|
Table Of Stars With Bayer Designations
This table lists those stars or other objects which have Bayer designations, grouped by the constellation part of the designation. See also * Greek alphabet * List of constellations * Table of stars with Flamsteed designations This table lists those stars/objects which have Flamsteed designations by the constellation in which those stars/objects lie. The name given is that of the article if it does not reflect the Flamsteed designation. Some articles are linked twice, ... Notes {{notelist Lists of stars * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Star
A star is an astronomical object comprising a luminous spheroid of plasma held together by its gravity. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked eye at night, but their immense distances from Earth make them appear as fixed points of light. The most prominent stars have been categorised into constellations and asterisms, and many of the brightest stars have proper names. Astronomers have assembled star catalogues that identify the known stars and provide standardized stellar designations. The observable universe contains an estimated to stars. Only about 4,000 of these stars are visible to the naked eye, all within the Milky Way galaxy. A star's life begins with the gravitational collapse of a gaseous nebula of material composed primarily of hydrogen, along with helium and trace amounts of heavier elements. Its total mass is the main factor determining its evolution and eventual fate. A star shines for most of its active life due t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xi Andromedae
Xi Andromedae (ξ Andromedae, abbreviated Xi And, ξ And), officially named Adhil , is a solitary star in the northern constellation of Andromeda. It has an apparent magnitude of +4.9. Based on parallax measurements obtained during the Gaia mission, it lies at a distance of roughly from the Sun. Nomenclature ''ξ Andromedae'' ( Latinised to ''Xi Andromedae'') is the star's Bayer designation. It also bears the Flamsteed designation ''46 Andromedae''. Johann Bayer labeled this star "ξ" in his '' Uranometria''. The star appeared in John Flamsteed's ''Atlas Coelestis'', but was unlabeled. It was later designated as ''46 And'' by Jérôme Lalande. The label "ξ" was used in ''Atlas Coelestis'', apparently erroneously, for what Bayer had labeled "A" (Bayer's ''A Andromedae'' has the Flamsteed designation ''49 Andromedae''). It bore the traditional name ''Adhil'', which is derived from the Arabic الذيل ''að-ðayl'' "the train" (lit. "the tail"). In 2016, the Intern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
49 Andromedae
49 Andromedae (abbreviated 49 And) is a star in the constellation Andromeda. ''49 Andromedae'' is the Flamsteed designation though it also bears the Bayer designation A Andromedae. It is visible to the naked eye under good viewing conditions with an apparent visual magnitude of 5.269. The distance to 49 Andromedae, as determined from its annual parallax shift of , is around 314 light-years. It is moving closer to the Sun with a heliocentric radial velocity of −11.5 km/s. With an estimated age of years, this is an aging red-clump giant star with a stellar classification of K0 III, indicating it is generating energy by helium fusion at its core. The spectrum displays "slightly strong" absorption lines of cyanogen (CN). It has 2.07 times the mass of the Sun and has expanded to 11 times the Sun's radius. The star is radiating 71 times the Sun's luminosity from its enlarged photosphere at an effective temperature The effective temperature of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
62 Andromedae
62 Andromedae, abbreviated 62 And, is a single star in the northern constellation Andromeda. ''62 Andromedae'' is the Flamsteed designation; it also bears the Bayer designation of c Andromedae. It is bright enough to be seen by the naked eye, with an apparent magnitude of 5.31. Based upon parallax measurements made during the Gaia mission, it is at a distance of roughly 273 light-years (84 parsecs) from Earth. The star is moving closer to the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of −30 km/s, and is predicted to come to within in 1,6 million years. This is an A-type main-sequence star with a stellar classification of A0 V. Abt and Morrel (1995) gave it a class of A1 III, matching a more evolved giant star. The star has 2.42 times the mass of the Sun, about 1.8 times the Sun's radius, and is spinning with a projected rotational velocity of 86 km/s. It is radiating 45 times the Sun's luminosity from its photosphere at an effective temperatu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
60 Andromedae
60 Andromedae (abbreviated 60 And) is a star system in the northern constellation of Andromeda, located to the west-northwest of Gamma Andromedae. ''60 Andromedae'' is the Flamsteed designation though the star also bears the Bayer designation b Andromedae. It is bright enough to be seen by the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.82. Based upon parallax measurements made during the Hipparcos mission, it is at a distance of roughly from Earth. This system is known to have three components. The primary is a giant star with a stellar classification of , meaning that an overabundance of barium ionized one time is observed in the spectrum of the star, making it a barium star. The secondary component is likely a white dwarf with a period of 748.2 days and an eccentricity of 0.34. There is a third component at an angular separation of 0.22 arcsecond A minute of arc, arcminute (arcmin), arc minute, or minute arc, denoted by the symbol , is a unit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Omega Andromedae
Omega Andromedae (ω And, ω Andromedae) is the Bayer designation for a slowly co-rotating binary star system in the northern constellation of Andromeda. Parallax measurements made during the ''Gaia'' mission make this system to be approximately from Earth. Its apparent visual magnitude is +4.83, which makes it bright enough to be seen with the naked eye. The primary component has a stellar classification of F5 IVe. The IV luminosity class indicates that it is probably a subgiant star that is in the process of evolving away from the main sequence as the supply of hydrogen at its core depletes. However, Abt (1985) gives a classification of F3 V, suggesting it is an F-type main-sequence star. The measured angular diameter of the primary star is . At the system's estimated distance this yields a size of about 2.2 times that of the Sun. It is emitting about seven times solar luminosity from its outer atmosphere at an effective temperature of . This heat giv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psi Andromedae
Psi Andromedae (ψ And, ψ Andromedae) is the Bayer designation for a triple star system in the northern constellation of Andromeda. The combined apparent visual magnitude of this system is 4.95. Based upon parallax measurements, is roughly from Earth, with a large margin of error. The primary component has a stellar classification of G5 Ib, which matches the spectrum of an evolved supergiant star. It forms a pair with a star of type B9 with an unknown luminosity class separated by 0.28 arcseconds. A third component has a separation of 0.14 arcseconds. Details of the orbital arrangement remain uncertain. Naming In Chinese, (), meaning '' Flying Serpent'', refers to an asterism consisting of ψ Andromedae, α Lacertae, 4 Lacertae, π2 Cygni, π1 Cygni, HD 206267, ε Cephei, β Lacertae, σ Cassiopeiae, ρ Cassiopeiae, τ Cassiopeiae, AR Cassiopeiae, 9 Lacertae, 3 Andromedae, 7 Andromedae, 8 Andromedae, λ Andromedae, κ Andromedae and ι Andromedae,. Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chi Andromedae
Chi Andromedae ( Andromedae, And) is the Bayer designation for a star in the northern constellation of Andromeda. It has an apparent visual magnitude of +5.01, which is relatively faint for a naked-eye star. Based upon parallax measurements made during the Gaia mission, Chi Andromedae is located around from Earth. χ Andromedae is a member of (), meaning ''Heaven's Great General'', together with γ Andromedae, φ Persei, 51 Andromedae, 49 Andromedae, θ Andromedae, τ Andromedae, 56 Andromedae, β Trianguli, γ Trianguli and δ Trianguli. Consequently, the Chinese name for χ Andromedae itself is (, en, the Fifth Star of Heaven's Great General.) This is most likely a spectroscopic binary system with an estimated orbital period of 20.8 years and an eccentricity of 0.37. The primary component has a stellar classification of G8 III, which indicates it is a giant star that has exhausted the supply of hydrogen at its core and evolved away from the main seque ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phi Andromedae
Phi Andromedae (φ Andromedae, φ And) is the Bayer designation for a binary star system near the border of the northern constellation of Andromeda. This system has a combined apparent visual magnitude of 4.25 and is visible to the naked eye. Based upon parallax measurements made during the Hipparcos mission, this star system is located at a distance of about from Earth. With χ And it forms the Chinese asterism 軍南門 (''Keun Nan Mun'', Mandarin ''jūnnánmén)'', "the South Gate of the Camp".In Chinese literature, φ Andromedae is stand alone in the asterism and χ Andromeda is member of Tien Ta Tseang (Heaven's Great General) asterism, seeAEEA (Activities of Exhibition and Education in Astronomy) 天文教育資訊網 2006 年 7 月 9 日and/ref> Components The 4.46 magnitude primary component is a Be star with a stellar classification of B7 Ve, indicating that it is a B-type main sequence star that shows prominent emission lines of hydrogen in its s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
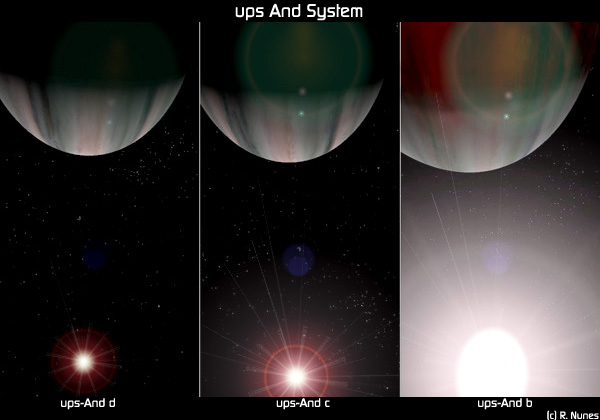
Upsilon Andromedae
Upsilon Andromedae (υ Andromedae, abbreviated Upsilon And, υ And) is a binary star located 44 light-years from Earth in the constellation of Andromeda. The system consists of an F-type main-sequence star (designated υ Andromedae A, officially named Titawin in the Amazigh language ) and a smaller red dwarf. , four extrasolar planets (designated Upsilon Andromedae b, c, d and e; the first three named Saffar, Samh and Majriti, respectively) are believed to orbit υ Andromedae A. All four are likely to be jovian planets that are comparable in size to Jupiter. This was both the first multiple- planet system to be discovered around a main-sequence star, and the first multiple-planet system known in a multiple-star system. Nomenclature ''υ Andromedae'' ( Latinised to ''Upsilon Andromedae'') is the system's Bayer designation. Under the rules for naming objects in binary star systems, the two components are designated A and B. Under the same rules, the first planet disc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tau Andromedae
Tau Andromedae, Latinized from τ Andromedae, is the Bayer designation for a single star in the northern constellation of Andromeda. It has an apparent visual magnitude of +4.94, which is bright enough to be viewed from dark suburban skies. From parallax measurements made during the Gaia mission, the distance to this star can be estimated as roughly from Earth. The brightness of this star is diminished by 0.24 in magnitude due to extinction caused by intervening gas and dust. It is drifting closer to the Sun with a radial velocity of −14 km/s. The spectrum of this star matches a stellar classification of B5 III, with the luminosity class of III indicating that this is a giant star. It is radiating about 851 times the luminosity of the Sun from its photosphere at an effective temperature of 12,670 K. The star is an estimated 217 million years old and is spinning with a high projected rotational velocity of ~74 km/s. Naming In Chinese, (), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sigma Andromedae
Sigma Andromedae, Latinized from σ Andromedae, is the Bayer designation for a single star in the northern constellation of Andromeda. It has an apparent visual magnitude of +4.5, which is bright enough to be seen with the naked eye from most locations. Parallax measurements made during the Gaia mission place it at a distance of about . The magnitude of the star is diminished by 0.08 from extinction caused by intervening gas and dust. It is drifting closer to the Sun with a radial velocity of –8 km/s. This star has a stellar classification of A2 V, which matches the spectrum of an A-type main sequence star. It is about 450 million years old and is spinning rapidly with a projected rotational velocity of 123 km/s. The star has 2.12 times the mass of the Sun and 2.13 times the Sun's girth. It is radiating 21 times the luminosity of the Sun from its photosphere at an effective temperature of 8,929 K, giving it the white-hued glow of an A-type star. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |