|
Sigma Andromedae
Sigma Andromedae, Latinized from σ Andromedae, is the Bayer designation for a single star in the northern constellation of Andromeda. It has an apparent visual magnitude of +4.5, which is bright enough to be seen with the naked eye from most locations. Parallax measurements made during the Gaia mission place it at a distance of about . The magnitude of the star is diminished by 0.08 from extinction caused by intervening gas and dust. It is drifting closer to the Sun with a radial velocity of –8 km/s. This star has a stellar classification of A2 V, which matches the spectrum of an A-type main sequence star. It is about 450 million years old and is spinning rapidly with a projected rotational velocity of 123 km/s. The star has 2.12 times the mass of the Sun and 2.13 times the Sun's girth. It is radiating 21 times the luminosity of the Sun from its photosphere at an effective temperature of 8,929 K, giving it the white-hued glow of an A-type star. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
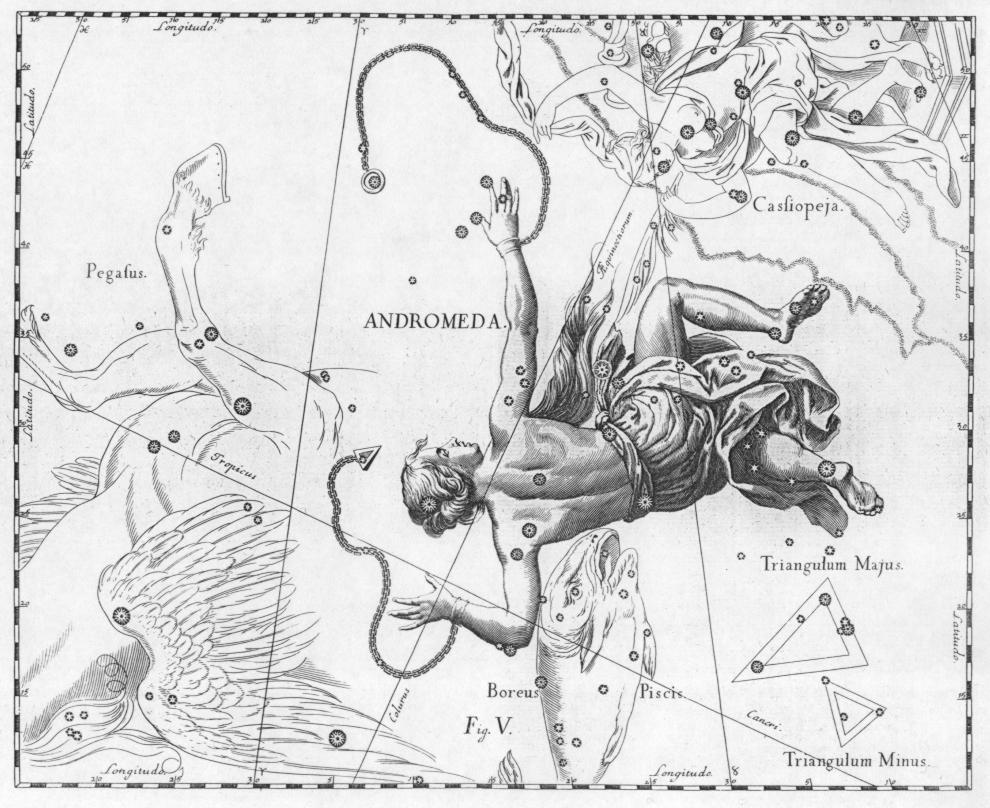
Andromeda (constellation)
Andromeda is one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century Greco-Roman astronomer Ptolemy, and one of the 88 modern constellations. Located in the northern celestial hemisphere, it is named for Andromeda, daughter of Cassiopeia, in the Greek myth, who was chained to a rock to be eaten by the sea monster Cetus. Andromeda is most prominent during autumn evenings in the Northern Hemisphere, along with several other constellations named for characters in the Perseus myth. Because of its northern declination, Andromeda is visible only north of 40° south latitude; for observers farther south, it lies below the horizon. It is one of the largest constellations, with an area of 722 square degrees. This is over 1,400 times the size of the full moon, 55% of the size of the largest constellation, Hydra, and over 10 times the size of the smallest constellation, Crux. Its brightest star, Alpha Andromedae, is a binary star that has also been counted as a part of Pegasu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Effective Temperature
The effective temperature of a body such as a star or planet is the temperature of a black body that would emit the same total amount of electromagnetic radiation. Effective temperature is often used as an estimate of a body's surface temperature when the body's emissivity curve (as a function of wavelength) is not known. When the star's or planet's net emissivity in the relevant wavelength band is less than unity (less than that of a black body), the actual temperature of the body will be higher than the effective temperature. The net emissivity may be low due to surface or atmospheric properties, including greenhouse effect. Star The effective temperature of a star is the temperature of a black body with the same luminosity per ''surface area'' () as the star and is defined according to the Stefan–Boltzmann law . Notice that the total ( bolometric) luminosity of a star is then , where is the stellar radius. The definition of the stellar radius is obviously not stra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A-type Main-sequence Stars
A type or type A may refer to: * A-type asteroid, a type of relatively uncommon inner-belt asteroids * A type blood, a type in the ABO blood group system * A-type inclusion, a type of cell inclusion * A-type potassium channel, a type of voltage-gated potassium channel * A type proanthocyanidin, a specific type of flavonoids * A-type star, a class of stars * Type A Dolby Noise Reduction, a type of Dolby noise-reduction system * Type A climate, a type in the Köppen climate classification * Type A flu, a type of influenza virus * Type A evaluation of uncertainty, an uncertainty in measurement that can be inferred, for example, from repeated measurement * Type A (label) A type or type A may refer to: * A-type asteroid, a type of relatively uncommon inner-belt asteroids * A type blood, a type in the ABO blood group system * A-type inclusion, a type of cell inclusion * A-type potassium channel, a type of voltage-g ..., a music label that for example produced the 2004 album '' What D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Star Names
Chinese star names ( Chinese: , ''xīng míng'') are named according to ancient Chinese astronomy and astrology. The sky is divided into star mansions (, ''xīng xiù'', also translated as "lodges") and asterisms (, ''xīng guān''). The system of 283 asterisms under Three Enclosures and Twenty-eight Mansions was established by Chen Zhuo of the Three Kingdoms period, who synthesized ancient constellations and the asterisms created by early astronomers Shi Shen, Gan De and Wuxian. Since the Han and Jin Dynasties, stars have been given reference numbers within their asterisms in a system similar to the Bayer or Flamsteed designations, so that individual stars can be identified. For example, Deneb (α Cyg) is referred to as (''Tiān Jīn Sì'', the Fourth Star of Celestial Ford). In the Qing Dynasty, Chinese knowledge of the sky was improved by the arrival of European star charts. ''Yixiang Kaocheng'', compiled in mid-18th century by then deputy Minister of Rites Ignaz Kö ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rho Andromedae
Rho Andromedae, Latinized from ρ Andromedae, is the Bayer designation for a star in the northern constellation of Andromeda. It has an apparent visual magnitude of +5.19, which, according to the Bortle Dark-Sky Scale, is bright enough to be seen with the naked eye from dark suburban skies. Based upon parallax measurements, this star is at a distance of approximately from the Sun. It is drifting further away with a radial velocity of +10 km/s. The stellar classification of this star is F5IV-V, showing mixed spectral features of a main sequence and subgiant stage. It is about 1.3 billion years old with 3.4 times the girth of the Sun and is spinning with a projected rotational velocity of 44 km/s. The outer envelope is radiating around 18 times the luminosity of the Sun from its photosphere at an effective temperature of 6,471 K, giving it the yellow-white hue of an F-type star. X-ray emissions were detected from this star during the EXOSAT mission. Nam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theta Andromedae
Theta Andromedae is a binary star system in the northern constellation of Andromeda. ''Theta Andromedae'', Latinized from θ Andromedae, is its Bayer designation. It is located at a distance of approximately from the Sun, and has an apparent visual magnitude of 4.6. On the Bortle Dark-Sky Scale, this makes it visible to the naked eye from outside urban regions. Based on its motion through space, this system appears to be a member of the Sirius supercluster. The brighter component is a white hued A-type main-sequence star with a stellar classification of A2 V. It is one of the least photometrically variable stars known. The star shows a high rate of rotation with a projected rotational velocity of 102 km/s. It has an estimated 2.8 times the mass of the Sun and is radiating 113 times the Sun's luminosity from its photosphere at an effective temperature of 8,960 K. The relatively high chemical abundances of iron and heavier elements suggests it may be a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wall (Chinese Constellation)
The Wall mansion () is one of the Twenty-eight mansions of the Chinese constellations. It is one of the northern mansions of the Black Tortoise The Black Tortoise () is one of the Four Symbols of the Chinese constellations. Despite its English name, it is usually depicted as a tortoise entwined together with a snake. The name used in East Asian languages does not mention either anima .... Asterisms {{Chinese constellation Chinese constellations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Astronomy
Astronomy in China has a long history stretching from the Shang dynasty, being refined over a period of more than 3,000 years. The ancient Chinese people have identified stars from 1300 BCE, as Chinese star names later categorized in the twenty-eight mansions have been found on oracle bones unearthed at Anyang, dating back to the mid-Shang dynasty. The core of the "mansion" (宿 ''xiù'') system also took shape around this period, by the time of King Wu Ding (1250–1192 BCE). Detailed records of astronomical observations began during the Warring States period (fourth century BCE) and flourished from the Han period onward. Chinese astronomy was equatorial, centered on close observation of circumpolar stars, and was based on different principles from those in traditional Western astronomy, where heliacal risings and settings of zodiac constellations formed the basic ecliptic framework. Joseph Needham has described the ancient Chinese as the most persistent and accurat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
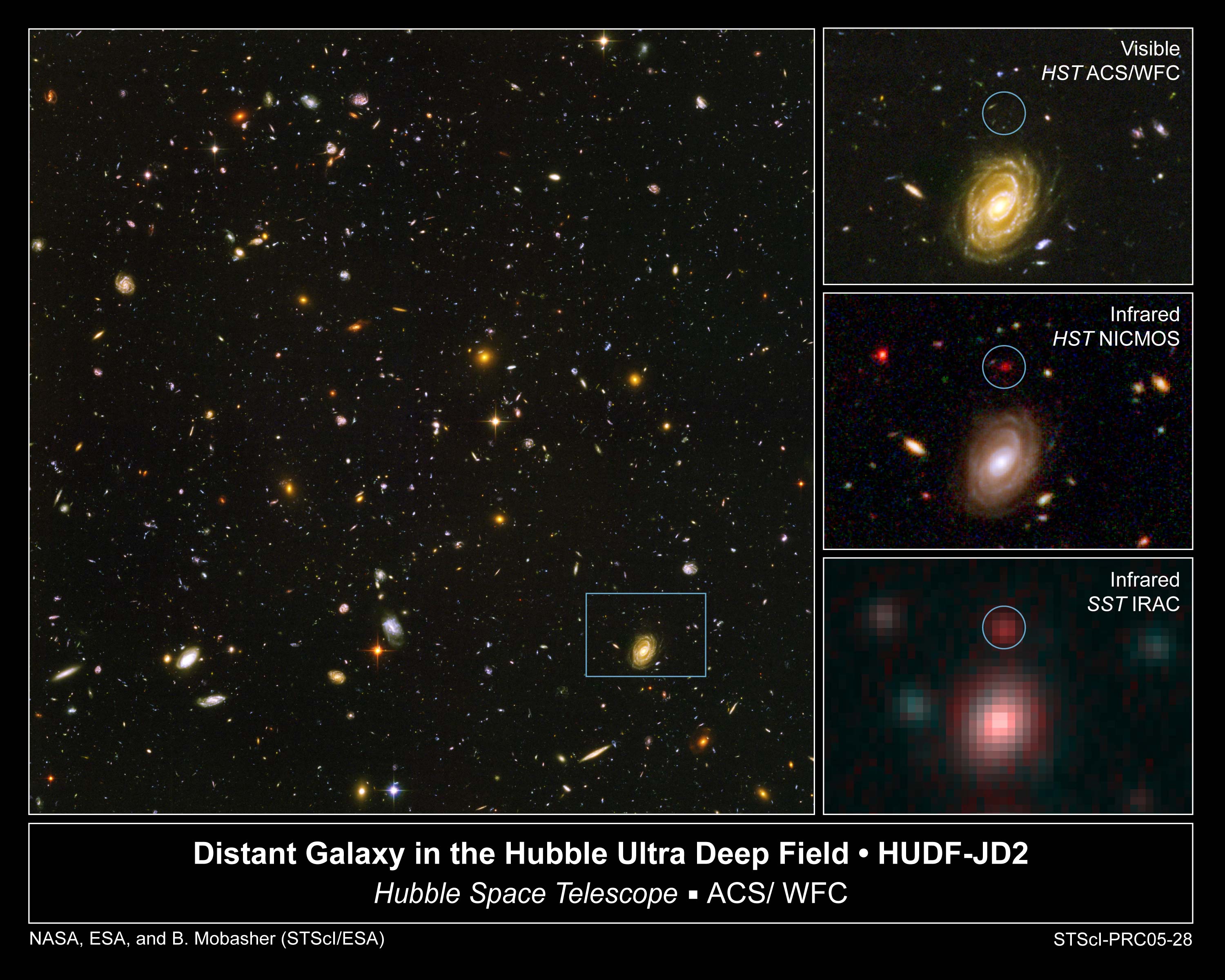
Spitzer Space Telescope
The Spitzer Space Telescope, formerly the Space Infrared Telescope Facility (SIRTF), was an infrared space telescope launched in 2003. Operations ended on 30 January 2020. Spitzer was the third space telescope dedicated to infrared astronomy, following IRAS (1983) and ISO (1995–1998). It was the first spacecraft to use an Earth-trailing orbit, later used by the Kepler planet-finder. The planned mission period was to be 2.5 years with a pre-launch expectation that the mission could extend to five or slightly more years until the onboard liquid helium supply was exhausted. This occurred on 15 May 2009. Without liquid helium to cool the telescope to the very low temperatures needed to operate, most of the instruments were no longer usable. However, the two shortest-wavelength modules of the IRAC camera continued to operate with the same sensitivity as before the helium was exhausted, and continued to be used into early 2020 in the Spitzer Warm Mission. During the warm missio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Debris Disk
A debris disk (American English), or debris disc (Commonwealth English), is a circumstellar disk of dust and debris in orbit around a star. Sometimes these disks contain prominent rings, as seen in the image of Fomalhaut on the right. Debris disks are found around stars with mature planetary systems, including at least one debris disk in orbit around an evolved neutron star. Debris disks can also be produced and maintained as the remnants of collisions between planetesimals, otherwise known as asteroids and comets. By 2001, more than 900 candidate stars had been found to possess a debris disk. They are usually discovered by examining the star system in infrared light and looking for an excess of radiation beyond that emitted by the star. This excess is inferred to be radiation from the star that has been absorbed by the dust in the disk, then re-radiated away as infrared energy. Debris disks are often described as massive analogs to the debris in the Solar System. Most known d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |