|
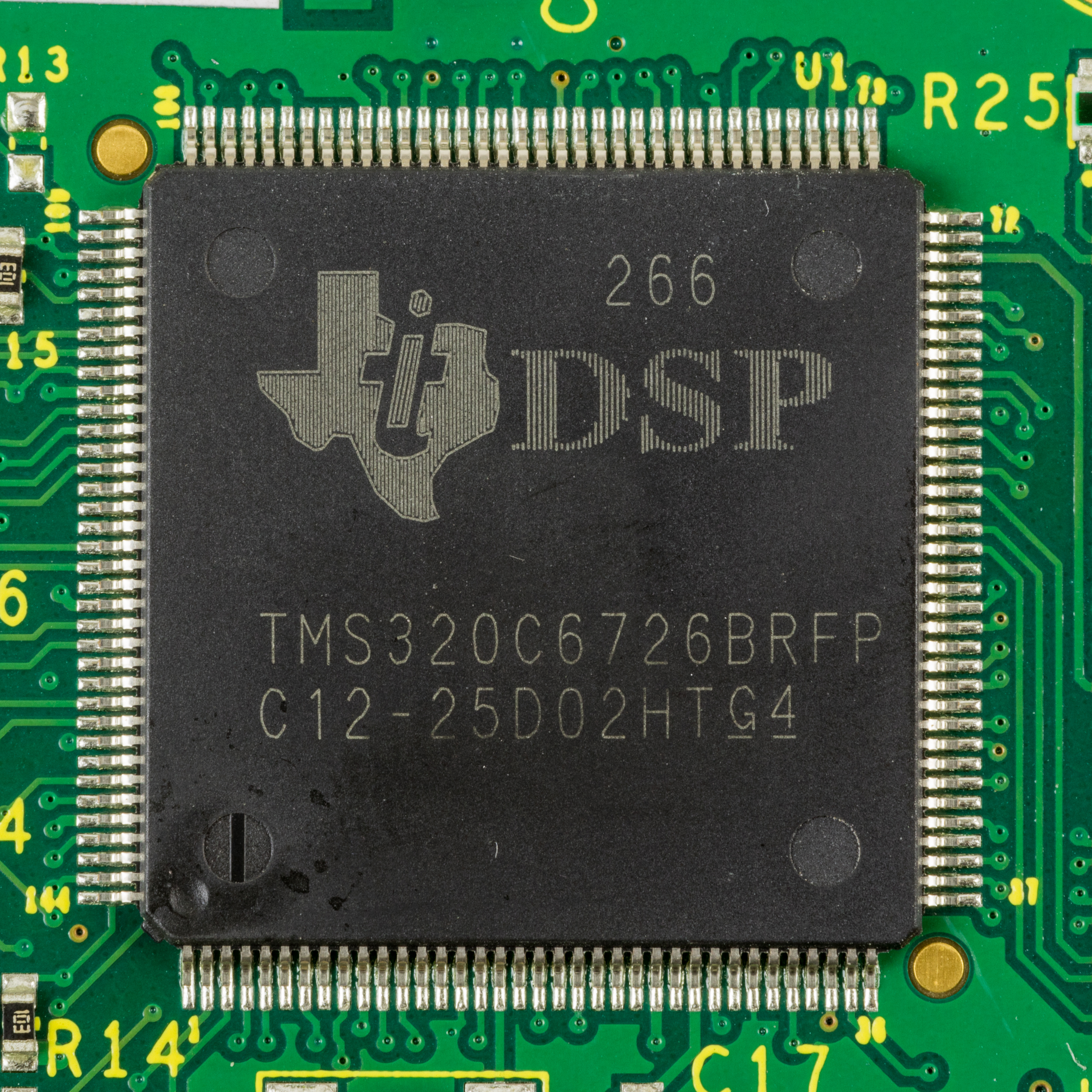
TMS320C4x
TMS320 is a blanket name for a series of digital signal processors (DSPs) from Texas Instruments. It was introduced on April 8, 1983, through the TMS32010 processor, which was then the fastest DSP on the market. The processor is available in many different variants, some with fixed-point arithmetic and some with floating-point arithmetic. The TMS320 processors were fabricated on MOS integrated circuit chips, including both NMOS and CMOS variants. The floating-point DSP TMS320C3x, which exploits delayed branch logic, has as many as three delay slots. This series of processors are used as a digital signal processing co-processor and as the main CPU in some applications. Newer implementations support standard IEEE JTAG control for boundary scan and/or in-circuit debugging. The original TMS32010 and its subsequent variants are an example of a CPU with a modified Harvard architecture, which features separate address spaces for instruction and data memory but the ability to read ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Branch Delay Slot
In computer architecture, a delay slot is an instruction slot being executed without the effects of a preceding instruction. The most common form is a single arbitrary instruction located immediately after a branch instruction on a RISC or DSP architecture; this instruction will execute even if the preceding branch is taken. This makes the instruction execute out-of-order compared to its location in the original assembler language code. Modern processor designs generally do not use delay slots, and instead perform ever more complex forms of branch prediction. In these systems, the CPU immediately moves on to what it believes will be the correct side of the branch and thereby eliminates the need for the code to specify some unrelated instruction, which may not always be obvious at compile-time. If the assumption is wrong, and the other side of the branch has to be called, this can introduce a lengthy delay. This occurs rarely enough that the speed up of avoiding the delay sl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KL TI TMS32020
KL, kL, kl, or kl. may refer to: Businesses and organizations * KLM, a Dutch airline (IATA airline designator KL) * Koninklijke Landmacht, the Royal Netherlands Army * Kvenna Listin ("Women's List"), a political party in Iceland * KL FM, a Malay language radio station Places * Kaiserslautern, Germany (license plate code KL) * Kerala, India (ISO 3166-2:IN sub-code KL) * Kirkland Lake, Ontario, Canada * Kowloon, Hong Kong * Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia Science, technology, and mathematics * KL engine, version of the Mazda K engine * Klepton (kl.), a type of species in zoology * Kiloliter (kL), a unit of volume * Kullback–Leibler divergence in mathematics * KL (gene), a gene which encodes the klotho enzyme in humans Other uses * Jeep Cherokee (KL) * Kalaallisut language (ISO 639 alpha-2 language code "kl") * Kl (digraph), used in the Zulu language to write /kʟ̥ʼ/ or /kxʼ/ * Konzentrationslager, or concentration camp, abbreviated KZ or KL * '' KL: A History of the Nazi Concentrat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Read-only Memory
Read-only memory (ROM) is a type of non-volatile memory used in computers and other electronic devices. Data stored in ROM cannot be electronically modified after the manufacture of the memory device. Read-only memory is useful for storing software that is rarely changed during the life of the system, also known as firmware. Software applications, such as video games, for programmable devices can be distributed as ROM cartridge, plug-in cartridges containing ROM. Strictly speaking, ''read-only memory'' refers to hard-wired memory, such as diode matrix or a #Solid-state ROM, mask ROM integrated circuit (IC), that cannot be electronically changed after manufacture. Although discrete circuits can be altered in principle, through the addition of Jump wire, bodge wires and the removal or replacement of components, ICs cannot. Correction of errors, or updates to the software, require new devices to be manufactured and to replace the installed device. Floating-gate ROM semiconductor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ARM7
ARM7 is a group of 32-bit RISC ARM processor cores licensed by ARM Holdings for microcontroller use. The ARM7 core family consists of ARM700, ARM710, ARM7DI, ARM710a, ARM720T, ARM740T, ARM710T, ARM7TDMI, ARM7TDMI-S, ARM7EJ-S. The ARM7TDMI and ARM7TDMI-S were the most popular cores of the family. ARM7 cores were released from 1993 to 2001 and no longer recommended for new IC designs; newer alternatives are ARM Cortex-M cores. Overview This generation introduced the Thumb 16-bit instruction set providing improved code density compared to previous designs. The most widely used ARM7 designs implement the ARMv4T architecture, but some implement ARMv3 or ARMv5TEJ. ARM7TDMI has 37 registers (31 GPR and 6 SPR). All these designs use a Von Neumann architecture, thus the few versions containing a cache do not separate data and instruction caches. Some ARM7 cores are obsolete. One historically significant model, the ARM7DI"ARM7DI Data Sheet"; Document Number ARM DDI 0027D; Issued: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ericsson
(), commonly known as Ericsson (), is a Swedish multinational networking and telecommunications company headquartered in Stockholm, Sweden. Ericsson has been a major contributor to the development of the telecommunications industry and is one of the leaders in 5G. Ericsson has over 57,000 granted patents and it is the inventor of Bluetooth technology. The company sells infrastructure, software, and services in information and communications technology for telecommunications service providers and enterprises, including, among others, cellular 4G and 5G equipment, and Internet Protocol (IP) and optical transport systems. The company employs around 100,000 people and operates in more than 180 countries. The company is listed on the Nasdaq Stockholm under the ticker symbols ERIC.A and ERIC.B and on the American Nasdaq under the ticker symbol ERIC. The company was founded in 1876 by Lars Magnus Ericsson and is jointly controlled by the Wallenberg family through its holding company ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nokia
Nokia Corporation is a Finnish multinational corporation, multinational telecommunications industry, telecommunications, technology company, information technology, and consumer electronics corporation, originally established as a pulp mill in 1865. Nokia's main headquarters are in Espoo, Finland, in the Helsinki metropolitan area, but the company's actual roots are in the Tampere region of Pirkanmaa.HS: Nokian juuret ovat Tammerkosken rannalla (in Finnish) In 2020, Nokia employed approximately 92,000 people across over 100 countries, did business in more than 130 countries, and reported annual revenues of around €23 billion. Nokia is a public limited company listed on the Nasdaq Helsinki and New York Stock Exchange. It was the world's 415th-largest company ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Power-line Communication
Power-line communication (PLC) is the carrying of data on a conductor (the ''power-line carrier'') that is also used simultaneously for AC electric power transmission or electric power distribution to consumers. A wide range of power-line communication technologies are needed for different applications, ranging from home automation to Internet access, which is often called broadband over power lines (BPL). Most PLC technologies limit themselves to one type of wires (such as premises wiring within a single building), but some can cross between two levels (for example, both the distribution network and premises wiring). Typically transformers prevent propagating the signal, which requires multiple technologies to form very large networks. Various data rates and frequencies are used in different situations. A number of difficult technical problems are common between wireless and power-line communication, notably those of spread spectrum radio signals operating in a crowded env ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Watchdog Timer
A watchdog timer (WDT, or simply a ''watchdog''), sometimes called a ''computer operating properly timer'' (''COP timer''), is an electronic or software timer that is used to detect and recover from computer malfunctions. Watchdog timers are widely used in computers to facilitate automatic correction of temporary hardware faults, and to prevent errant or malevolent software from disrupting system operation. During normal operation, the computer regularly restarts the watchdog timer to prevent it from elapsing, or ''timeout (computing), timing out''. If, due to a hardware fault or program error, the computer fails to restart the watchdog, the timer will elapse and generate a timeout signal. The timeout signal is used to initiate corrective actions. The corrective actions typically include placing the computer and associated hardware in a safe state and invoking a computer reboot. Microcontrollers often include an integrated, on-chip watchdog. In other computers the watchdog may re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CAN Bus
A controller area network bus (CAN bus) is a vehicle bus standard designed to enable efficient communication primarily between electronic control units (ECUs). Originally developed to reduce the complexity and cost of electrical wiring in automobiles through multiplexing, the CAN bus protocol has since been adopted in various other contexts. This Broadcasting (networking), broadcast-based, Message passing, message-oriented protocol ensures data integrity and prioritization through a process called Arbiter (electronics), arbitration, allowing the highest priority device to continue transmitting if multiple devices attempt to send data simultaneously, while others back off. Its reliability is enhanced by Differential signalling, differential signaling, which mitigates electrical noise. Common versions of the CAN protocol include CAN 2.0, CAN FD, and CAN XL which vary in their data rate capabilities and maximum data payload sizes. History Development of the CAN Bus (computing), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serial Peripheral Interface Bus
Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) is a de facto standard (with many #Variations, variants) for Comparison of synchronous and asynchronous signalling, synchronous serial communication, used primarily in embedded systems for short-distance wired communication between integrated circuits. SPI follows a master–slave (technology), master–slave architecture, where a master device Signaling (telecommunications), orchestrates communication with one or more slave devices by driving the clock signal, clock and chip select signals. Some devices support changing master and slave roles on the fly. Motorola's original specification (from the early 1980s) uses four logic signals, aka lines or wires, to support full duplex communication. It is sometimes called a ''four-wire'' serial bus to contrast with Serial Peripheral Interface#Three-wire, three-wire variants which are half duplex, and with the ''two-wire'' I²C and 1-Wire serial buses. Typical #Applications, applications include interf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |