|
Talesh Mountains
Talysh Mountains (, , ) is a mountain range in far southeastern Azerbaijan and far northwestern Iran within Ardabil Province and Gilan Province. Geography The Talysh Mountains extend southeastward from the Lankaran Lowland in southeastern Azerbaijan to the lower part of the Sefid Rud (''White River'') in northwestern Iran. A few peaks rise above 10,000 ft (3,000 m). Geology Geologically, the Talish Mountain Range is made mainly of the Late Cretaceous volcano-sedimentary deposits with a strip of Paleozoic rocks and a band of Triassic and Jurassic rocks in the southern parts, both in a north-west-southeast direction. Ecology The maximum annual precipitation in the Talysh Mountains is between 1,600 mm to 1,800 mm, which along the Lankaran Lowland is the highest precipitation in both Azerbaijan and Iran. The humid semi-subtropical coastal lowlands along the Caspian Sea, including the Lankaran Lowland, lie at the eastern base of the mountains. The Talysh Mountains a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subtropical Climate
The subtropical zones or subtropics are geographical and climate zones immediately to the north and south of the tropics. Geographically part of the temperate zones of both hemispheres, they cover the middle latitudes from to approximately 35° to 40° north and south. The horse latitudes lie within this range. Subtropical climates are often characterized by hot summers and mild winters with infrequent frost. Most subtropical climates fall into two basic types: humid subtropical (Köppen climate classification: Cfa/Cwa), where rainfall is often concentrated in the warmest months, for example Southeast China and the Southeastern United States, and dry summer or Mediterranean climate (Köppen climate classification: Csa/Csb), where seasonal rainfall is concentrated in the cooler months, such as the Mediterranean Basin or Southern California. Subtropical climates can also occur at high elevations within the tropics, such as in the southern end of the Mexican Plateau and in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lerik District
Lerik District () is one of the 66 districts of Azerbaijan. It is located in the southeast of the country and belongs to the Lankaran-Astara Economic Region. The district borders the districts of Yardimli, Masally, Lankaran, Astara and the Ardabil Province of Iran. Its capital and largest city is Lerik. As of 2020, the district had a population of 87,000. It is located between the Talysh Mountains and the agricultural plain of the Lankaran Lowland. History Lerik district was established in August 1930. It was called "Zuvand District" until January 1938. 29 municipalities operate in the district. The district includes a city and 162 villages with a total area of 1084 square kilometer. In accordance with the presidential decree dated June 13, 2008, the settlement of Lerik was granted the status of a city. The territory of the Lerik district is one of the oldest settlements in Azerbaijan. There exist some caves which are considered to belong to the Bronze Age. These caves are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lankaran District
Lankaran District () is one of the 66 Administrative divisions of Azerbaijan, districts of Azerbaijan. It is located in the south-east of the country, in the Lankaran-Astara Economic Region. The district borders the districts of Astara District, Astara, Lerik District, Lerik, Masally District, Masally, and Neftchala District, Neftchala. Its capital and largest city is Lankaran, although the city is technically not part of the district and is subordinate to the Republic. As of 2020, the district had a population of 232,000. History Archaeological excavations indicate that people have lived in the region since at least the Bronze Age (3rd or 2nd millennia BC). The area around Lankaran has fertile soil, rich water reserves and a humid subtropical climate with a maximum annual precipitation of 1,600 to 1,800 mm, the highest precipitation in Azerbaijan, leading to abundant agriculture, cattle-breeding, gardening, fishing, bee-keeping and silk production. Blacksmith, copper-smith, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astara District
Astara District () is one of the 66 districts of Azerbaijan. It is located in the southeast of the country, in the Lankaran-Astara Economic Region. The district borders the districts of Lankaran and Lerik, as well as the Ardabil and Gilan provinces of Iran. Its capital and largest city is Astara. As of 2020, the district had a population of 110,000. History Ancient history A famous mathematician, astronomer and geographer Alexandria Claudius Ptolomey (AD 100 – c. 170) was one of the oldest researchers who also visited the territory of Azerbaijan. He compiled a map of the Caspian Sea in the second century, has given a clear overview on the geographical names, objects and settlements located on its shores. The names of many cities and villages belonging to Albania, as well as the name “Astara” (Greek: Astarata) are found on this map. Another scholar of the ancient world, Strabon also pointed out the name “Astara” in his "Historical Sketches" (Historicahypomne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landforms Of Gilan Province
A landform is a land feature on the solid surface of the Earth or other planetary body. They may be natural or may be anthropogenic (caused or influenced by human activity). Landforms together make up a given terrain, and their arrangement in the landscape is known as topography. Landforms include hills, mountains, canyons, and valleys, as well as shoreline features such as bays, peninsulas, and seas, including submerged features such as mid-ocean ridges, volcanoes, and the great oceanic basins. Physical characteristics Landforms are categorized by characteristic physical attributes such as elevation, slope, orientation, structure stratification, rock exposure, and soil type. Gross physical features or landforms include intuitive elements such as berms, cliffs, hills, mounds, peninsulas, ridges, rivers, valleys, volcanoes, and numerous other structural and size-scaled (e.g. ponds vs. lakes, hills vs. mountains) elements including various kinds of inland and oceanic waterbodi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountain Ranges Of Iran
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually higher than a hill, typically rising at least above the surrounding land. A few mountains are isolated summits, but most occur in mountain ranges. Mountains are formed through tectonic forces, erosion, or volcanism, which act on time scales of up to tens of millions of years. Once mountain building ceases, mountains are slowly leveled through the action of weathering, through slumping and other forms of mass wasting, as well as through erosion by rivers and glaciers. High elevations on mountains produce colder climates than at sea level at similar latitude. These colder climates strongly affect the ecosystems of mountains: different elevations have different plants and animals. Because of the less hospitable terrain and climate, mountains te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountain Ranges Of Azerbaijan
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually higher than a hill, typically rising at least above the surrounding land. A few mountains are isolated summits, but most occur in mountain ranges. Mountains are formed through tectonic forces, erosion, or volcanism, which act on time scales of up to tens of millions of years. Once mountain building ceases, mountains are slowly leveled through the action of weathering, through slumping and other forms of mass wasting, as well as through erosion by rivers and glaciers. High elevations on mountains produce colder climates than at sea level at similar latitude. These colder climates strongly affect the ecosystems of mountains: different elevations have different plants and animals. Because of the less hospitable terrain and climate, mountai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
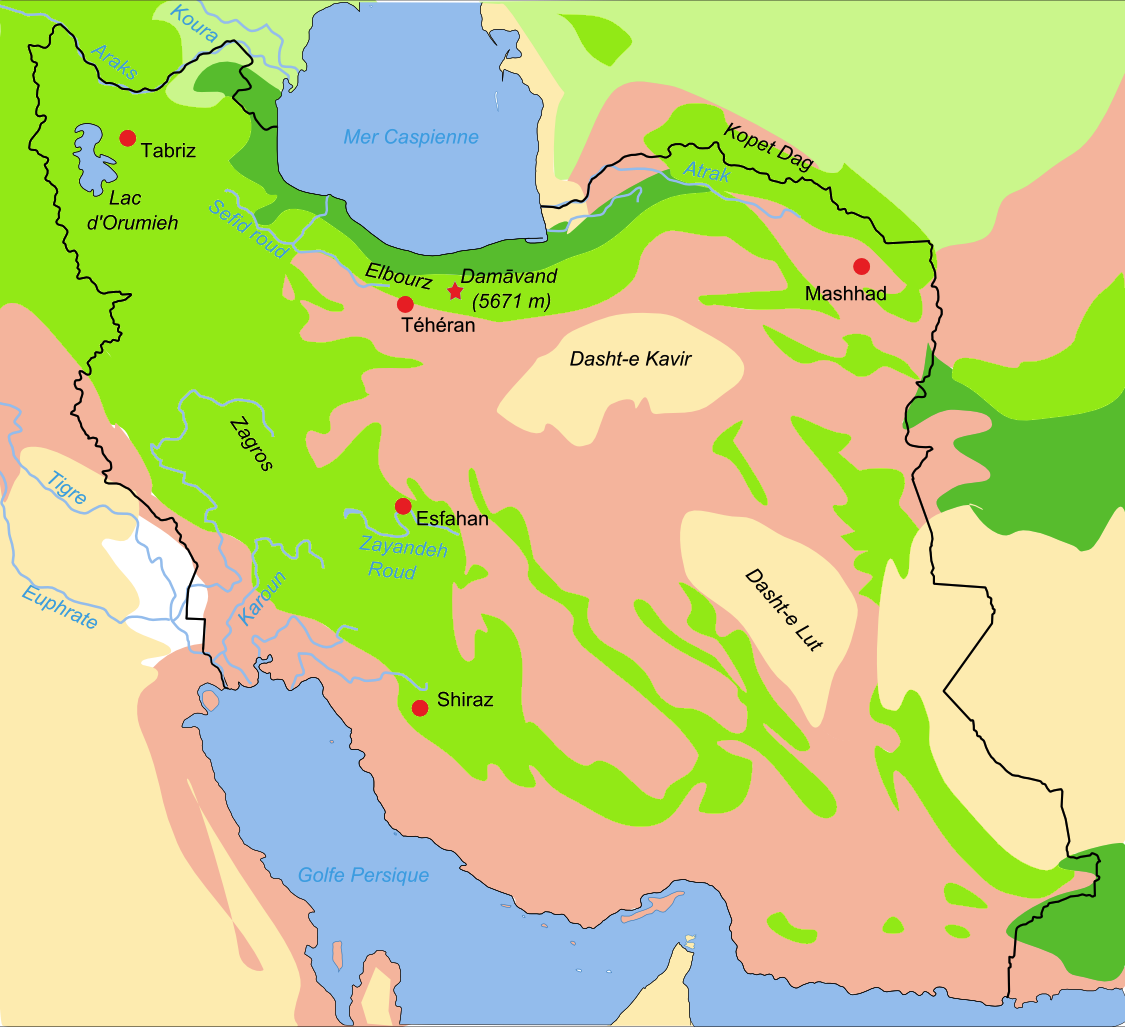
Alborz (mountain Range)
The Alborz ( ) range, also spelled as Alburz, Elburz or Elborz, is a mountain range in northern Iran that stretches from the border of Azerbaijan along the western and entire southern coast of the Caspian Sea and finally runs northeast and merges into the smaller Aladagh Mountains and borders in the northeast on the parallel mountain ridge Kopet Dag in the northern parts of Greater Khorasan, Khorasan. All these mountains are part of the much larger Alpide belt. The Alborz range is divided into the Western, Central, and Eastern Alborz Mountains. The Western Alborz Range (usually called the Talysh Mountains, Talysh) runs south-southeastward almost along the western coast of the Caspian Sea. The Central Alborz (the Alborz Mountains in the strictest sense) runs from west to east along the entire southern coast of the Caspian Sea, while the Eastern Alborz Range runs in a northeasterly direction, toward the northern parts of the Khorasan region, southeast of the Caspian Sea. Mount Damav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caspian Tiger
The Caspian tiger was a '' Panthera tigris tigris'' population native to eastern Turkey, northern Iran, Mesopotamia, the Caucasus around the Caspian Sea, Central Asia to northern Afghanistan and the Xinjiang region in western China. Until the Middle Ages, it was also present in southern Russia. It inhabited sparse forests and riverine corridors in this region until the 1970s. This population was regarded as a distinct subspecies and assessed as extinct in 2003. Results of a phylogeographic analysis evinces that the Caspian and Siberian tiger populations shared a common continuous geographic distribution until the early 19th century. Some Caspian tigers were intermediate in size between Siberian and Bengal tigers. It was also called Balkhash tiger, Hyrcanian tiger, Turanian tiger, and Mazandaran tiger. Taxonomy ''Felis virgata'' was a scientific name used by Johann Karl Wilhelm Illiger in 1815 for the greyish tiger in the area surrounding the Caspian Sea. ''Tigris septentrio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caspian Hyrcanian Mixed Forests
The Hyrcanian forests (; ) are a zone of lush lowland and montane forests covering about near the shores of the Caspian Sea in Iran and Azerbaijan. The forest is named after the ancient region of Hyrcania. The World Wide Fund for Nature refers to the ecoregion as the Caspian Hyrcanian mixed forests. Since 5 July 2019, the Hyrcanian Forests have been designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site. In September 2023, the heritage site expanded to incorporate portions of the forest located in Azerbaijan. Geography In Iran, the Hyrcanian ecoregion comprises a long strip along the southern coast of the Caspian Sea and the northern slopes of the Alborz mountains. It covers parts of five provinces, from east to west: North Khorasan Province, North Khorasan, Golestan Province, Golestan ( being its south and southwest plus eastern regions of the Gorgan plain), Mazandaran Province, Mazandaran, Gilan Province, Gilan and Ardabil Province, Ardabil. The Golestan National Park spans the boundary of G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |