|
Tabatha Cicero
Sandra Tabatha Cicero is an American esoteric writer and lecturer, best known for her work in the field of Hermeticism. Early life Born in rural Wisconsin in 1959, Cicero graduated from the University of Wisconsin–Milwaukee with a Bachelor's Degree in Fine Arts in 1982. She worked as an entertainer, typesetter, editor, commercial artist, and computer graphics illustrator. She met her husband Chic Cicero in the early 1980s.Cicero, Sandra Tabatha. The Book of the Concourse of the Watchtowers, Elfers, FL: HOGD Books, 2012, P. vi Writings Along with her husband, Cicero has co-authored several books on the Hermetic Order of the Golden Dawn, Golden Dawn, Tarot, Kabbalah, and the Western mystery tradition including ''The Essential Golden Dawn'', which won a Coalition of Visionary Resources (COVR) award in 2004 as one of the year's best titles in the field of magic (paranormal), magic. Together, the Ciceros have edited, annotated and added new material to recent editions of classic magi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Esoteric
Western esotericism, also known as the Western mystery tradition, is a wide range of loosely related ideas and movements that developed within Western society. These ideas and currents are united since they are largely distinct both from orthodox Judeo-Christian, Judeo-Christian religion and Age of Enlightenment rationalism. It has influenced, or contributed to, various forms of Western philosophy, mysticism, Western religions, religion, science, pseudoscience, Western art history, art, Western literature, literature, and Western culture#Music, music. The idea of grouping a wide range of Western traditions and philosophies together under the term ''esotericism'' developed in 17th-century Europe. Various academics have debated numerous definitions of Western esotericism. One view adopts a definition from certain esotericist schools of thought themselves, treating "esotericism" as a perennial philosophy, perennial hidden inner tradition. A second perspective sees esotericism as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
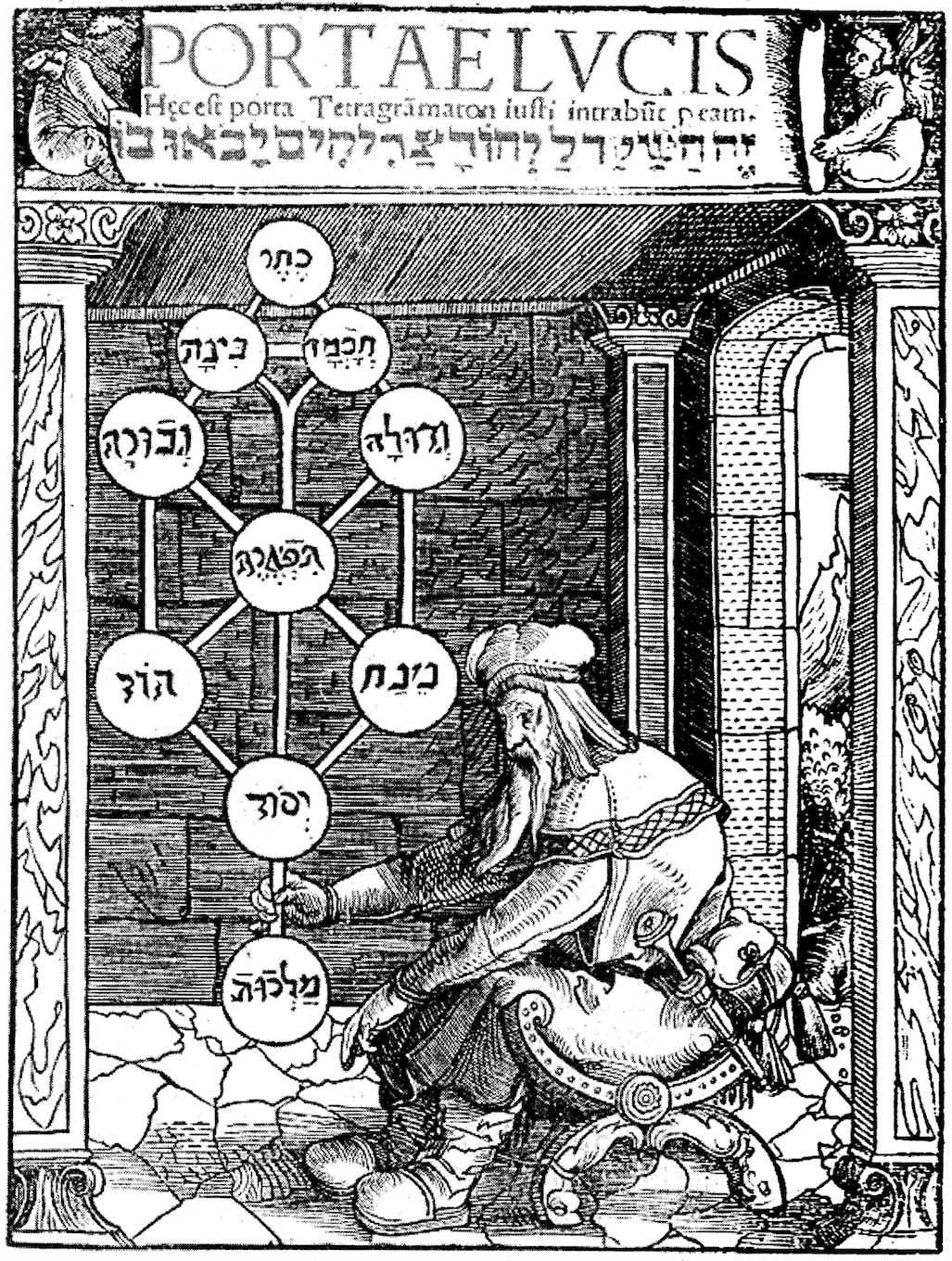
The Middle Pillar
''The'' is a grammatical article in English, denoting nouns that are already or about to be mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with nouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a consonant sound, and as (homophone of the archaic pronoun ''thee' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Living People
Purpose: Because living persons may suffer personal harm from inappropriate information, we should watch their articles carefully. By adding an article to this category, it marks them with a notice about sources whenever someone tries to edit them, to remind them of WP:BLP (biographies of living persons) policy that these articles must maintain a neutral point of view, maintain factual accuracy, and be properly sourced. Recent changes to these articles are listed on Special:RecentChangesLinked/Living people. Organization: This category should not be sub-categorized. Entries are generally sorted by family name In many societies, a surname, family name, or last name is the mostly hereditary portion of one's personal name that indicates one's family. It is typically combined with a given name to form the full name of a person, although several give .... Maintenance: Individuals of advanced age (over 90), for whom there has been no new documentation in the last ten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Writers From Wisconsin
A writer is a person who uses written words in different writing styles, genres and techniques to communicate ideas, to inspire feelings and emotions, or to entertain. Writers may develop different forms of writing such as novels, short stories, monographs, travelogues, plays, screenplays, teleplays, songs, and essays as well as reports, educational material, and news articles that may be of interest to the general public. Writers' works are nowadays published across a wide range of media. Skilled writers who are able to use language to express ideas well, often contribute significantly to the cultural content of a society. The term "writer" is also used elsewhere in the arts and music, such as songwriter or a screenwriter, but also a stand-alone "writer" typically refers to the creation of written language. Some writers work from an oral tradition. Writers can produce material across a number of genres, fictional or non-fictional. Other writers use multiple media such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artists From Wisconsin
An artist is a person engaged in an activity related to creating art, practicing the arts, or demonstrating the work of art. The most common usage (in both everyday speech and academic discourse) refers to a practitioner in the visual arts only. However, the term is also often used in the entertainment business to refer to actors, musicians, singers, dancers and other performers, in which they are known as ''Artiste'' instead. ''Artiste'' (French) is a variant used in English in this context, but this use has become rare. The use of the term "artist" to describe writers is valid, but less common, and mostly restricted to contexts such as critics' reviews; "author" is generally used instead. Dictionary definitions The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' defines the older, broader meanings of the word "artist": * A learned person or Master of Arts * One who pursues a practical science, traditionally medicine, astrology, alchemy, chemistry * A follower of a pursuit in which skill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1959 Births
Events January * January 1 – Cuba: Fulgencio Batista flees Havana when the forces of Fidel Castro advance. * January 2 – Soviet lunar probe Luna 1 is the first human-made object to attain escape velocity from Earth. It reaches the vicinity of Earth's Moon, where it was intended to crash-land, but instead becomes the first spacecraft to go into heliocentric orbit. * January 3 ** Alaska is admitted as the 49th U.S. state. ** The southernmost island of the Maldives archipelago, Addu Atoll, declares its independence from the Kingdom of the Maldives, initiating the United Suvadive Republic. * January 4 ** In Cuba, rebel troops led by Che Guevara and Camilo Cienfuegos enter the city of Havana. ** Léopoldville riots: At least 49 people are killed during clashes between the police and participants of a meeting of the ABAKO Party in Kinshasa, Léopoldville in the Belgian Congo. * January 6 – The International Maritime Organization is inaugurated. * January 7 – The United ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martinist
Martinism is a form of Christian mysticism and esoteric Christianity concerned with the fall of the first man, his materialistic state of being, deprived of his own, divine source, and the process of his eventual (if not inevitable) return, called 'Reintegration'. As a mystical tradition, it was first transmitted through a Masonic high-degree system established around 1740 in France by Martinez de Pasqually, and later propagated in different forms by his two students Louis Claude de Saint-Martin and Jean-Baptiste Willermoz. The term ''Martinism'' applies to both this particular doctrine and the teachings of the reorganized "Martinist Order" founded in 1886 by Augustin Chaboseau and Gérard Encausse (aka Papus). It was not used at the tradition's inception in the 18th century. This confusing disambiguation has been a problem since the late 18th century, where the term ''Martinism'' was already used interchangeably between the teachings of Louis-Claude de Saint-Martin and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rosicrucian
Rosicrucianism () is a spirituality, spiritual and cultural movement that arose in early modern Europe in the early 17th century after the publication of several texts announcing to the world a new Western esotericism, esoteric order. Rosicrucianism is symbolized by the Rose Cross or Rosy Cross. There have been several Rosicrucian (or Rosicrucian-inspired) organizations since the initial movement was founded, including the Order of the Golden and Rosy Cross (1750s–1790s), the Societas Rosicruciana in Anglia (1865–present), and the Hermetic Order of the Golden Dawn (1887–1903). History Between 1610 and 1615, two anonymous manifestos appeared in Germany in the early modern period, early modern Germany and soon after were published throughout Early modern Europe, Europe. The Fama Fraternitatis, ''Fama Fraternitatis Rosae Crucis'' (The Fame of the Brotherhood of the Rosy Cross) was circulated in manuscript among German Occult, occultists since about 1610, and published at K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A Garden Of Pomegranates
''A Garden of Pomegranates'' is a 160-page book, written by Israel Regardie in 1931. History The first edition was published in 1932. The book was printed four times, with a second edition being published in 1970 by Llewellyn Publications. The title pays homage to Moses ben Jacob Cordovero's '' Pardes Rimonim'', or "Pomegranate Orchard." A third edition was printed in 1999, by Llewellyn Publications. This edition includes two introductions by Regardie, and one from Chic and Sandra Tabatha Cicero. The third edition is also furnished with a series of annotations done by the Ciceros, and an additional 320-page qabalistic textbook, titled ''Skrying On The Tree of Life''. Regardie dedicates the book to Aleister Crowley and identifies the text as a theoretical introduction to the foundation of the magical work of the Hermetic Order of the Golden Dawn The Hermetic Order of the Golden Dawn (), more commonly the Golden Dawn (), was a secret society devoted to the study and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Israel Regardie
Francis Israel Regardie (; né Regudy; November 17, 1907 – March 10, 1985) was an English and American occultist, ceremonial magician, and writer who spent much of his life in the United States. He wrote fifteen books on the subject of occultism. Born to a working-class Orthodox Jewish family in the East End of London, Regardie and his family soon moved to Washington, D.C., in the United States. Regardie rejected Orthodox Judaism during his teenage years and took an interest in Theosophy, Hinduism, Buddhism, and Jewish mysticism. It was through his interest in yoga that he encountered the writings of the occultist Aleister Crowley. Contacting Crowley, he was invited to serve as the occultist's secretary, necessitating a move to Paris, France in 1928. He followed Crowley to England before their association ended. Living in England, he wrote two books on the Qabalah, ''A Garden of Pomegranates'' and ''The Tree of Life''. In 1934 he then joined the Stella Matutina—a ceremonia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hermeticism
Hermeticism, or Hermetism, is a philosophical and religious tradition rooted in the teachings attributed to Hermes Trismegistus, a syncretism, syncretic figure combining elements of the Greek god Hermes and the Egyptian god Thoth. This system encompasses a wide range of Western esotericism, esoteric knowledge, including aspects of alchemy, astrology, and theurgy, and has significantly influenced various mystical and occult traditions throughout history. The writings attributed to Hermes Trismegistus, often referred to as the ''Hermetica'', were produced over a period spanning many centuries () and may be very different in content and scope. One particular form of Hermetic teaching is the religio-philosophical system found in a specific subgroup of Hermetic writings known as the Hermetica#Religio-philosophical Hermetica, 'religio-philosophical' ''Hermetica''. The most famous of these are the ''Corpus Hermeticum'', a collection of seventeen Ancient Greek, Greek treatises written b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magic (paranormal)
Magic, sometimes spelled magick, is the application of beliefs, rituals or actions employed in the belief that they can manipulate natural or supernatural beings and forces. It is a category into which have been placed various beliefs and practices sometimes considered separate from both religion and science. Connotations have varied from positive to negative at times throughout history. Within Western culture, magic has been linked to ideas of the Other, foreignness, and primitivism; indicating that it is "a powerful marker of cultural difference" and likewise, a non-modern phenomenon. During the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries, Western intellectuals perceived the practice of magic to be a sign of a primitive mentality and also commonly attributed it to marginalised groups of people. Aleister Crowley (1875–1947), a British occultist, defined " magick" as "the Science and Art of causing Change to occur in conformity with Will", adding a 'k' to distinguish c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |