|
Tang Ruowang
Johann Adam Schall von Bell (1 May 1591 – 15 August 1666) was a German Jesuit, astronomer and instrument-maker. He spent most of his life as a missionary in China (where he is remembered as "Tang Ruowang") and became an adviser to the Shunzhi Emperor of the Qing dynasty. Life Schall von Bell was born to noble parents in Cologne or nearby Lüftelberg (today part of Meckenheim) in the Holy Roman Empire. After he graduated from the Jesuit Gymnasium in Cologne he moved to Rome and studied subjects such as mathematics and astronomy at the Collegium Germanicum. In 1611 he joined the Society of Jesus and continued his education at the Gregorianum. In 1618 he left for China on a Portuguese ship with a group of missionaries under the lead of Nicolas Trigault. The next year the group reached the Portuguese trading port of Macau where Schall von Bell spent some time learning Chinese. He started missionary work inside China in 1622, but allegedly his success was limited. He par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Society Of Jesus
The Society of Jesus (; abbreviation: S.J. or SJ), also known as the Jesuit Order or the Jesuits ( ; ), is a religious order of clerics regular of pontifical right for men in the Catholic Church headquartered in Rome. It was founded in 1540 by Ignatius of Loyola and six companions, with the approval of Pope Paul III. The Society of Jesus is the largest religious order in the Catholic Church and has played significant role in education, charity, humanitarian acts and global policies. The Society of Jesus is engaged in evangelization and apostolic ministry in 112 countries. Jesuits work in education, research, and cultural pursuits. They also conduct retreats, minister in hospitals and parishes, sponsor direct social and humanitarian works, and promote ecumenical dialogue. The Society of Jesus is consecrated under the patronage of Madonna della Strada, a title of the Blessed Virgin Mary, and it is led by a superior general. The headquarters of the society, its general ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meckenheim
Meckenheim (; ) is a town in the Rhein-Sieg district, in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. Geography Geographical situation Meckenheim is situated approximately 15 km south-west of Bonn and separated from the German former capital (1949–1990) and seat of government (1949–1999) by the Kottenforst forest in the southernmost part of the Cologne Lowland. The highest point in the municipality is at 386.1 m above sea level near the village of Ersdorf at the beginning of the Eifel (also known as the Voreifel) while its lowest point is where the Swist leaves the municipal area to the northwest at 159.5 m above sea level. The North Rhine-Westphalian town borders (clockwise) on Alfter, Bonn, Wachtberg, Grafschaft and Rheinbach, whereby Alfter, Wachtberg and Rheinbach, like Meckenheim itself, belong to the Rhein-Sieg district; Grafschaft is in the district of Ahrweiler, which already belongs to Rhineland-Palatinate. The total area of the city is 34.8 km², with a maxim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
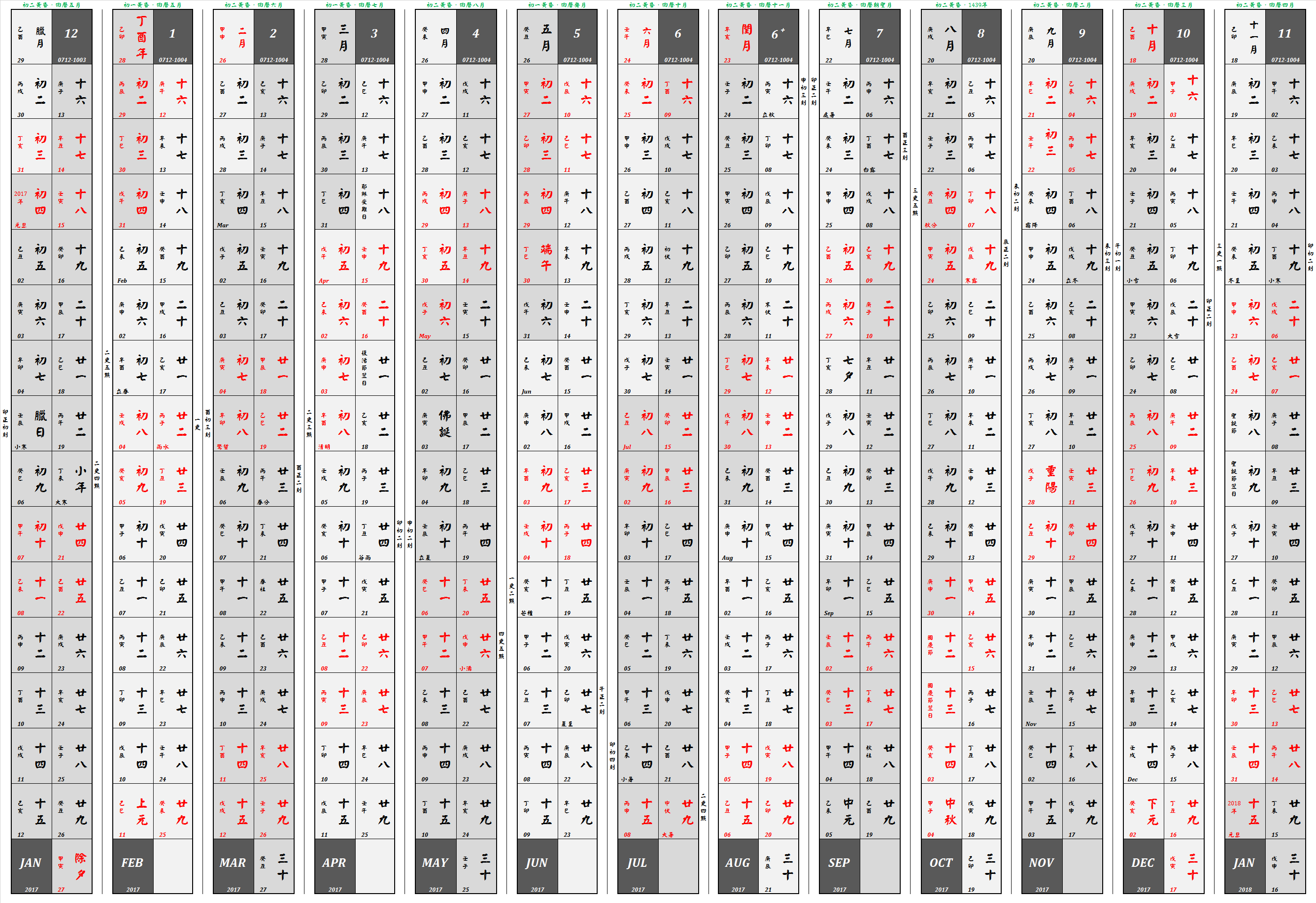
Chongzhen Calendar
The Chongzhen calendar () or Shixian calendar () was a historical edition of the lunisolar Chinese calendar from 1645 to 1913. It was developed by the lead of Xu Guangqi with the assistance of the Jesuit scholars Johann Schreck and Johann Adam Schall von Bell from 1624 to 1644, and was dedicated to the Chongzhen Emperor. When he died a year after it was released, it was propagated in the first year of the Qing dynasty by the Shunzhi Emperor, who changed its name to Shíxiàn calendar. This calendar is notable for systematically introducing the concepts and development of European mathematics and astronomy to China for the first time, and constituted the first major collaboration between scientists from Europe and from the Far East. Documented in more than 100 volumes of books, It offered an encyclopedic account of Euclidean geometry, spherical geometry and trigonometry, with extensive translations and references to Euclid's Elements The ''Elements'' ( ) is a mathematics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xu Guangqi
Xu Guangqi or Hsü Kuang-ch'i (April 24, 1562– November 8, 1633), also known by his baptismal name Paul or Paul Siu, was a Chinese agronomist, astronomer, mathematician, scholar-bureaucrat, politician, and writer during the late Ming dynasty. Xu was appointed by the Chinese Emperor in 1629 to be the leader of the Chongzhen calendar, Shixian calendar reform, which he embarked on with the assistance of Jesuits. Xu was a colleague and collaborator of the Italian Jesuits Matteo Ricci and Sabatino de Ursis and assisted their translation of several classic Western texts into Chinese, including part of Euclid's ''Euclid's Elements, Elements''. He was also the author of the ''Nong Zheng Quan Shu'', a treatise on agriculture. He is one of the "Three Pillars of Chinese Catholicism". The Roman Catholic Church considers him a Servant of God, one of the stages towards formal sainthood. On April 15, 2011, Holy See, Vatican spokesman Federico Lombardi announced the start of a beatification ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Calendar
The traditional Chinese calendar, dating back to the Han dynasty, is a lunisolar calendar that blends solar, lunar, and other cycles for social and agricultural purposes. While modern China primarily uses the Gregorian calendar for official purposes, the traditional calendar remains culturally significant. It determines the timing of Chinese New Year with traditions like the twelve animals of the Chinese zodiac, Chinese Zodiac still widely observed. The traditional Chinese calendar uses the Sexagenary cycle, sexagenary cycle, a repeating system of Heavenly Stems and Earthly Branches, to mark years, months, and days. This system, along with astronomical observations and mathematical calculations, was developed to align solar and lunar cycles, though some approximations are necessary due to the natural differences between these cycles. Over centuries, the calendar was refined through advancements in astronomy and horology, with dynasties introducing variations to improve accu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Schreck
Johann(es) Schreck, also Terrenz or Terrentius Constantiensis, Deng Yuhan Hanpo 鄧玉函, Deng Zhen Lohan, (1576, Bingen, Baden-Württemberg or Constance – 11 May 1630, Beijing) was a German Jesuit, missionary to China and polymath. He is credited with the development of scientific-technical terminology in Chinese. Early life Schreck studied medicine starting in 1590 at the Albert Ludwigs University of Freiburg, the University of Altdorf. After graduating, he is also known to have worked as an assistant to the mathematician François Viète in Paris in around 1600. After Viète's death in 1603, he moved to the University of Padua, where he was a student of Galileo Galilei, but studied medicine.E Schreck had an exceptional facility with languages; he spoke German, Italian, Portuguese, French and English. Like most educated men of his time, he wrote his letters in Latin. He also mastered Ancient Greek, Hebrew and Biblical Aramaic. Later in his life, he learned Chinese. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giacomo Rho
Giacomo Rho (1593, Milan – 27 April 1638, Beijing) was an Italian Jesuit missionary in China. There he adopted the Chinese name Luo Yagu (羅雅谷) and was also known by his courtesy name Weishao (味韶). Life Rho, the son of a jurist, entered the Society of Jesus at the age of twenty. While later proficient in mathematics, he was a poor student initially. Following his ordination in Rome by Cardinal Bellarmine, he sailed for the Far East in 1617 with forty-four companions. After a brief stay in Goa, he proceeded to Macao. During the siege of that city by Dutch forces in 1622, he was attributed by Jesuit sources to be the one who fired a cannon shot that landed on a barrel of gunpowder in the midst of the Dutch formation, which turned the tide of the battle and saved the city from the attack. This service opened China to him. Rho rapidly acquired knowledge of the Chinese language, and in 1631, he was summoned to Beijing by the emperor to work on reforming the Chinese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Macau
The Battle of Macau in 1622 was a conflict of the Dutch–Portuguese War fought in the Portuguese settlement of Macau, in southeastern China. The Portuguese, outnumbered and without adequate fortification, managed to repel the Dutch in a much-celebrated victory on 24 June after a three-day battle. The battle is the only major engagement that was fought primarily between two European powers on the Chinese mainland. Background After the Portuguese gained permission from the Ming mandarins in Guangdong to establish a permanent settlement and trade base in Macau in 1557, the port of Macau benefited greatly from being the intermediary of the lucrative China–Japan trade, since the direct routes were banned by the Ming court due to fears of the ''wokou'' pirates. Portugal's success in Macau drew the envy of other European maritime powers who were slower to gain a foothold in East Asia. When Philip II of Spain became King of Portugal after the 1580 Portuguese succession crisis, P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Language
Chinese ( or ) is a group of languages spoken natively by the ethnic Han Chinese majority and List of ethnic groups in China, many minority ethnic groups in China, as well as by various communities of the Chinese diaspora. Approximately 1.39 billion people, or 17% of the global population, speak a variety of Chinese as their first language. Chinese languages form the Sinitic languages, Sinitic branch of the Sino-Tibetan language family. The spoken varieties of Chinese are usually considered by native speakers to be dialects of a single language. However, their lack of mutual intelligibility means they are sometimes considered to be separate languages in a Language family, family. Investigation of the historical relationships among the varieties of Chinese is ongoing. Currently, most classifications posit 7 to 13 main regional groups based on phonetic developments from Middle Chinese, of which the most spoken by far is Mandarin Chinese, Mandarin with 66%, or around 800&nb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macau
Macau or Macao is a special administrative regions of China, special administrative region of the People's Republic of China (PRC). With a population of about people and a land area of , it is the most List of countries and dependencies by population density, densely populated region in the world. Formerly a Portuguese Empire, Portuguese colony, the territory of Portuguese Macau was first leased to Portugal by the Ming dynasty as a trading post in 1557. Portugal paid an annual rent and administered the territory under Chinese sovereignty until 1887, when Portugal gained perpetual colonial rights with the signing of the Sino-Portuguese Treaty of Peking. The colony remained under Portuguese rule until the 1999 handover to China. Macau is a Special administrative regions of China, special administrative region of China, which maintains separate governing and economic systems from those of mainland China under the principle of "one country, two systems".. The unique blend of Port ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicolas Trigault
Nicolas Trigault (1577–1628) was a Jesuit, and a missionary in China. He was also known by his latinised name Nicolaus Trigautius or Trigaultius, and his Chinese name Jin Nige (). Life and work Born in Douai (then part of the County of Flanders in the Spanish Netherlands, now part of France), he became a Jesuit in 1594. Trigault left Europe to do missionary work in Asia around 1610, eventually arriving at Nanjing, China in 1611. He was later brought by the Chinese Catholic Li Zhizao to his hometown of Hangzhou where he worked as one of the first missionaries ever to reach that city and was eventually to die there in 1628. In late 1612, Trigault was appointed by the China Mission's Superior, Niccolo Longobardi as the China Mission's procurator (recruitment and PR representative) in Europe. He sailed from Macau on February 9, 1613, and arrived in Rome on October 11, 1614, by way of India, the Persian Gulf and Egypt. His tasks involved reporting on the mission's progress to P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomy
Astronomy is a natural science that studies celestial objects and the phenomena that occur in the cosmos. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and their overall evolution. Objects of interest include planets, natural satellite, moons, stars, nebulae, galaxy, galaxies, meteoroids, asteroids, and comets. Relevant phenomena include supernova explosions, gamma ray bursts, quasars, blazars, pulsars, and cosmic microwave background radiation. More generally, astronomy studies everything that originates beyond atmosphere of Earth, Earth's atmosphere. Cosmology is a branch of astronomy that studies the universe as a whole. Astronomy is one of the oldest natural sciences. The early civilizations in recorded history made methodical observations of the night sky. These include the Egyptian astronomy, Egyptians, Babylonian astronomy, Babylonians, Greek astronomy, Greeks, Indian astronomy, Indians, Chinese astronomy, Chinese, Maya civilization, M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |