|
Tabula Rasa
''Tabula rasa'' (; Latin for "blank slate") is the idea of individuals being born empty of any built-in mental content, so that all knowledge comes from later perceptions or sensory experiences. Proponents typically form the extreme "nurture" side of the nature versus nurture debate, arguing that humans are born without any "natural" psychological traits and that all aspects of one's personality, social and emotional behaviour, knowledge, or sapience are later imprinted by one's environment onto the mind as one would onto a wax tablet. This idea is the central view posited in the theory of knowledge known as empiricism. Empiricists disagree with the doctrines of innatism or rationalism, which hold that the mind is born already in possession of specific knowledge or rational capacity. Etymology ''Tabula rasa'' is a Latin phrase often translated as ''clean slate'' in English and originates from the Roman '' tabula'', a wax-covered tablet used for notes, which was blanked ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
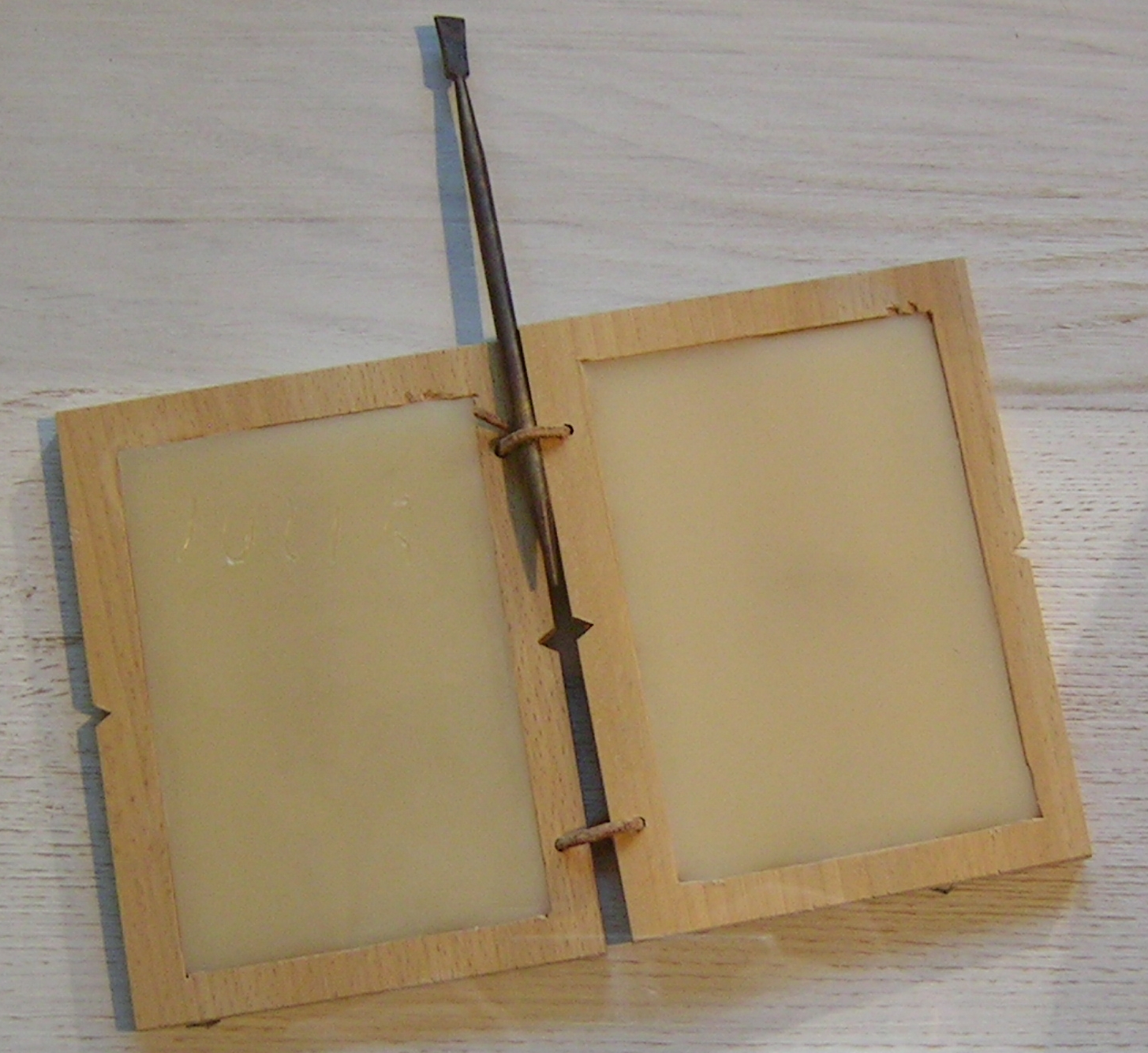
Slate (writing)
A slate is a thin piece of hard flat material, historically slate stone, which is used as a medium for writing on. Writing on a slate is impermanent and easily erased, and the same slate is then reused. Usage The writing slate consisted of a piece of slate, typically either 4x6 inches or 7x10 inches, encased in a wooden frame. Split slate was prepared by scraping with a steel edge, grinding with a flat stone and, finally, polishing with a mix of slate powder in water. Pencils were of a softer stone, such as shale, chalk or soapstone. In 1853 Charles Goodyear patented a compound of hard-vulcanised rubber with powdered porcelain, from which to make white pencils for writing on slates. Usually, a piece of cloth or slate sponge, sometimes attached with a string to the bottom of the writing slate, was used to erase it for reuse. History The exact origins of the writing slate remain unclear. References to its use can be found in the fourteenth century and evidence suggests t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zeno Of Citium
Zeno of Citium (; , ; c. 334 – c. 262 BC) was a Hellenistic philosophy, Hellenistic philosopher from Kition, Citium (, ), Cyprus. He was the founder of the Stoicism, Stoic school of philosophy, which he taught in Athens from about 300 BC. Based on the moral ideas of the Cynicism (philosophy), Cynics, Stoicism laid great emphasis on good and evil, goodness and calmness, peace of mind gained from living a life of virtue in accordance with nature. It proved very popular, and flourished as one of the Hellenistic philosophy, major schools of philosophy from the Hellenistic period through to the Roman era, and enjoyed revivals in the Renaissance as Neostoicism and in the current era as Modern Stoicism. Life Zeno was born c. 334 BC, in the colony of Kition, Citium in Classical Cyprus, Cyprus. His ancestry is disputed between Phoenician and Greeks, Greek, because Citium contained both Phoenician and Greek inhabitants. While a number of contemporary and modern historians regard Zeno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diogenes Laërtius
Diogenes Laërtius ( ; , ; ) was a biographer of the Greek philosophers. Little is definitively known about his life, but his surviving book ''Lives and Opinions of Eminent Philosophers'' is a principal source for the history of ancient Greek philosophy. His reputation is controversial among scholars because he often repeats information from his sources without critically evaluating it. In many cases, he focuses on insignificant details of his subjects' lives while ignoring important details of their philosophical teachings and he sometimes fails to distinguish between earlier and later teachings of specific philosophical schools. However, unlike many other ancient secondary sources, Diogenes Laërtius tends to report philosophical teachings without trying to reinterpret or expand on them, and so his accounts are often closer to the primary sources. Due to the loss of so many of the primary sources on which Diogenes relied, his work has become the foremost surviving source on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambridge University Press
Cambridge University Press was the university press of the University of Cambridge. Granted a letters patent by King Henry VIII in 1534, it was the oldest university press in the world. Cambridge University Press merged with Cambridge Assessment to form Cambridge University Press and Assessment under Queen Elizabeth II's approval in August 2021. With a global sales presence, publishing hubs, and offices in more than 40 countries, it published over 50,000 titles by authors from over 100 countries. Its publications include more than 420 academic journals, monographs, reference works, school and university textbooks, and English language teaching and learning publications. It also published Bibles, runs a bookshop in Cambridge, sells through Amazon, and has a conference venues business in Cambridge at the Pitt Building and the Sir Geoffrey Cass Sports and Social Centre. It also served as the King's Printer. Cambridge University Press, as part of the University of Cambridge, was a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Sedley
David Neil Sedley FBA (born 30 May 1947) is a British philosopher and historian of philosophy. He was the seventh Laurence Professor of Ancient Philosophy at Cambridge University. Early life Sedley was educated at Trinity College, Oxford where he was awarded a first class honours degree in Literae Humaniores in 1969. He was awarded a PhD in 1974 by University College London for a text, translation and commentary on Book XXVIII of Epicurus' ''On Nature''. He is the younger brother of Sir Stephen Sedley. Academic career Since 1976 Sedley has been a fellow of Christ's College, Cambridge; from 1996 he was Professor of Ancient Philosophy at Cambridge University before in July 2000 being elevated to the Laurence Professorship of Ancient Philosophy. He retired from this position at the end of September 2014. He was succeeded in this post by his former student, Gábor Betegh. He has held visiting appointments at Princeton University (September 1981 – March 1982), University ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walther Kranz
Walther Kranz (; 23 November 1884 in Georgsmarienhütte – 18 September 1960 in Bonn) was a German classical philologist (the study of classical antiquity) and historian of philosophy. Biography Kranz studied classical philology at the University of Berlin from 1903 to 1907 with Ulrich von Wilamowitz-Moellendorf, Hermann Diels and Eduard Norden. He received his doctorate in 1910 with Wilamowitz-Moellendorf. For several years he was a teacher at the Berlin-Grunewald experimental school. In 1932, he joined the University of Halle as an honorary professor of classical languages. He took over the publication of ''Die Fragmente der Vorsokratiker'' ('' The Fragments of the Pre-Socratics'') from the 5th edition onwards. After the takeover by the Nazis, he experienced political difficulties because his wife was Jewish. In 1937 he lost his full teaching license, and in 1943 he accepted an invitation from the University of Istanbul and taught there until 1950. From 1950 to 1955 he ser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hermann Alexander Diels
Hermann Alexander Diels (; 18 May 1848 – 4 June 1922) was a German classical scholar, who was influential in the area of early Greek philosophy and is known for his standard work ''Die Fragmente der Vorsokratiker''. Diels helped to import the term Presocratic into classical scholarship and developed the Diels–Kranz numbering system for ancient Greek Pre-Socratic texts. Biography Hermann Alexander Diels was born to Ludwig A Diels, a railroad stationmaster and Anna D. Diels in Wiesbaden-Biebrich, Hesse on May 18, 1848, and attended a Gymnasium in Wiesbaden (1858-67) before pursuing studies in higher education. He was educated at the universities of Bonn and Berlin but did not have enough money to complete a habilitation. As a result, Diles became a teacher at a Gymnasium in Flensburg, the Gelehrtenschule des Johanneums in Hamburg and the Konigstadtische Realschule in Berlin. In 1882, Diels joined the faculty of the Humboldt University of Berlin and in 1886 became professo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aetius (philosopher)
Aetius (; ) was a 1st- or 2nd-century AD doxographer and Eclecticism#Origin, Eclectic Philosophy, philosopher. Works None of Aetius' works survives today, but he solves a mystery about two major compilations of philosophical quotes. There are two extant books named ''Moralia, De Placita Philosophorum'' (Περὶ τῶν ἀρεσκόντων φιλοσόφοις φυσικῶν δογμάτων, "Opinions of the Philosophers") and ''Stobaeus, Eclogae Physicae'' (Ἐκλογαὶ φυσικαὶ καὶ ἠθικαί, "Physical and Moral Extracts"). The first of these is by Pseudo-Plutarch and the second is by Stobaeus. They are clearly both abridgements of a larger work. Hermann Diels, in his great ''Doxographi Graeci'' (1879), discovered that the 5th-century CE theologian Theodoret had full versions of the quotes which were shortened in the abridgements. This means that Theodoret had managed to procure the original book which Pseudo-Plutarch and Stobaeus had shortened. He calls t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doxography
Doxography ( – "an opinion", "a point of view" + – "to write", "to describe") is a term used especially for the works of classical historians, describing the points of view of past philosophers and scientists. The term was coined by the German classical scholar Hermann Alexander Diels. In Ancient Greek philosophy A great many philosophical works have been lost; our limited knowledge of such lost works comes chiefly through the doxographical works of later philosophers, commentators, and biographers. The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy lists the following works as being representative doxographies: * Cicero - '' Academica'', '' De Finibus'', ''De Natura Deorum'', '' De Fato'', ''De Officiis'' * Aetius - '' Vetusta Placita'' * Clement of Alexandria - ''Stromata'' * Diogenes Laertius - '' Lives and Opinions of Eminent Philosophers'' * Hippolytus of Rome - '' Refutation of All Heresies'' Philosophers such as Plato and Aristotle also act as doxographers, as thei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stoicism
Stoicism is a school of Hellenistic philosophy that flourished in ancient Greece and Rome. The Stoics believed that the universe operated according to reason, ''i.e.'' by a God which is immersed in nature itself. Of all the schools of ancient philosophy, Stoicism made the greatest claim to being utterly systematic. The Stoics provided a unified account of the world, constructed from ideals of logic, monistic physics, and naturalistic ethics. These three ideals constitute virtue which is necessary for 'living a well reasoned life', seeing as they are all parts of a logos, or philosophical discourse, which includes the mind's rational dialogue with itself. Stoicism was founded in the ancient Agora of Athens by Zeno of Citium around 300 BC, and flourished throughout the Greco-Roman world until the 3rd century AD, and among its adherents was Roman Emperor Marcus Aurelius. Along with Aristotelian term logic, the system of propositional logic developed by the Stoics was one of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greek Philosophy
Ancient Greek philosophy arose in the 6th century BC. Philosophy was used to make sense of the world using reason. It dealt with a wide variety of subjects, including astronomy, epistemology, mathematics, political philosophy, ethics, metaphysics, ontology, logic, biology, rhetoric and aesthetics. Greek philosophy continued throughout the Hellenistic period and later evolved into Roman philosophy. Greek philosophy has influenced much of Western culture since its inception, and can be found in many aspects of public education. Alfred North Whitehead once claimed: "The safest general characterization of the European philosophical tradition is that it consists of a series of footnotes to Plato". Clear, unbroken lines of influence lead from ancient Greek and Hellenistic philosophers to Roman philosophy, early Islamic philosophy, medieval scholasticism, the European Renaissance and the Age of Enlightenment. Greek philosophy was influenced to some extent by the older wisdom litera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |