|
TUBB3
Tubulin beta-3 chain, Class III β-tubulin, βIII-tubulin (β3-tubulin) or β-tubulin III, is a microtubule element of the tubulin family found almost exclusively in neurons, and in testis cells. In humans, it is encoded by the ''TUBB3'' gene. It is possible to use monoclonal antibodies and immunohistochemistry to identify neurons in samples of brain tissue, separating neurons from glial cells, which do not express tubulin beta-3 chain. Class III β-tubulin is one of the seven β-tubulin isotypes identified in the human genome, predominantly in neurons and the testis. It is conditionally expressed in a number of other tissues after exposure to a toxic microenvironment featured by hypoxia and poor nutrient supply. Posttranslational changes including phosphorylation and glycosylation are required for functional activity. Class III β-tubulin's role in neural development has warranted its use as an early biomarker of neural cell differentiation from multi potent progenitors. TUBB3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microlissencephaly
Microlissencephaly (MLIS) is a rare congenital brain disorder that combines severe microcephaly (small head) with lissencephaly (smooth brain surface due to absent Sulcus (neuroanatomy), sulci and gyri). Microlissencephaly is a heterogeneous disorder, i.e. it has many different causes and a variable clinical course. Microlissencephaly is a malformation of cortical development (MCD) that occurs due to failure of neuronal migration between the third and fifth month of gestation as well as stem cell population abnormalities. Numerous genes have been found to be associated with microlissencephaly, however, the pathophysiology is still not completely understood. The combination of lissencephaly with severe congenital microcephaly is designated as microlissencephaly only when the Cerebral cortex, cortex is abnormally thick. If such combination exists with a normal cortical thickness (2.5 to 3 mm), it is known as "microcephaly with simplified gyral pattern" (MSGP). Both MLIS and MSGP ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
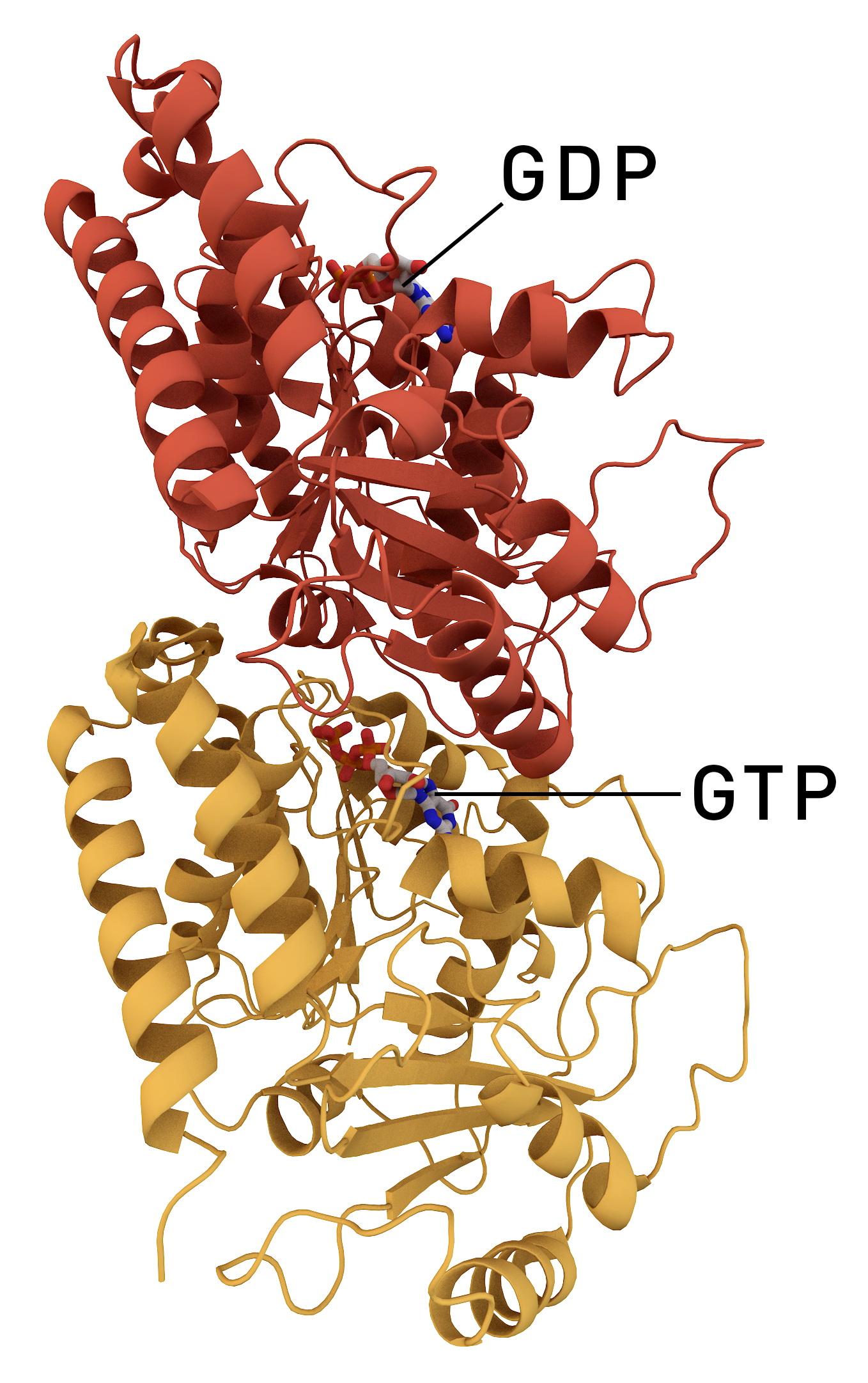
Tubulin
Tubulin in molecular biology can refer either to the tubulin protein superfamily of globular proteins, or one of the member proteins of that superfamily. α- and β-tubulins polymerize into microtubules, a major component of the eukaryotic cytoskeleton. It was discovered and named by Hideo Mōri in 1968. Microtubules function in many essential cellular processes, including mitosis. Discovery and development of tubulin inhibitors, Tubulin-binding drugs kill cancerous cells by inhibiting microtubule dynamics, which are required for DNA segregation and therefore cell division. #Eukaryotic, In eukaryotes, there are six members of the tubulin superfamily, although not all are present in all species.Turk E, Wills AA, Kwon T, Sedzinski J, Wallingford JB, Stearns "Zeta-Tubulin Is a Member of a Conserved Tubulin Module and Is a Component of the Centriolar Basal Foot in Multiciliated Cells"Current Biology (2015) 25:2177-2183. Both α and β tubulins have a mass of around 50 kDa and are thus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
β-tubulin
Tubulin in molecular biology can refer either to the tubulin protein superfamily of globular proteins, or one of the member proteins of that superfamily. α- and β-tubulins polymerize into microtubules, a major component of the eukaryotic cytoskeleton. It was discovered and named by Hideo Mōri in 1968. Microtubules function in many essential cellular processes, including mitosis. Tubulin-binding drugs kill cancerous cells by inhibiting microtubule dynamics, which are required for DNA segregation and therefore cell division. In eukaryotes, there are six members of the tubulin superfamily, although not all are present in all species.Turk E, Wills AA, Kwon T, Sedzinski J, Wallingford JB, Stearns "Zeta-Tubulin Is a Member of a Conserved Tubulin Module and Is a Component of the Centriolar Basal Foot in Multiciliated Cells"Current Biology (2015) 25:2177-2183. Both α and β tubulins have a mass of around 50 kDa and are thus in a similar range compared to actin (with a mass of ~42 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microtubule
Microtubules are polymers of tubulin that form part of the cytoskeleton and provide structure and shape to eukaryotic cells. Microtubules can be as long as 50 micrometres, as wide as 23 to 27 nanometer, nm and have an inner diameter between 11 and 15 nm. They are formed by the polymerization of a Protein dimer, dimer of two globular proteins, Tubulin#Eukaryotic, alpha and beta tubulin into #Structure, protofilaments that can then associate laterally to form a hollow tube, the microtubule. The most common form of a microtubule consists of 13 protofilaments in the tubular arrangement. Microtubules play an important role in a number of cellular processes. They are involved in maintaining the structure of the cell and, together with microfilaments and intermediate filaments, they form the cytoskeleton. They also make up the internal structure of cilia and flagella. They provide platforms for intracellular transport and are involved in a variety of cellular processes, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Anatomy
Cell most often refers to: * Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life * Cellphone, a phone connected to a cellular network * Clandestine cell, a penetration-resistant form of a secret or outlawed organization * Electrochemical cell, a device used to convert chemical energy to electrical energy * Prison cell, a room used to hold people in prisons Cell may also refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media Fictional entities * Cell (comics), a Marvel comic book character * Cell (''Dragon Ball''), a character in the manga series ''Dragon Ball'' Literature * ''Cell'' (novel), a 2006 horror novel by Stephen King * "Cells", poem, about a hungover soldier in gaol, by Rudyard Kipling * ''The Cell'' (play), an Australian play by Robert Wales Music * Cell (music), a small rhythmic and melodic design that can be isolated, or can make up one part of a thematic context * Cell (American band) * Cell (Japanese band) * ''Cell'' (album), a 2004 album by Plastic Tree * ''Cells'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene (journal)
''Gene'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal in genetics and molecular biology, focusing on the cloning, structure, function, as well as the biomedical and biotechnological importance of genes. The scope of the journal includes all biological organisms including viruses, prokaryotes, and eukaryotes. It is organized into topics, which include Human Genetics, Cancer Genetics, Neurogenetics, Animal Genetics, Genome Editing, Molecular Ecology, Plant Genetics, Parasitology and Virology, as well as Microbiology. The journal is part of the Gene Family of journals and was established in 1976. It is published by Elsevier Elsevier ( ) is a Dutch academic publishing company specializing in scientific, technical, and medical content. Its products include journals such as ''The Lancet'', ''Cell (journal), Cell'', the ScienceDirect collection of electronic journals, ... and the editor-in-chief is Marianna Kruithof-de Julio ( University of Bern) The Gene Family of journals compris ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GSTM4
Glutathione S-transferase Mu 4 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''GSTM4'' gene In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protei .... Cytosolic and membrane-bound forms of glutathione S-transferase are encoded by two distinct supergene families. At present, eight distinct classes of the soluble cytoplasmic mammalian glutathione S-transferases have been identified: alpha, kappa, mu, omega, pi, sigma, theta and zeta. This gene encodes a glutathione S-transferase that belongs to the mu class. The mu class of enzymes functions in the detoxification of electrophilic compounds, including carcinogens, therapeutic drugs, environmental toxins and products of oxidative stress, by conjugation with glutathione. The genes encoding the mu class of enzymes are organized in a gene cluster ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FMO4
Dimethylaniline monooxygenase -oxide-forming4 is an enzyme in humans encoded by the ''FMO4'' gene. Function Metabolic N-oxidation of the diet-derived amino-trimethylamine (TMA) is mediated by flavin-containing monooxygenase and is subject to an inherited FMO3 polymorphism in man resulting in a small subpopulation with reduced TMA N-oxidation capacity resulting in fish odor syndrome Trimethylaminuria. Three forms of the enzyme, FMO1 found in fetal liver, FMO2 found in adult liver, and FMO3 are encoded by genes clustered in the 1q23-q25 region. Flavin-containing monooxygenases are NADPH-dependent flavoenzymes that catalyzes the oxidation of soft nucleophilic heteroatom centers in drugs, pesticides, and xenobiotics. Cancer FMO4 gene has been observed progressively downregulated in Human papillomavirus Human papillomavirus infection (HPV infection) is caused by a DNA virus from the ''Papillomaviridae'' family. Many HPV infections cause no symptoms and 90% resolve spo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytoskeleton
The cytoskeleton is a complex, dynamic network of interlinking protein filaments present in the cytoplasm of all cells, including those of bacteria and archaea. In eukaryotes, it extends from the cell nucleus to the cell membrane and is composed of similar proteins in the various organisms. It is composed of three main components: microfilaments, intermediate filaments, and microtubules, and these are all capable of rapid growth and or disassembly depending on the cell's requirements. Cytoskeleton can perform many functions. Its primary function is to give the cell its shape and mechanical resistance to deformation, and through association with extracellular connective tissue and other cells it stabilizes entire tissues. The cytoskeleton can also contract, thereby deforming the cell and the cell's environment and allowing cells to migrate. Moreover, it is involved in many cell signaling pathways and in the uptake of extracellular material ( endocytosis), the segregation of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NEK6
Serine/threonine-protein kinase Nek6 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''NEK6'' gene. Function The ''Aspergillus nidulans ''Aspergillus nidulans'' (also called '' Emericella nidulans'' when referring to its sexual form, or teleomorph) is one of many species of filamentous fungi in the phylum Ascomycota. It has been an important research organism for studying eukary ...'' 'never in mitosis A' (NIMA) gene encodes a serine/threonine kinase that controls initiation of mitosis. NIMA-related kinases (NEKs) are a group of protein kinases that are homologous to NIMA. Evidence suggests that NEKs perform functions similar to those of NIMA. It is a protein kinase which plays an important role in mitotic cell cycle progression. Required for chromosome segregation at metaphase-anaphase transition, robust mitotic spindle formation and cytokinesis. Phosphorylates ATF4, CIR1, PTN, RAD26L, RBBP6, RPS7, RPS6KB1, TRIP4, STAT3 and histones H1 and H3. Phosphorylates KIF11 to promot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PIM1
Proto-oncogene serine/threonine-protein kinase Pim-1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''PIM1'' gene. Pim-1 is a proto-oncogene which encodes for the serine/threonine kinase of the same name. The pim-1 oncogene was first described in relation to murine T-cell lymphomas, as it was the locus most frequently activated by the Moloney murine leukemia virus. Subsequently, the oncogene has been implicated in multiple human cancers, including prostate cancer, acute myeloid leukemia and other hematopoietic malignancies. Primarily expressed in spleen, thymus, bone marrow, prostate, oral epithelial, hippocampus and fetal liver cells, Pim-1 has also been found to be highly expressed in cell cultures isolated from human tumors. Pim-1 is mainly involved in cell cycle progression, apoptosis and transcriptional activation, as well as more general signal transduction pathways. Pim-1's role in oncogenic signalling has led to it becoming a widely studied target in cancer research, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GBP1
Interferon-induced guanylate-binding protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''GBP1'' gene. It belongs to the dynamin superfamily of large GTPases. Function Guanylate binding protein expression is induced by interferon Interferons (IFNs, ) are a group of signaling proteins made and released by host cells in response to the presence of several viruses. In a typical scenario, a virus-infected cell will release interferons causing nearby cells to heighten .... Guanylate binding proteins are characterized by their ability to specifically bind guanine nucleotides (GMP, GDP, and GTP) and are distinguished from the GTP-binding proteins by the presence of 2 binding motifs rather than 3. References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{gene-1-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |