the People. After Morocco had regained independence from the French, the movement effectively ceased to exist, as the Sultan managed to take control of the state. Meanwhile, the Moroccan Nationalist Movement was turned into an opposition party. Context Following the French bombardment of Casablanca and conquest of Morocco, the 1912 Treaty of Fes officially ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bni Makada
Bni Makada is one of the four ''arrondissements'' or districts of the city of Ṭanja, Morocco Morocco, officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It has coastlines on the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to Algeria–Morocc .... Administratively it is part of the prefecture of Ṭanja-Aẓila in the region of Ṭanja-Tiṭwan-Elḥusima. The 2014 Moroccan census recorded a population of 386,191 people living in 91,737 households. Name Bni Makada is named after a tribe of the Houara, who settled in the area in the late 17th century during the reign of Sultan Moulay Ismail ibn Sharif. References Tangier {{TangerTetouanAlHoceima-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |