|
Taihei Genpō
(aka: 大平󠄁元寶) is an early form of Japanese silver currency which is recorded in the Shoku Nihongi of the Nara period. Historical documents confirm that this coinage was established in the 4th year of Tenpyō-hōji, along with copper Mannen Tsuho and gold Kaiki Shoho coins. While their history is confirmed, no actual genuine coins have ever been found. Overview The Imperial edict for Taihei Genpō coins appears in the Shoku Nihongi where it is entered for March 16 in the 4th year of Tenpyo Hoji (760) during the reign of Emperor Junnin. This edict stipulates that 10 silver Taihei Genpo coins were to be used for 1 gold Kaiki Shoho coin. 1 silver Taihei Genpo coin could also be exchanged for 10 Mannen Tsuho (new copper coins). The right to issue these coins was given to Fujiwara no Nakamaro (Emi no Oshikatsu), who had been appointed Daijō-daijin the previous year. As with Mannen Tsuho and Kaiki Shoho coins, Taihei Genpō are presumed to have been round with square-holes. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Currency
Japanese currency has a history covering the period from the 8th century CE to the present. After the traditional usage of rice as a commodity currency, currency medium, Japan adopted History of Chinese currency, currency systems and designs from China before developing a separate system of its own. History Commodity money Before the 7th-8th centuries CE, Japan used commodity money for trading. This generally consisted of material that was compact and easily transportable and had a widely recognized value. Commodity money was a great improvement over simple barter, in which commodities were simply exchanged against others. Ideally, commodity money had to be widely accepted, easily portable and storable, and easily combined and divided in order to correspond to different values. The main items of commodity money in Japan were arrowheads, rice grains and gold powder. This contrasted somewhat with countries like China, where one of the most important items of commodity money ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kurokawa Institute Of Ancient Cultures
The is a private research institute in Hyōgo Prefecture, Japan that preserves, researches, publishes, and exhibits materials relating to the arts, crafts, archaeology, history, and cultures of East Asia, in particular China and Japan. Established in 1950, the Institute relocated from Ashiya to Nishinomiya 270px, Nishinomiya City Hall 270px, Aerial view of Nishinomiya city center 1985 270px, Hirota Shrine is a city located in Hyōgo Prefecture, Japan. , the city had an estimated population of 484,368 in 218,948 households and a population density ... in 1974. The collection numbers some 8,500 works (20,000 individual items). See also * List of National Treasures of Japan (crafts: swords) References External links *Kurokawa Institute of Ancient Cultures {{Authority control Nishinomiya Museums in Hyōgo Prefecture Research institutes in Japan 1950 establishments in Japan Museums established in 1950 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coins Of Japan
The is the official currency of Japan. It is the third-most traded currency in the foreign exchange market, after the United States dollar and the euro. It is also widely used as a third reserve currency after the US dollar and the euro. The New Currency Act of 1871 introduced Japan's modern currency system, with the yen defined as of gold, or of silver, and divided decimally into 100 ''sen'' or 1,000 ''rin''. The yen replaced the previous Tokugawa coinage as well as the various ''hansatsu'' paper currencies issued by feudal ''han'' (fiefs). The Bank of Japan was founded in 1882 and given a monopoly on controlling the money supply. Following World War II, the yen lost much of its pre-war value as Japan faced a debt crisis and hyperinflation. Under the Bretton Woods system, the yen was pegged to the US dollar alongside other major currencies. After this system was abandoned in 1971 with the Nixon Shock, the short-lived Smithsonian Agreement temporarily reinstated a fixed e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
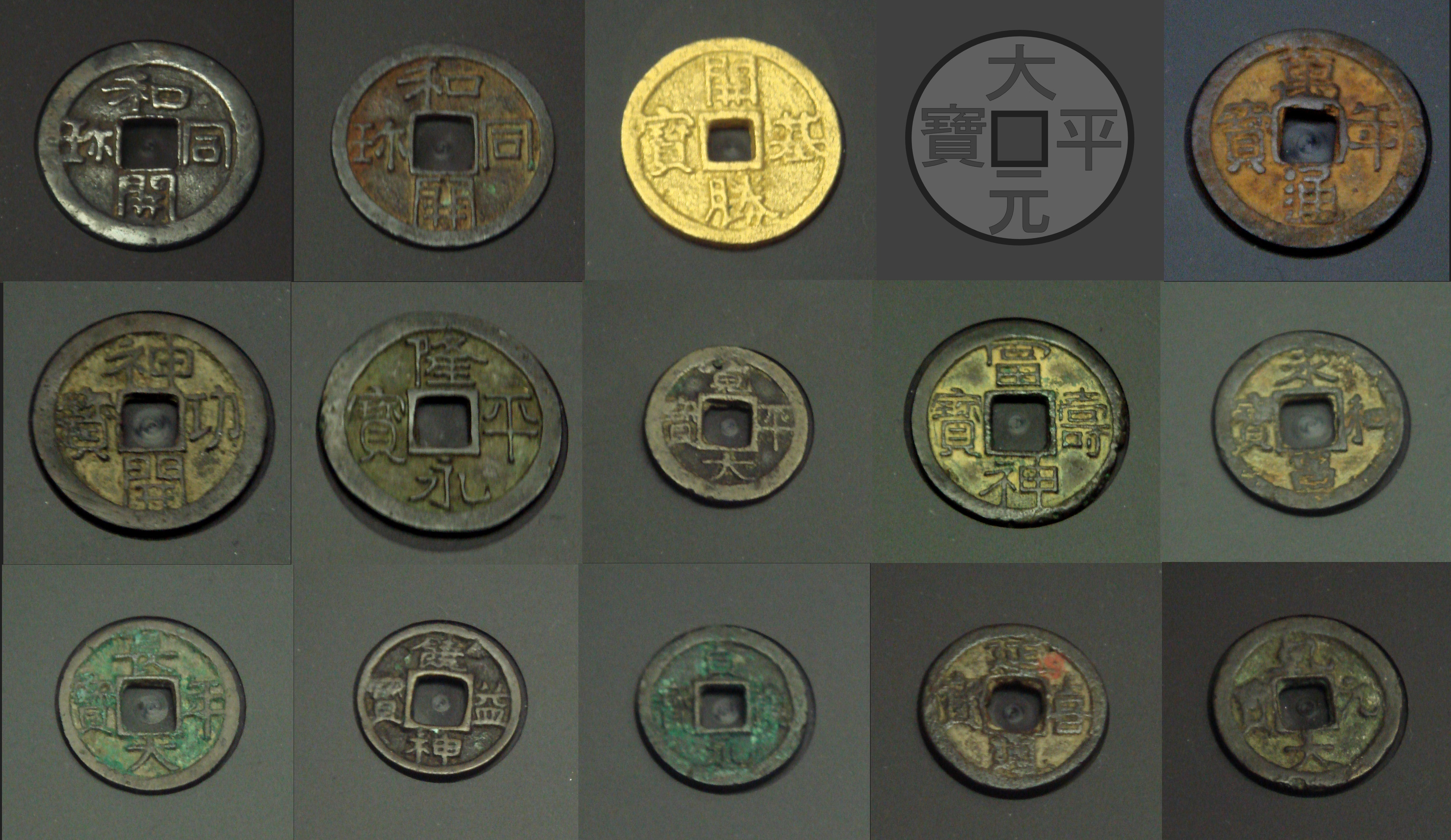
List Of Japanese Cash Coins By Inscription
Cash coins were introduced to Japan in the century inspired by the Chinese Kaiyuan Tongbao, Kaigen Tsūhō (開元通寳) Cash (Chinese coin), cash coins from the Tang dynasty. Chinese cash coins also circulated in other countries and inspired similar currencies such as the Korean mun, Ryukyuan mon, Vietnamese văn, while they also Cash coins in Indonesia, circulated as far south as Indonesia. Because these currencies were so similar cash coins around the Far East were interchangeable and Japanese cash coins circulated in other countries while foreign cash coins also circulated in Japan. The first Japanese cash coins were the Wadōkaichin (和同開珎) which were produced from 29 August 708. In 760 Japanese currency was reformed and gold and silver cash coins were introduced, however by the end of the 10th century the value of Japanese coinage had severely fallen combined with a weak central government led the Japanese to return to barter. From the 12th century onwards the Japane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial Household Agency
The (IHA) is an agency of the government of Japan in charge of state matters concerning the Imperial House of Japan, Imperial Family, and the keeping of the Privy Seal of Japan, Privy Seal and State Seal of Japan. From around the 8th century AD until the Second World War, it was known as the . The Agency is unique among conventional government agencies and ministries in that it does not directly report to the Prime Minister of Japan, Prime Minister at the cabinet level, nor is it affected by legislation that establishes it as an Independent Administrative Institution. Organization and functions The Imperial Household Agency is headed by its director-general, assisted by the deputy director, appointed by the Cabinet.Imperial Household AgencyOrganization/ref> Its main organizational positions are: * the Grand Steward's Secretariat * the Board of Chamberlains * the Crown Prince's Household * the Board of Ceremonies * the Archives and Mausolea Department * the Maintenance and W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shōsōin
The is the wikt:treasure house, treasure house of Tōdai-ji Temple in Nara, Nara, Nara, Japan. The building is in the ''azekura'' (log-cabin) style with a raised floor. It lies to the northwest of the Great Buddha Hall. The Shōsō-in houses artifacts connected to Emperor Shōmu (聖武天皇)(701–756) and Empress Kōmyō (光明皇后)(701–760), as well as arts and crafts of the Tenpyō, Tempyō (天平) era of History of Japan, Japanese history. History The construction of the Tōdai-ji Buddhist temple complex was ordained by Emperor Shōmu as part of a national project of Buddhist temple construction. During the Tenpyō, Tempyō period, the years during which Emperor Shōmu reigned, multiple disasters struck Japan as well as political uproar and epidemics. Because of these reasons Emperor Shōmu launched a project of provincial temples. The Tōdai-ji was appointed as the head temple of these provincial temples. Emperor Shōmu was a strong supporter of Buddhism and he tho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nara National Museum
The is one of the pre-eminent national art museums in Japan. Introduction The Nara National Museum is located in Nara, which was the capital of Japan from 710 to 784. Katayama Tōkuma (1854–1917) designed the original building, which is a representative Western-style building of the Meiji period and has been designated an Important Cultural Property in Japan. Junzō Yoshimura (1908–1997) designed a supplemental building in 1973. Collections The museum is noted for its collection of Buddhist art, including images, sculpture, and altar articles. The museum houses and displays works of art belonging to temples and shrines in the Nara area. Properties kept in the Shōsōin repository are exhibited each year in the autumn. In the museum's collection is the 12th-century , 11th or 12th-century mandala Jōdo mandara-zu, and the 9th-century sculpture of the seated Buddha Yakushi. History The Nara National Museum was established in 1889 as the Imperial Nara Museum ''(帝国奈 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fujiwara No Nakamaro Rebellion
The , also known as the Emi Rebellion, was a short-lived and unsuccessful Nara period military confrontation in Japan resulting from a power struggle between former Empress Kōken and the main political figure of the time, Fujiwara no Nakamaro from the powerful Fujiwara clan. Through the support of Emperor Shōmu and Empress Kōmyō, with whom he had family-ties, Nakamaro rapidly climbed the career ladder during the 740s and 750s achieving some of the highest ranks and court positions. During the early years of the reign of Emperor Junnin, whom he supported, Nakamaro ruled the country ''de facto''. Following the death of Kōmyō in 760, the retired Empress Kōken started to take government affairs into her hand resulting in a conflict between Nakamaro/Junnin on one side and Kōken and her close associate Dōkyō on the other. In order to restore authority, on the 11th day of the 9th month, Tenpyō-hōji 8 (October 14, 764), Nakamaro seized the signs of imperial authority and lef ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitsuo Tokumitsu
Mitsuo (written: , , , , , , , , , or in hiragana) is a masculine Japanese given name. Notable people with the name include: * Mitsuo Aoki (1914–2010), American theologian *, Japanese naval aviator * Mitsuo Fujikura, Japanese mixed martial artist *, Japanese anime director * Mitsuo Harada (born 1964), Japanese golfer *, Japanese anime director *, Japanese manga artist *, Japanese cross-country skier *, Japanese politician *, Japanese sport wrestler *, Japanese animator and anime director *, Japanese motorcycle racer *, Japanese voice actor *, Japanese archaeologist and academic *, Japanese footballer and manager *, Japanese footballer *, Japanese activist *, Japanese politician *, Japanese professional wrestler *, pen-name of Koba Ichiro, Japanese writer *, Japanese sprint canoeist *, Japanese footballer *, Japanese sport shooter *, Japanese voice actor *, Japanese art, film and music director *, Japanese physicist *, Japanese baseball player *, Tsunku , known professionall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wadōkaichin
, also romanized as ''Wadō-kaichin'' or called ''Wadō-kaihō'', is the oldest official Japanese currency, Japanese coinage, first mentioned for 29 August 708 on order of Empress Genmei. It was long considered to be the first type of coin produced in Japan. Analyses of several findings of ''Fuhonsen, Fuhon-sen'' (富夲銭) in Asuka have shown that those coins were manufactured from 683. Description The ''wadōkaichin'' was first produced following the discovery of large copper deposits in Japan during the early 8th century at what is now the Wadō Archaeological Site. The coins, which are round with a square hole in the center, remained in circulation until 958 CE. These were the first of a series of coins collectively called ''jūnizeni'' or .Nussbaum p. 539./ref> This coinage was inspired by the Chinese Tang dynasty coinage (唐銭) named ''Kaiyuan Tongbao, Kaigen Tsūhō'' (Chinese: 開元通宝, ''Kāiyuán tōngbǎo''), first minted in Chang'an in 621 CE. The ''wad� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shoku Nihongi
The is an imperially-commissioned Japanese history text. Completed in 797, it is the second of the '' Six National Histories'', coming directly after the and followed by ''Nihon Kōki''. Fujiwara no Tsugutada and Sugano no Mamichi served as the primary editors. It is one of the most important primary historical sources for information about Japan's Nara period. The work covers the 95-year period from the beginning of Emperor Monmu's reign in 697 until the 10th year of Emperor Kanmu's reign in 791, spanning nine imperial reigns. It was completed in 797 AD. The text is forty volumes in length. It is primarily written in kanbun, a Japanese form of Classical Chinese Classical Chinese is the language in which the classics of Chinese literature were written, from . For millennia thereafter, the written Chinese used in these works was imitated and iterated upon by scholars in a form now called Literary ..., as was normal for formal Japanese texts at the time. How ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |