|
Tabes Dorsalis
Tabes dorsalis is a late consequence of neurosyphilis, characterized by the slow degeneration (specifically, demyelination) of the neural tracts primarily in the Dorsal root ganglion, dorsal root ganglia of the spinal cord (nerve root). These patients have lancinating nerve root pain which is aggravated by coughing, and features of sensory ataxia with ocular involvement. Signs and symptoms Signs and symptoms may not appear for decades after the initial infection and include weakness, hyporeflexia, diminished reflexes, paresthesias (shooting and burning pains, pricking sensations, and formication), hypoesthesias (abnormally diminished sense of touch), tabetic gait (locomotor ataxia), progressive degeneration of the joints, loss of coordination, episodes of intense pain and disturbed sensation (including glossodynia), personality changes, urinary incontinence, dementia, Hearing loss, deafness, visual impairment, positive Romberg's test, and impaired response to light (Argyll Robertso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurosyphilis
Neurosyphilis is the infection of the central nervous system by '' Treponema pallidum'', the bacterium that causes the sexually transmitted infection syphilis. In the era of modern antibiotics, the majority of neurosyphilis cases have been reported in HIV-infected patients. There is a wide variety of symptoms that neurosyphilis can present with depending on the affected structure of the central nervous system. While early neurosyphilis is often asymptomatic, meningitis is the most common neurological presentation of the early stage. Late neurosyphilis typically involves the brain and spinal cord parenchyma, manifesting as tabes dorsalis and general paresis. Tertiary syphilis can involve several different organ systems, though neurosyphilis may occur at any stage of infection. Clinical history, a physical neurological examination, and a lumbar puncture to obtain cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) for analysis are crucial for diagnosing neurosyphilis. There is no single laboratory t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argyll Robertson Pupil
Argyll Robertson pupils (AR pupils) are bilateral small pupils that reduce in size on a near object (i.e., they accommodate), but do ''not'' constrict when exposed to bright light (i.e., they do not react). They are a highly specific sign of neurosyphilis; however, Argyll Robertson pupils may also be a sign of diabetic neuropathy. In general, pupils that accommodate but do not react are said to show light-near dissociation (i.e., it is the absence of a miotic reaction to light, both direct and consensual, with the preservation of a miotic reaction to near stimulus (accommodation/convergence)). AR pupils are extremely uncommon in the developed world. There is continued interest in the underlying pathophysiology, but the scarcity of cases makes ongoing research difficult. Pathophysiology The two different types of near response are caused by different underlying disease processes. '' Adie's pupil'' is caused by damage to ''peripheral'' pathways to the pupil (parasympathetic neu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerebrospinal Fluid
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear, colorless transcellular body fluid found within the meningeal tissue that surrounds the vertebrate brain and spinal cord, and in the ventricles of the brain. CSF is mostly produced by specialized ependymal cells in the choroid plexuses of the ventricles of the brain, and absorbed in the arachnoid granulations. It is also produced by ependymal cells in the lining of the ventricles. In humans, there is about 125 mL of CSF at any one time, and about 500 mL is generated every day. CSF acts as a shock absorber, cushion or buffer, providing basic mechanical and immunological protection to the brain inside the skull. CSF also serves a vital function in the cerebral autoregulation of cerebral blood flow. CSF occupies the subarachnoid space (between the arachnoid mater and the pia mater) and the ventricular system around and inside the brain and spinal cord. It fills the ventricles of the brain, cisterns, and sulci, as well as the ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treponema Pallidum
''Treponema pallidum'', formerly known as ''Spirochaeta pallida'', is a Microaerophile, microaerophilic, Gram-negative bacteria, gram-negative, spirochaete bacterium with subspecies that cause the diseases syphilis, bejel (also known as endemic syphilis), and yaws. It is known to be transmitted only among humans and baboons. ''T. pallidum'' can enter the host through mucosal membranes or open lesions in the skin and is primarily spread through sexual contact. It is a helically coiled microorganism usually 6–15 μm long and 0.1–0.2 μm wide. ''T. pallidum'''s lack of both a Citric acid cycle, tricarboxylic acid cycle and processes for oxidative phosphorylation results in minimal metabolic activity. As a Chemoorganoheterotrophic, chemoorganoheterotroph, ''Treponema pallidum'' is an obligate parasite that acquires its glucose carbon source from its host. Glucose can be used not only as a primary carbon source but also in glycolytic mechanisms to generate ATP needed to power the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacterium
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit the air, soil, water, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of Earth's crust. Bacteria play a vital role in many stages of the nutrient cycle by recycling nutrients and the fixation of nitrogen from the atmosphere. The nutrient cycle includes the decomposition of dead bodies; bacteria are responsible for the putrefaction stage in this process. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, extremophile bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, such as hydrogen sulphide and methane, to energy. Bacteria also live in mutualistic, commensal and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spirochete
A spirochaete () or spirochete is a member of the phylum Spirochaetota (also called Spirochaetes ), which contains distinctive diderm (double-membrane) Gram-negative bacteria, most of which have long, helically coiled (corkscrew-shaped or spiraled, hence the name) cells. Spirochaetes are chemoheterotrophic in nature, with lengths between 3 and 500 μm and diameters around 0.09 to at least 3 μm. Spirochaetes are distinguished from other bacterial phyla by the location of their flagella, called endoflagella, or periplasmic flagella, which are sometimes called ''axial filaments''. Endoflagella are anchored at each end (pole) of the bacterium within the periplasmic space (between the inner and outer membranes) where they project backwards to extend the length of the cell. These cause a twisting motion which allows the spirochaete to move. When reproducing, a spirochaete will undergo asexual transverse binary fission. Most spirochaetes are free-living and anaerob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tertiary Syphilis
Syphilis () is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium ''Treponema pallidum'' subspecies ''pallidum''. The signs and symptoms depend on the stage it presents: primary, secondary, latent or tertiary. The primary stage classically presents with a single chancre (a firm, painless, non-itchy skin ulceration usually between 1 cm and 2 cm in diameter), though there may be multiple sores. In secondary syphilis, a diffuse rash occurs, which frequently involves the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. There may also be sores in the mouth or vagina. Latent syphilis has no symptoms and can last years. In tertiary syphilis, there are gummas (soft, non-cancerous growths), neurological problems, or heart symptoms. Syphilis has been known as " the great imitator", because it may cause symptoms similar to many other diseases. Syphilis is most commonly spread through sexual activity. It may also be transmitted from mother to baby during pregnancy or at bir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demyelinating Disease
A demyelinating disease refers to any disease affecting the nervous system where the myelin sheath surrounding neurons is damaged. This damage disrupts the transmission of signals through the affected nerves, resulting in a decrease in their conduction ability. Consequently, this reduction in conduction can lead to deficiencies in sensation, movement, cognition, or other functions depending on the nerves affected. Various factors can contribute to the development of demyelinating diseases, including genetic predisposition, infectious agents, autoimmune reactions, and other unknown factors. Proposed causes of demyelination include genetic predisposition, environmental factors such as viral infections or exposure to certain chemicals. Additionally, exposure to commercial insecticides like sheep dip, weed killers, and flea treatment preparations for pets, which contain organophosphates, can also lead to nerve demyelination. Chronic exposure to neuroleptic medications may also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proprioception
Proprioception ( ) is the sense of self-movement, force, and body position. Proprioception is mediated by proprioceptors, a type of sensory receptor, located within muscles, tendons, and joints. Most animals possess multiple subtypes of proprioceptors, which detect distinct kinesthetic parameters, such as joint position, movement, and load. Although all mobile animals possess proprioceptors, the structure of the sensory organs can vary across species. Proprioceptive signals are transmitted to the central nervous system, where they are integrated with information from other Sensory nervous system, sensory systems, such as Visual perception, the visual system and the vestibular system, to create an overall representation of body position, movement, and acceleration. In many animals, sensory feedback from proprioceptors is essential for stabilizing body posture and coordinating body movement. System overview In vertebrates, limb movement and velocity (muscle length and the rate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gait
Gait is the pattern of Motion (physics), movement of the limb (anatomy), limbs of animals, including Gait (human), humans, during Animal locomotion, locomotion over a solid substrate. Most animals use a variety of gaits, selecting gait based on speed, terrain, the need to wikt:maneuver, maneuver, and energetic efficiency. Different animal species may use different gaits due to differences in anatomy that prevent use of certain gaits, or simply due to evolved innate preferences as a result of habitat differences. While various gaits are given specific names, the complexity of biological systems and interacting with the environment make these distinctions "fuzzy" at best. Gaits are typically classified according to footfall patterns, but recent studies often prefer definitions based on mechanics. The term typically does not refer to limb-based propulsion through fluid mediums such as water or air, but rather to propulsion across a solid substrate by generating reactive forces against ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photophobia
Photophobia is a medical symptom of abnormal intolerance to visual perception of light. As a medical symptom, photophobia is not a morbid fear or phobia, but an experience of discomfort or pain to the eyes due to light exposure or by presence of actual physical sensitivity of the eyes, though the term is sometimes additionally applied to abnormal or irrational fear of light, such as heliophobia. The term ''photophobia'' comes . Causes Patients may develop photophobia as a result of several different medical conditions, related to the human eye, eye, the nervous system, genetic, or other causes. Photophobia may manifest itself in an increased response to light starting at any step in the visual system, such as: * Too much light entering the eye. Too much light can enter the eye if it is damaged, such as with corneal abrasion and retinal damage, or if its pupil is unable to normally constrict (seen with damage to the oculomotor nerve). * Due to albinism, the lack of pigment in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
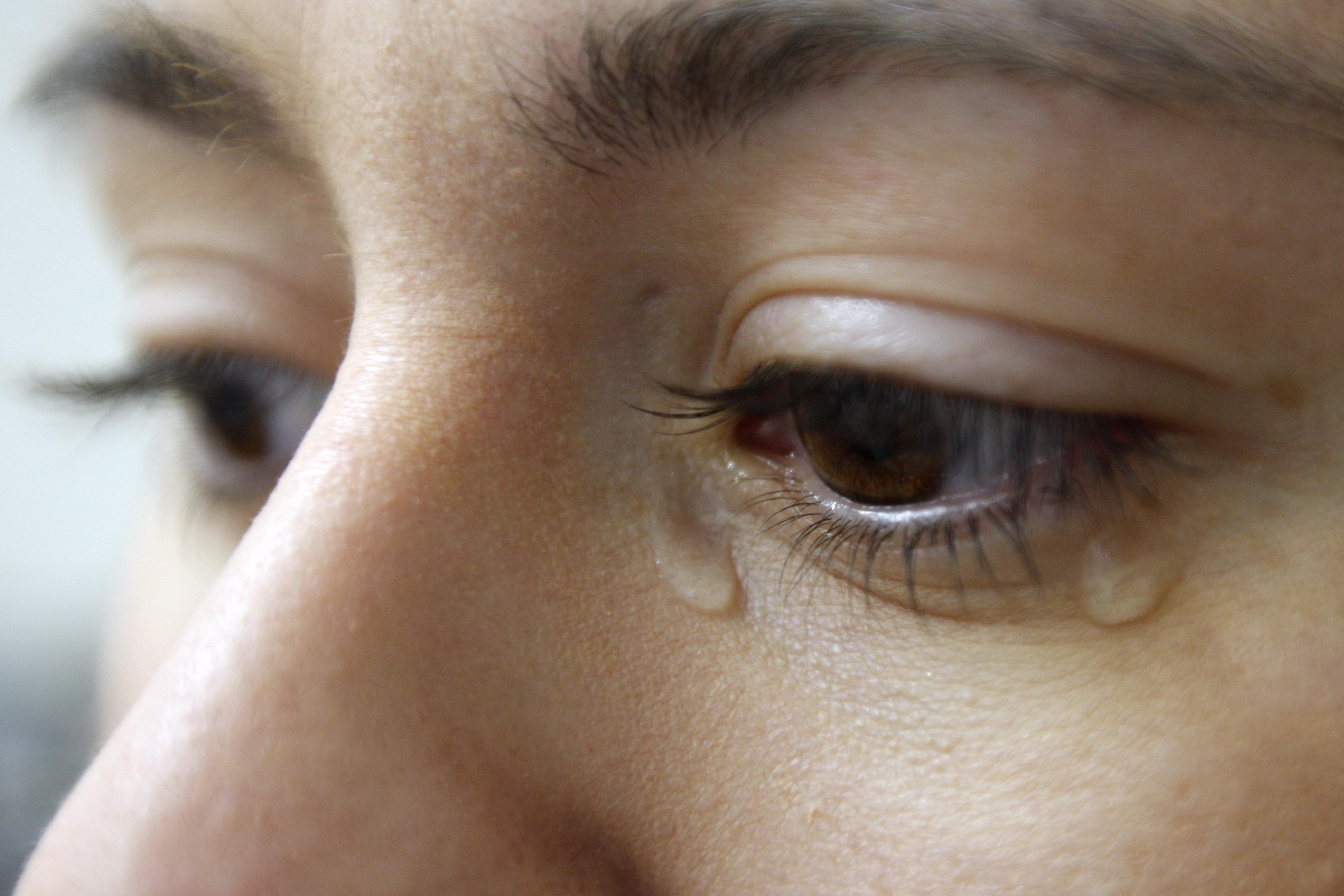
Lacrimation
Tears are a clear liquid secreted by the lacrimal glands (tear gland) found in the eyes of all land mammals. Tears are made up of water, electrolytes, proteins, lipids, and mucins that form layers on the surface of eyes. The different types of tears—basal, reflex, and emotional—vary significantly in composition. The functions of tears include lubricating the eyes (basal tears), removing irritants (reflex tears), and also aiding the immune system. Tears also occur as a part of the body's natural pain response. Emotional secretion of tears may serve a biological function by excreting stress-inducing hormones built up through times of emotional distress. Tears have symbolic significance among humans. Physiology Chemical composition Tears are made up of three layers: lipid, aqueous, and mucous. Tears are composed of water, salts, antibodies, and lysozymes (antibacterial enzymes); though composition varies among different tear types. The composition of tears caused by an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |