|
Tacheng Tick Virus
TachengThe official spelling according to (), also known as Tarbagatay, Chuguchak or Qoqek, is a county-level city and the administrative seat of Tacheng Prefecture, in northern Ili Kazakh Autonomous Prefecture, Xinjiang. The Chinese name "Tacheng" is an abbreviation of "Tarbagatay City", a reference to the Tarbagatay Mountains. Tacheng is located in the Dzungarian Basin, some from the Chinese border with Kazakhstan. For a long time it has been a major center for trade with Central Asia because it is an agricultural hub. Its industries include food processing, textiles, and utilities. History In the mid-19th century, Chuguchak was considered the most important commercial center of Western China after Ghulja (Yining), being an important center of trade between China and Russia, in particular in tea. The city, surrounded by an earth wall, was the residence of two Qing ambans and had a garrison of some 1,000 Chinese soldiers and 1,500 Manchu and Mongol soldiers. Chuguchak suffere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
County-level City
A county-level city () is a County-level divisions of China, county-level administrative division of the China, People's Republic of China. County-level cities have judiciary, judicial but no legislature, legislative rights over their own local ordinance, local law and are usually governed by Administrative divisions of China#Prefectural level (2nd), prefecture-level divisions, but a few are governed directly by Administrative divisions of China#Provincial level (1st), province-level divisions. A county-level city is a "city" () and "county" () that have been merged into one unified jurisdiction. As such, it is simultaneously a city, which is a municipal entity, and a county, which is an administrative division of a prefecture. Most county-level cities were created in the 1980s and 1990s by replacing denser populated Counties of China, counties. County-level cities are not "city, cities" in the strictest sense of the word, since they usually contain rural areas many times the size ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a landlocked country primarily in Central Asia, with a European Kazakhstan, small portion in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the Kazakhstan–Russia border, north and west, China to the China–Kazakhstan border, east, Kyrgyzstan to the Kazakhstan–Kyrgyzstan border, southeast, Uzbekistan to the Kazakhstan–Uzbekistan border, south, and Turkmenistan to the Kazakhstan–Turkmenistan border, southwest, with a coastline along the Caspian Sea. Its capital is Astana, while the largest city and leading cultural and commercial hub is Almaty. Kazakhstan is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, ninth-largest country by land area and the largest landlocked country. Steppe, Hilly plateaus and plains account for nearly half its vast territory, with Upland and lowland, lowlands composing another third; its southern and eastern frontiers are composed of low mountainous regions. Kazakhstan has a population of 20 mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hui People
The Hui people are an East Asian ethnoreligious group predominantly composed of Islam in China, Chinese-speaking adherents of Islam. They are distributed throughout China, mainly in the Northwest China, northwestern provinces and in the Zhongyuan region. According to the 2010 census, China is home to approximately 10.5 million Hui people. Outside China, the 170,000 Dungan people of Kazakhstan and Kyrgyzstan, the Panthays in Myanmar, and many of the Chin Haws in Thailand are also considered part of the Hui ethnicity. The Hui were referred to as Hanhui during the Qing dynasty to be distinguished from the Turkic peoples, Turkic Muslims, which were referred to as Chanhui. The Republic of China (1912–1949), Republic of China government also recognised the Hui as a branch of the Han Chinese rather than a separate ethnic group. In the National Assembly (Republic of China), National Assembly of the Republic of China, the Hui were referred to as 1947 Chinese National Assembly election ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kazakhs
The Kazakhs (Kazakh language, Kazakh: , , , ) are a Turkic peoples, Turkic ethnic group native to Central Asia and Eastern Europe. They share a common Culture of Kazakhstan, culture, Kazakh language, language and History of Kazakhstan, history that is closely related to those of other Turkic peoples of Western and Central Asia. The majority of ethnic Kazakhs live in their transcontinental nation state of Kazakhstan. Ethnic Kazakh communities are present in Kazakhstan's border regions in Russia, northern Uzbekistan, northwestern China (Ili Kazakh Autonomous Prefecture), western Mongolia (Bayan-Ölgii Province) and Iran (Golestan province). The Kazakhs arose from the merging of various medieval tribes of Turkic and Mongolic origin in the 15th century. Kazakh identity was shaped following the foundation of the Kazakh Khanate between 1456 and 1465, when following the disintegration of the Turkification, Turkified state of Golden Horde, several tribes under the rule of the sultans J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Han Chinese
The Han Chinese, alternatively the Han people, are an East Asian people, East Asian ethnic group native to Greater China. With a global population of over 1.4 billion, the Han Chinese are the list of contemporary ethnic groups, world's largest ethnic group, making up about 17.5% of the world population. The Han Chinese represent 91.11% of the population in China and 97% of the population in Taiwan. Han Chinese are also a significant Overseas Chinese, diasporic group in Southeast Asian countries such as Thailand, Malaysia, and Indonesia. In Singapore, people of Han Chinese or Chinese descent make up around 75% of the country's population. The Han Chinese have exerted a primary formative influence in the development and growth of Chinese civilization. Originating from Zhongyuan, the Han Chinese trace their ancestry to the Huaxia people, a confederation of agricultural tribes that lived along the middle and lower reaches of the Yellow River in the north central plains of Chin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kazakh SSR
The Kazakh Soviet Socialist Republic, also known as Soviet Kazakhstan, the Kazakh SSR, KSSR, or simply Kazakhstan, was one of the transcontinental constituent republics of the Soviet Union (USSR) from 1936 to 1991. Located in northern Central Asia, it was created on 5 December 1936 from the Kazakh ASSR, an autonomous republic of the Russian SFSR. At in area, it was the second-largest republic in the USSR, after the Russian SFSR. Its capital was Alma-Ata (today known as Almaty). During its existence as a Soviet Socialist Republic, it was ruled by the Communist Party of the Kazakh SSR (QKP). On 25 October 1990, the Supreme Soviet of the Kazakh SSR declared its sovereignty on its soil. QKP first secretary Nursultan Nazarbayev was elected president in April of that year – a role he remained in until 2019. The Kazakh SSR was renamed the Republic of Kazakhstan on 10 December 1991, which declared its independence six days later, as the last republic to secede from the USSR ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yi–Ta Incident
The Yi–Ta incident ( zh, c=伊塔事件) was a mass exodus of people from China to the Soviet Union in early 1962. At least 60,000 Chinese citizens migrated to the Soviet Union by crossing the border between the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region and the Kazakh Soviet Socialist Republic from March to May 1962. The migrants were predominantly ethnic Kazakhs, but many Kyrgyz, Russians, Tatars, Uyghurs, and Uzbeks also left, driven by deteriorating living conditions in Xinjiang, the Chinese government's perceived bias towards the Han Chinese, and claims of Soviet citizenship being granted to migrants of " Soviet nationalities". The exodus occurred amid a climate of panic and uncertainty surrounding the Sino–Soviet split, with rumours spreading among Xinjiang's populace that, among other things, the Sino–Soviet border would soon be closed and a war would erupt between the two countries. The exodus ended when the Chinese authorities pressured their Soviet counterparts to close ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Kazakhstan Region
East Kazakhstan Region (; ) is a region of Kazakhstan. It occupies the easternmost part of Kazakhstan, and includes parts of the Irtysh River, Lake Markakol, and Lake Zaysan. Its administrative center is Öskemen (also known as Ust'-Kamenogorsk). The region borders Altai Krai and Altai republic in Russia in the north and northeast and the People's Republic of China, via Xinjiang, in the south and southeast. The easternmost point of the Oblast is within about 50 kilometres of the westernmost tip of Mongolia; however, Kazakhstan and Mongolia do not share a common border, the two countries being separated by a small part of the China–Russia border. The region was created by the merger of two Soviet-era Kazakhstan oblasts: the old Vostochno-Kazakhstanskaya (East Kazakhstan) Oblast and Semipalatinsk Oblast. On 17 March 2022, it was announced that East Kazakhstan region would be divided, creating the Abai Region. This came into force on 8 June 2022, with eight districts of East Ka ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xinjiang Internment Camps
The Xinjiang internment camps, officially called vocational education and training centers by the government of the People's Republic of China, are internment camps operated by the government of Xinjiang and the Chinese Communist Party Provincial Standing Committee. Human Rights Watch says that they have been used to indoctrinate Uyghurs and other Muslims since 2017 as part of a " people's war on terror", a policy announced in 2014. Thirty-seven countries have expressed support for China's government for "counter-terrorism and de-radicalization measures", including countries such as Russia, Saudi Arabia, Cuba, and Venezuela; meanwhile 22 or 43 countries, depending on sources, have called on China to respect the human rights of the Uyghur community, including countries such as Canada, Germany and Japan. Xinjiang internment camps have been described as "the most extreme example of China's inhumane policies against Uighurs". The camps have been criticized by the subcommittee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internment Camp
Internment is the imprisonment of people, commonly in large groups, without Criminal charge, charges or Indictment, intent to file charges. The term is especially used for the confinement "of enemy citizens in wartime or of terrorism suspects". Thus, while it can simply mean imprisonment, it tends to refer to preventive confinement rather than confinement ''after'' having been convicted of some crime. Use of these terms is subject to debate and political sensitivities. The word ''internment'' is also occasionally used to describe a neutral country's practice of detaining belligerent Military, armed forces and equipment on its territory during times of war, under the Hague Conventions of 1899 and 1907#Hague Convention of 1907, Hague Convention of 1907. Interned persons may be held in prisons or in facilities known as internment camps or Concentration camp, concentration camps. The term ''concentration camp'' originates from the Spanish–Cuban Ten Years' War when Spanish forces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
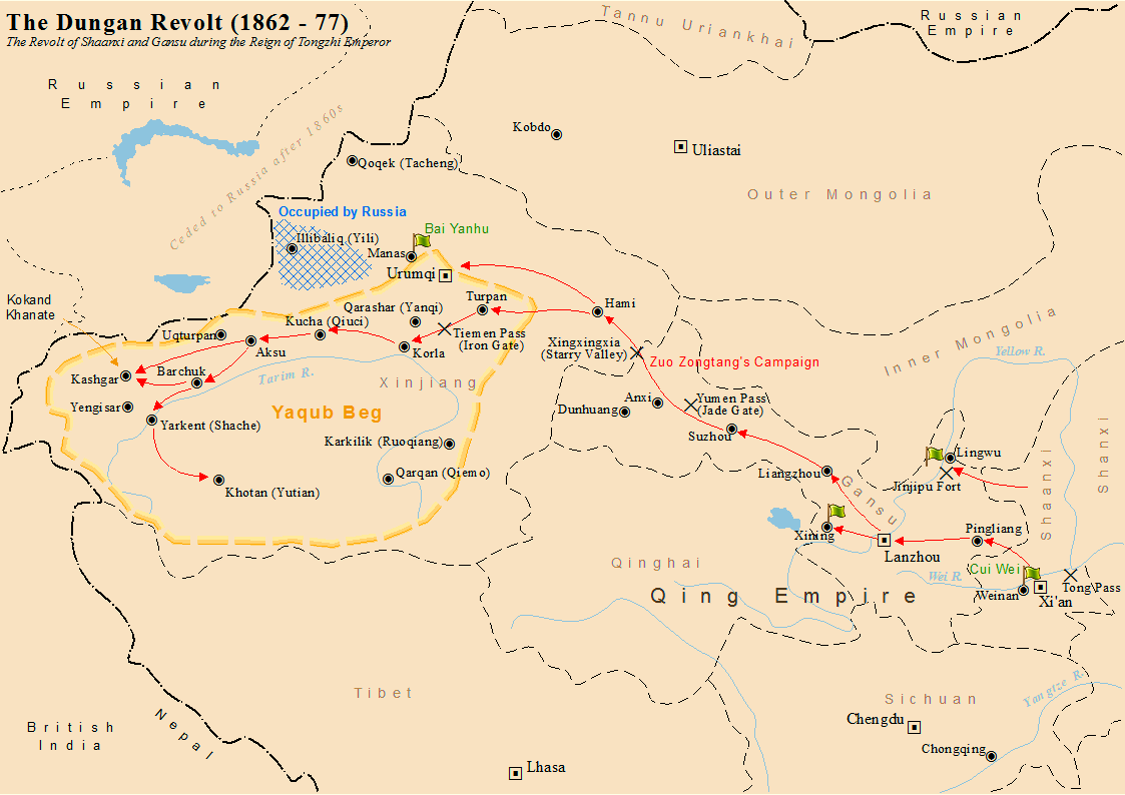
Dungan Revolt (1862–1877)
The Dungan Revolt (1862–1877), also known as the Tongzhi Hui Revolt (, Xiao'erjing: تُجِ خُوِ لُوًا, ) or Hui (Muslim) Minorities War, was a war fought in 19th-century western China, mostly during the reign of the Tongzhi Emperor (r. 1861–1875) of the Qing dynasty. The term sometimes includes the Panthay Rebellion in Yunnan, which occurred during the same period. However, this article refers specifically to two waves of uprising by various Chinese Muslims, mostly Hui people, Hui people, in Shaanxi, Gansu and Ningxia Province of China, provinces in the first wave, and then in Xinjiang in the second wave, between 1862 and 1877. The uprising was eventually suppressed by Qing forces led by Zuo Zongtang. The conflict began with riots by the Hui people, Hui and massacres of the Han Chinese, followed by the revenge massacres of the Hui by the Han. It resulted in massive demographic shifts in Northwest China, and led to a population loss of 21 million people from a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qing Dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing, was a Manchu-led Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China and an early modern empire in East Asia. The last imperial dynasty in Chinese history, the Qing dynasty was preceded by the Ming dynasty and succeeded by the Republic of China (1912–1949), Republic of China. At its height of power, the empire stretched from the Sea of Japan in the east to the Pamir Mountains in the west, and from the Mongolian Plateau in the north to the South China Sea in the south. Originally emerging from the Later Jin (1616–1636), Later Jin dynasty founded in 1616 and proclaimed in Shenyang in 1636, the dynasty seized control of the Ming capital Beijing and North China in 1644, traditionally considered the start of the dynasty's rule. The dynasty lasted until the Xinhai Revolution of October 1911 led to the abdication of the last emperor in February 1912. The multi-ethnic Qing dynasty Legacy of the Qing dynasty, assembled the territoria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |