|
Tanaocrossus
''Tanaocrossus'' (Ancient Greek for "outstretched fringe", referring to its distinctive dorsal fin) is an extinct genus of primitive freshwater ray-finned fish that inhabited southwestern and eastern North America during the Late Triassic period. It contains a single known species, ''T. kalliokoskii'', known from the United States, with indeterminate species also known. It is primarily known from the Norian to Rhaetian of the Chinle Formation of Colorado and Utah. Indeterminate remains are known from the Dockum Group of Texas and New Mexico (Bull Canyon Formation). A single fragmentary but distinctive fossilized fin from the earlier Carnian-aged Doswell Formation of Virginia, which shares the genus's distinctive fin rays, was long the only record from the eastern United States, but a partial specimen was also later identified from the Manassas Sandstone. Morphologically, it can be easily distinguished from other co-occurring fishes by its highly elongated dorsal fin that stretc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cladistia
Cladistia is a subclass of bony fishes whose only living members are the bichirs of tropical Africa. Their major synapomorphies are a heterocercal tail in which the dorsal fin has independent rays, and a posteriorly elongated parasphenoid. Cladistia are the earliest diverging branch of living Actinopterygii, and are thought to have diverged from the Actinopteri, the group which includes all other living ray finned fish, by the Carboniferous. However, the fossil range for the only extant order ( Polypteriformes) is comparatively young, only reaching as far back as the mid-Cretaceous of South America and Africa, and the two extant genera of bichir only diverged around the Miocene. Aside from bichirs, other extinct fish groups thought to be members of the group include the Scanilepiformes, known from Triassic (and possibly Permian) of the Northern Hemisphere. The Guildayichthyiformes of Carboniferous North America are also sometimes considered cladistians, but this is thought ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scanilepiformes
Cladistia is a subclass of bony fishes whose only living members are the bichirs of tropical Africa. Their major synapomorphies are a heterocercal tail in which the dorsal fin has independent rays, and a posteriorly elongated parasphenoid. Cladistia are the earliest diverging branch of living Actinopterygii, and are thought to have diverged from the Actinopteri, the group which includes all other living ray finned fish, by the Carboniferous. However, the fossil range for the only extant order (Polypteriformes) is comparatively young, only reaching as far back as the mid-Cretaceous of South America and Africa, and the two extant genera of bichir only diverged around the Miocene. Aside from bichirs, other extinct fish groups thought to be members of the group include the Scanilepiformes, known from Triassic (and possibly Permian) of the Northern Hemisphere. The Guildayichthyiformes of Carboniferous North America are also sometimes considered cladistians, but this is thought to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cladistia
Cladistia is a subclass of bony fishes whose only living members are the bichirs of tropical Africa. Their major synapomorphies are a heterocercal tail in which the dorsal fin has independent rays, and a posteriorly elongated parasphenoid. Cladistia are the earliest diverging branch of living Actinopterygii, and are thought to have diverged from the Actinopteri, the group which includes all other living ray finned fish, by the Carboniferous. However, the fossil range for the only extant order ( Polypteriformes) is comparatively young, only reaching as far back as the mid-Cretaceous of South America and Africa, and the two extant genera of bichir only diverged around the Miocene. Aside from bichirs, other extinct fish groups thought to be members of the group include the Scanilepiformes, known from Triassic (and possibly Permian) of the Northern Hemisphere. The Guildayichthyiformes of Carboniferous North America are also sometimes considered cladistians, but this is thought ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bull Canyon Formation
The Bull Canyon Formation is a geological Formation (geology), formation of Late Triassic (Norian) age in eastern New Mexico and the Texas Panhandle. It is one of several formations encompassed by the Dockum Group. The Bull Canyon Formation preserves reptile fossils of the Revueltian "faunachron", and it is generally considered time-equivalent to the upper Cooper Canyon Formation, which crops out further south in west-central Texas. History and geology Triassic rocks in the Tucumcari Basin of east-central New Mexico have been prospected for fossils since the 1890s. The bulk of early fossil collecting in the formation was done by University of Michigan paleontologist Ermine Cowles Case, E.C. Case (starting in the 1910s) and Yale University, Yale paleontologist Joseph T. Gregory (starting in the 1940s). For much of the 20th century, all Late Triassic strata in New Mexico was assumed to belong to the Chinle Formation. Kelley (1972) informally labelled a unit of fine-grained sedimen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doswell Formation
The Doswell Formation (also known as the Doswell Group) is a geologic unit of Upper Triassic age, part of the Newark Supergroup. The Doswell Formation was originally named to refer to a geological sequence which forms the lower part of the sedimentary fill of the Taylorsville Basin in Virginia and Maryland. This sequence was deposited by lakes and rivers in the developing rift basin. A 2016 study argued that several geological layers in Pennsylvania as well as the neighboring Richmond Basin of Virginia also qualified as components of the Doswell Formation. The most diverse and fossiliferous component of the Doswell formation is the Vinita member, also sometimes known as the Turkey Branch, Tuckahoe, or Falling Creek Formations in earlier publications, and frequently referred to as the Vinita Formation by many authors. The Doswell formation is biostratigraphically characterized by a fauna including the fish '' Dictyopyge macrurus'' and the conchostracan '' Laxitextella multireticul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extinction
Extinction is the termination of an organism by the death of its Endling, last member. A taxon may become Functional extinction, functionally extinct before the death of its last member if it loses the capacity to Reproduction, reproduce and recover. As a species' potential Range (biology), range may be very large, determining this moment is difficult, and is usually done retrospectively. This difficulty leads to phenomena such as Lazarus taxon, Lazarus taxa, where a species presumed extinct abruptly "reappears" (typically in the Fossil, fossil record) after a period of apparent absence. Over five billion species are estimated to have died out. It is estimated that there are currently around 8.7 million species of eukaryotes globally, possibly many times more if microorganisms are included. Notable extinct animal species include Dinosaur, non-avian dinosaurs, Machairodontinae, saber-toothed cats, and mammoths. Through evolution, species arise through the process of specia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinle Fauna
Chinle () is a census-designated place (CDP) in Apache County, Arizona, United States. The name in Navajo means and is a reference to the location where the water flows out of the Canyon de Chelly. The population was 4,518 at the 2010 census. History In the Spanish colonial period, Chinle was a base for both trade and war. After acquisition of this area by the United States following the Mexican–American War, relations between the peoples deteriorated in the 1860s. The United States conducted a peace conference through their representative Kit Carson and the Navajo people in order to end the war between the Navajo and the U.S. The first trading post operated out of a tent and was established here in 1882. By 1885 a full-sized camp had developed. The Chinle Boarding School was established in 1910 by the Bureau of Indian Affairs (BIA). Khalil Anthony Johnson Jr., a PhD candidate at Yale University, wrote an article in 2014 that said, with this school, the federal government ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhaetian Genus Extinctions
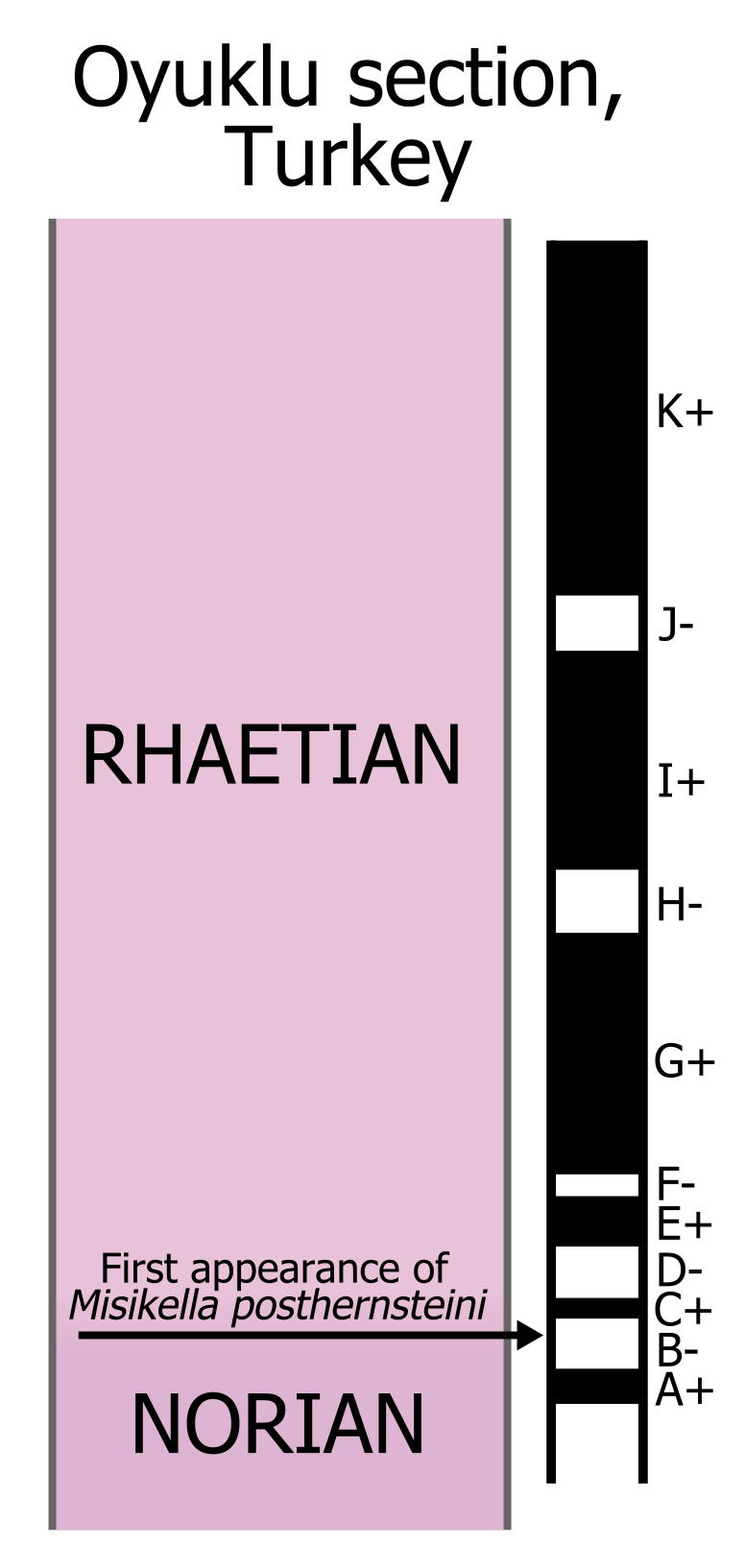
The Rhaetian is the latest age of the Triassic Period (in geochronology) or the uppermost stage of the Triassic System (in chronostratigraphy). It was preceded by the Norian and succeeded by the Hettangian (the lowermost stage or earliest age of the Jurassic). The base of the Rhaetian lacks a formal GSSP, though candidate sections include Steinbergkogel in Austria (since 2007) and Pignola-Abriola in Italy (since 2016). The end of the Rhaetian (and the base of the overlying Hettangian Stage) is more well-defined. According to the current ICS (International Commission on Stratigraphy) system, the Rhaetian ended ± 0.2 Ma (million years ago). In 2010, the base of the Rhaetian (i.e. the Norian-Rhaetian boundary) was voted to be defined based on the first appearance of '' Misikella posthernsteini'', a marine conodont. However, there is still much debate over the age of this boundary, as well as the evolution of ''M. posthernsteini''. The most comprehensive source of precise age d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norian Genera
The Norian is a division of the Triassic Period. It has the rank of an age (geochronology) or stage (chronostratigraphy). It lasted from ~227.3 to million years ago. It was preceded by the Carnian and succeeded by the Rhaetian. Stratigraphic definitions The Norian was named after the Noric Alps in Austria. The stage was introduced into scientific literature by Austrian geologist Edmund Mojsisovics von Mojsvar in 1869. The Norian Stage begins at the base of the ammonite biozones of '' Klamathites macrolobatus'' and '' Stikinoceras kerri'', and at the base of the conodont biozones of '' Metapolygnathus communisti'' and '' Metapolygnathus primitius''. A global reference profile for the base (a GSSP) had in 2009 not yet been appointed. The top of the Norian (the base of the Rhaetian) is at the first appearance of ammonite species '' Cochloceras amoenum''. The base of the Rheatian is also close to the first appearance of conodont species '' Misikella spp.'' and '' Epigondolella ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carnian Genus First Appearances
The Carnian (less commonly, Karnian) is the lowermost stage of the Upper Triassic Series (or earliest age of the Late Triassic Epoch). It lasted from 237 to 227.3 million years ago (Ma). The Carnian is preceded by the Ladinian and is followed by the Norian. Its boundaries are not characterized by major extinctions or biotic turnovers, but a climatic event (known as the Carnian pluvial episode characterized by substantial rainfall) occurred during the Carnian and seems to be associated with important extinctions or biotic radiations. Another extinction occurred at the Carnian-Norian boundary, ending the Carnian age. Stratigraphic definitions The Carnian was named in 1869 by Mojsisovics. It is unclear if it was named after the Carnic Alps or after the Austrian region of Carinthia (''Kärnten'' in German) or after the Carnia historical region in northeastern Italy. The name, however, was first used referring to a part of the Hallstatt Limestone cropping out in Austria. The b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Triassic Fish
Late or LATE may refer to: Everyday usage * Tardy, or late, not being on time * Late (or the late) may refer to a person who is dead Music * ''Late'' (The 77s album), 2000 * Late (Alvin Batiste album), 1993 * Late!, a pseudonym used by Dave Grohl on his ''Pocketwatch'' album * Late (rapper), an underground rapper from Wolverhampton * "Late", a song by Kanye West from ''Late Registration'' Other uses * Late (Tonga), an uninhabited volcanic island southwest of Vavau in the kingdom of Tonga * "Late" (''The Handmaid's Tale''), a television episode * LaTe, Oy Laivateollisuus Ab, a defunct shipbuilding company * Limbic-predominant age-related TDP-43 encephalopathy, a proposed form of dementia * Local-authority trading enterprise, a New Zealand business law * Local average treatment effect, a concept in econometrics * Late, a synonym for ''cooler'' in stellar classification See also * * * ''Lates'', a genus of fish in the lates perch family * Later (other) Later may refer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triassic Bony Fish
The Triassic ( ; sometimes symbolized 🝈) is a geologic period and system which spans 50.5 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.4 Mya. The Triassic is the first and shortest period of the Mesozoic Era and the seventh period of the Phanerozoic Eon. Both the start and end of the period are marked by major extinction events. The Triassic Period is subdivided into three epochs: Early Triassic, Middle Triassic and Late Triassic. The Triassic began in the wake of the Permian–Triassic extinction event, which left the Earth's biosphere impoverished; it was well into the middle of the Triassic before life recovered its former diversity. Three categories of organisms can be distinguished in the Triassic record: survivors from the extinction event, new groups that flourished briefly, and other new groups that went on to dominate the Mesozoic Era. Reptiles, especially archosaurs, were the chief te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |