|
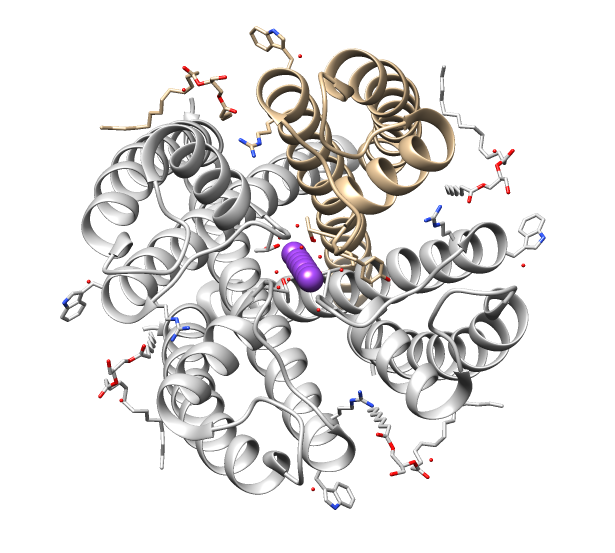
TRPML
TRPML (transient receptor potential cation channel, mucolipin subfamily) comprises a group of three evolutionarily related proteins that belongs to the large family of transient receptor potential ion channels. The three proteins TRPML1, TRPML2 and TRPML3 are encoded by the mucolipin-1 ('' MCOLN1''), mucolipin-2 ('' MCOLN2'') and mucolipin-3 ('' MCOLN3'') genes, respectively. The three members of the TRPML ("ML" for mucolipin) sub-family are not extremely well characterized. TRPML1 is known to be localized in late endosomes. This subunit also contains a lipase domain between its S1 and S2 segments. While the function of this domain is unknown it has been proposed that it is involved in channel regulation. Physiological studies have described TRPML1 channels as proton A proton is a stable subatomic particle, symbol , H+, or 1H+ with a positive electric charge of +1 ''e'' elementary charge. Its mass is slightly less than that of a neutron and 1,836 times the mass of an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TRPML3
Mucolipin-3 also known as TRPML3 (transient receptor potential cation channel, mucolipin subfamily, member 3) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''MCOLN3'' gene. It is a member of the small family of the TRPML channels, a subgroup of the large protein family of TRP ion channels. Gene In human, the ''MCOLN3'' gene resides on the short arm of chromosome 1 at 1p22.3. The gene is split in 12 exons, which entail the open reading frame of 1659 nucleotides. The encoded protein, TRPML3, has 553 amino acid with a predicted molecular weight of ≈64 kDa. Computational analyses of the secondary structure predict the presence of six transmembrane domains, an ion transport motif (PF00520) and a transient receptor potential motif (PS50272). In the mouse, ''Mcoln3'', is located on the distal end of chromosome 3 at cytogenetic band qH2. Human and mouse TRPML3 proteins share 91% sequence identity. All vertebrate species, for which a genomic sequence is available, harbor the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MCOLN3
Mucolipin-3 also known as TRPML3 (transient receptor potential cation channel, mucolipin subfamily, member 3) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''MCOLN3'' gene. It is a member of the small family of the TRPML channels, a subgroup of the large protein family of TRP ion channels. Gene In human, the ''MCOLN3'' gene resides on the short arm of chromosome 1 at 1p22.3. The gene is split in 12 exons, which entail the open reading frame of 1659 nucleotides. The encoded protein, TRPML3, has 553 amino acid with a predicted molecular weight of ≈64 kDa. Computational analyses of the secondary structure predict the presence of six transmembrane domains, an ion transport motif (PF00520) and a transient receptor potential motif (PS50272). In the mouse, ''Mcoln3'', is located on the distal end of chromosome 3 at cytogenetic band qH2. Human and mouse TRPML3 proteins share 91% sequence identity. All vertebrate species, for which a genomic sequence is available, harbor the ''MC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transient Receptor Potential
Transient receptor potential channels (TRP channels) are a group of ion channels located mostly on the plasma membrane of numerous animal cell types. Most of these are grouped into two broad groups: Group 1 includes TRPC ( "C" for canonical), TRPV ("V" for vanilloid), TRPVL ("VL" for vanilloid-like), TRPM ("M" for melastatin), TRPS ("S" for soromelastatin), TRPN ("N" for no mechanoreceptor potential C), and TRPA ("A" for ankyrin). Group 2 consists of TRPP ("P" for polycystic) and TRPML ("ML" for mucolipin). Other less-well categorized TRP channels exist, including yeast channels and a number of Group 1 and Group 2 channels present in non-animals. Many of these channels mediate a variety of sensations such as pain, temperature, different kinds of tastes, pressure, and vision. In the body, some TRP channels are thought to behave like microscopic thermometers and used in animals to sense hot or cold. Some TRP channels are activated by molecules found in spices like garlic (a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TRPML1
Mucolipin-1 also known as TRPML1 (transient receptor potential cation channel, mucolipin subfamily, member 1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''MCOLN1'' gene. It is a member of the small family of the TRPML channels, a subgroup of the large protein family of TRP ion channels. TRPML1 is a 65 kDa protein associated with mucolipidosis type IV. Its predicted structure includes six transmembrane domains, a transient receptor potential (TRP) cation-channel domain, and an internal channel pore. TRPML1 is believed to channel iron ions across the endosome/lysosome membrane into the cell and so its malfunction causes cellular iron deficiency. It is important in lysosome function and plays a part in processes such as vesicular trafficking, exocytosis and autophagy Autophagy (or autophagocytosis; from the Ancient Greek , , meaning "self-devouring" and , , meaning "hollow") is the natural, conserved degradation of the cell that removes unnecessary or dysfunctional compo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MCOLN1
Mucolipin-1 also known as TRPML1 (transient receptor potential cation channel, mucolipin subfamily, member 1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''MCOLN1'' gene. It is a member of the small family of the TRPML channels, a subgroup of the large protein family of TRP ion channels. TRPML1 is a 65 kDa protein associated with mucolipidosis type IV. Its predicted structure includes six transmembrane domains, a transient receptor potential (TRP) cation-channel domain, and an internal channel pore. TRPML1 is believed to channel iron ions across the endosome/ lysosome membrane into the cell and so its malfunction causes cellular iron deficiency. It is important in lysosome function and plays a part in processes such as vesicular trafficking, exocytosis and autophagy. Ligands ;Agonists * ML-SA1 * MK6-83 See also * transient receptor potential cation channel, mucolipin subfamily, member 2 (MCOLN2) * transient receptor potential cation channel, mucolipin subfamily, membe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mucolipin-1
Mucolipin-1 also known as TRPML1 (transient receptor potential cation channel, mucolipin subfamily, member 1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''MCOLN1'' gene. It is a member of the small family of the TRPML channels, a subgroup of the large protein family of TRP ion channels. TRPML1 is a 65 kDa protein associated with mucolipidosis type IV. Its predicted structure includes six transmembrane domains, a transient receptor potential (TRP) cation-channel domain, and an internal channel pore. TRPML1 is believed to channel iron ions across the endosome/lysosome membrane into the cell and so its malfunction causes cellular iron deficiency. It is important in lysosome function and plays a part in processes such as vesicular trafficking, exocytosis and autophagy. Ligands ;Agonists * ML-SA1 * MK6-83 See also * transient receptor potential cation channel, mucolipin subfamily, member 2 (MCOLN2) * transient receptor potential cation channel, mucolipin subfamily, member 3 (MC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TRPML2
Mucolipin-2 also known as TRPML2 (transient receptor potential cation channel, mucolipin subfamily, member 2) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''MCOLN2'' gene In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a b .... It is a member of the small family of the TRPML channels, a subgroup of the large protein family of TRP ion channels. TRPML2 is associated with the Arf6-regulated trafficking pathway and is involved in the intracellular transport of membranes and membrane proteins. See also * transient receptor potential cation channel, mucolipin subfamily, member 1 ( MCOLN1) * transient receptor potential cation channel, mucolipin subfamily, member 3 ( MCOLN3) * TRPML References External links * {{membrane-protein-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MCOLN2
Mucolipin-2 also known as TRPML2 (transient receptor potential cation channel, mucolipin subfamily, member 2) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''MCOLN2'' gene. It is a member of the small family of the TRPML channels, a subgroup of the large protein family of TRP ion channels. TRPML2 is associated with the Arf6-regulated trafficking pathway and is involved in the intracellular transport of membranes and membrane proteins. See also * transient receptor potential cation channel, mucolipin subfamily, member 1 (MCOLN1) * transient receptor potential cation channel, mucolipin subfamily, member 3 (MCOLN3) * TRPML TRPML (transient receptor potential cation channel, mucolipin subfamily) comprises a group of three evolutionarily related proteins that belongs to the large family of transient receptor potential ion channels. The three proteins TRPML1, TRPML2 ... References External links * {{membrane-protein-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ion Channel
Ion channels are pore-forming membrane proteins that allow ions to pass through the channel pore. Their functions include establishing a resting membrane potential, shaping action potentials and other electrical signals by gating the flow of ions across the cell membrane, controlling the flow of ions across secretory and epithelial cells, and regulating cell volume. Ion channels are present in the membranes of all cells. Ion channels are one of the two classes of ionophoric proteins, the other being ion transporters. The study of ion channels often involves biophysics, electrophysiology, and pharmacology, while using techniques including voltage clamp, patch clamp, immunohistochemistry, X-ray crystallography, fluoroscopy, and RT-PCR. Their classification as molecules is referred to as channelomics. Basic features There are two distinctive features of ion channels that differentiate them from other types of ion transporter proteins: #The rate of ion transpor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endosome
Endosomes are a collection of intracellular sorting organelles in eukaryotic cells. They are parts of endocytic membrane transport pathway originating from the trans Golgi network. Molecules or ligands internalized from the plasma membrane can follow this pathway all the way to lysosomes for degradation or can be recycled back to the cell membrane in the endocytic cycle. Molecules are also transported to endosomes from the trans Golgi network and either continue to lysosomes or recycle back to the Golgi apparatus. Endosomes can be classified as early, sorting, or late depending on their stage post internalization. Endosomes represent a major sorting compartment of the endomembrane system in cells. Function Endosomes provide an environment for material to be sorted before it reaches the degradative lysosome. For example, low-density lipoprotein (LDL) is taken into the cell by binding to the LDL receptor at the cell surface. Upon reaching early endosomes, the LDL dissoc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proton
A proton is a stable subatomic particle, symbol , H+, or 1H+ with a positive electric charge of +1 ''e'' elementary charge. Its mass is slightly less than that of a neutron and 1,836 times the mass of an electron (the proton–electron mass ratio). Protons and neutrons, each with masses of approximately one atomic mass unit, are jointly referred to as "nucleons" (particles present in atomic nuclei). One or more protons are present in the Atomic nucleus, nucleus of every atom. They provide the attractive electrostatic central force which binds the atomic electrons. The number of protons in the nucleus is the defining property of an element, and is referred to as the atomic number (represented by the symbol ''Z''). Since each chemical element, element has a unique number of protons, each element has its own unique atomic number, which determines the number of atomic electrons and consequently the chemical characteristics of the element. The word ''proton'' is Greek language, G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lysosome
A lysosome () is a membrane-bound organelle found in many animal cells. They are spherical vesicles that contain hydrolytic enzymes that can break down many kinds of biomolecules. A lysosome has a specific composition, of both its membrane proteins, and its lumenal proteins. The lumen's pH (~4.5–5.0) is optimal for the enzymes involved in hydrolysis, analogous to the activity of the stomach. Besides degradation of polymers, the lysosome is involved in various cell processes, including secretion, plasma membrane repair, apoptosis, cell signaling, and energy metabolism. Lysosomes act as the waste disposal system of the cell by digesting used materials in the cytoplasm, from both inside and outside the cell. Material from outside the cell is taken up through endocytosis, while material from the inside of the cell is digested through autophagy. The sizes of the organelles vary greatly—the larger ones can be more than 10 times the size of the smaller ones. They we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |