|
TERF2
Telomeric repeat-binding factor 2 is a protein Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respon ... that is present at telomeres throughout the cell cycle. It is also known as TERF2, TRF2, and TRBF2, and is encoded in humans by the ''TERF2'' gene. It is a component of the shelterin Nucleoprotein, nucleoprotein complex and a second negative regulator of telomere length, playing a key role in the protective activity of telomeres. It was first reported in 1997 in the lab of Titia de Lange, where a DNA, DNA sequence similar, but not identical, to TERF1 was discovered, with respect to the Myb domain, Myb-domain. De Lange isolated the new Myb-containing protein sequence and called it TERF2. Structure and domains TERF2 has a similar structure to that of TERF1. Both proteins carry a C-termi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid resid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Domain (protein)
In molecular biology, a protein domain is a region of a protein's polypeptide chain that is self-stabilizing and that folds independently from the rest. Each domain forms a compact folded three-dimensional structure. Many proteins consist of several domains, and a domain may appear in a variety of different proteins. Molecular evolution uses domains as building blocks and these may be recombined in different arrangements to create proteins with different functions. In general, domains vary in length from between about 50 amino acids up to 250 amino acids in length. The shortest domains, such as zinc fingers, are stabilized by metal ions or disulfide bridges. Domains often form functional units, such as the calcium-binding EF hand domain of calmodulin. Because they are independently stable, domains can be "swapped" by genetic engineering between one protein and another to make chimeric proteins. Background The concept of the domain was first proposed in 1973 by Wetlaufer afte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TINF2
TERF1-interacting nuclear factor 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TINF2'' gene. TINF2 is a component of the shelterin protein complex found at the end of telomeres. Interactions TINF2 has been shown to interact with ACD, POT1 and TERF1 Telomeric repeat-binding factor 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TERF1'' gene. Gene The human TERF1 gene is located in the chromosome 8 at 73,921,097-73,960,357 bp. Two transcripts of this gene are alternatively spliced produ .... References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * External links GeneReviews/NCBI/NIH/UW entry on Dyskeratosis CongenitaPDBe-KBprovides an overview of all the structure information available in the PDB for Human TERF1-interacting nuclear factor 2 (TINF2) Telomere-related proteins {{gene-14-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
XRCC3
DNA repair protein XRCC3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''XRCC3'' gene. Function This gene encodes a member of the RecA/Rad51-related protein family that participates in homologous recombination to maintain chromosome stability and repair DNA damage. This gene functionally complements Chinese hamster irs1SF, a repair-deficient mutant that exhibits hypersensitivity to a number of different DNA-damaging agents and is chromosomally unstable. A rare microsatellite polymorphism in this gene is associated with cancer in patients of varying radiosensitivity. The XRCC3 protein is one of five paralogs of RAD51, including RAD51B ( RAD51L1), RAD51C (RAD51L2), RAD51D (RAD51L3), XRCC2 and XRCC3. They each share about 25% amino acid sequence identity with RAD51 and each other. The RAD51 paralogs are all required for efficient DNA double-strand break repair by homologous recombination and depletion of any paralog results in significant decreases in homologous recombination fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avian Myeloblastosis
''Alpharetrovirus'' is a genus of the family Retroviridae. It has type C morphology. Members can cause sarcomas, other tumors, and anaemia of wild and domestic birds and also affect rat Rats are various medium-sized, long-tailed rodents. Species of rats are found throughout the order Rodentia, but stereotypical rats are found in the genus ''Rattus''. Other rat genera include '' Neotoma'' ( pack rats), '' Bandicota'' (bandico ...s. Species include the Rous sarcoma virus, avian leukosis virus, and avian myeloblastosis virus (AMV). Not all animals that can infect develop cancer. The tumor caused by the virus is usually in the form of lymphoma and leukemia. It occurs after a long and latent process. The tumor cells formed consist of a single progenitor cell and are clonal. However, infection from retroviruses does not directly produce tumors, but only placement and recombination events leading to tumor cell formation. References External links * ICTVdb Alpharetro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viral Protein
A viral protein is both a component and a product of a virus. Viral proteins are grouped according to their functions, and groups of viral proteins include structural proteins, nonstructural proteins, regulatory proteins, and accessory proteins. Viruses are non-living and do not have the means to reproduce on their own, instead depending on their host cell's resources in order to reproduce. Thus, viruses do not code for many of their own viral proteins, and instead use the host cell's machinery to produce the viral proteins they require for replication. Viral structural proteins Most viral structural proteins are components for the capsid and the envelope of the virus. Capsid The genetic material of a virus is stored within a viral protein structure called the capsid. The capsid is a "shield" that protects the viral nucleic acids from getting degraded by host enzymes or other types of pesticides or pestilences. It also functions to attach the virion to its host, and enable ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Double-stranded
A base pair (bp) is a fundamental unit of double-stranded nucleic acids consisting of two nucleobases bound to each other by hydrogen bonds. They form the building blocks of the DNA double helix and contribute to the folded structure of both DNA and RNA. Dictated by specific hydrogen bonding patterns, "Watson–Crick" (or "Watson–Crick–Franklin") base pairs (guanine–cytosine and adenine–thymine) allow the DNA helix to maintain a regular helical structure that is subtly dependent on its nucleotide sequence. The complementary nature of this based-paired structure provides a redundant copy of the genetic information encoded within each strand of DNA. The regular structure and data redundancy provided by the DNA double helix make DNA well suited to the storage of genetic information, while base-pairing between DNA and incoming nucleotides provides the mechanism through which DNA polymerase replicates DNA and RNA polymerase transcribes DNA into RNA. Many DNA-binding proteins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MYB (gene)
Myb genes are part of a large gene family of transcription factors found in animals and plants. In humans, it includes Myb proto-oncogene like 1 and Myb-related protein B in addition to MYB proper. Members of the extended SANT/Myb family also include the SANT domain and other similar all-helical homeobox-like domains. Function Viral The Myb gene family is named after the eponymous gene in Avian myeloblastosis virus. The viral Myb (v-Myb, ) recognizes the sequence 5'-YAACKG-3'. It causes myeloblastosis (myeloid leukemia) in chickens. Compared to the normal animal cellular Myb (c-myb), v-myb contains deletions in the C-terminal regulatory domain, leading to aberrant activation of other oncogenes. Animals Myb proto-oncogene protein is a member of the MYB (myeloblastosis) family of transcription factors. The protein contains three domains, an N-terminal DNA-binding domain, a central transcriptional activation domain and a C-terminal domain involved in transcriptional repr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scaffold Protein
In biology, scaffold proteins are crucial regulators of many key signalling pathways. Although scaffolds are not strictly defined in function, they are known to interact and/or bind with multiple members of a signalling pathway, tethering them into complexes. In such pathways, they regulate signal transduction and help localize pathway components (organized in complexes) to specific areas of the cell such as the plasma membrane, the cytoplasm, the nucleus, the Golgi, endosomes, and the mitochondria. History The first signaling scaffold protein discovered was the Ste5 protein from the yeast ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae''. Three distinct domains of Ste5 were shown to associate with the protein kinases Ste11, Ste7, and Fus3 to form a multikinase complex. Function Scaffold proteins act in at least four ways: tethering signaling components, localizing these components to specific areas of the cell, regulating signal transduction by coordinating positive and negative feedb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Repair
DNA repair is a collection of processes by which a cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. In human cells, both normal metabolic activities and environmental factors such as radiation can cause DNA damage, resulting in tens of thousands of individual molecular lesions per cell per day. Many of these lesions cause structural damage to the DNA molecule and can alter or eliminate the cell's ability to transcribe the gene that the affected DNA encodes. Other lesions induce potentially harmful mutations in the cell's genome, which affect the survival of its daughter cells after it undergoes mitosis. As a consequence, the DNA repair process is constantly active as it responds to damage in the DNA structure. When normal repair processes fail, and when cellular apoptosis does not occur, irreparable DNA damage may occur, including double-strand breaks and DNA crosslinkages (interstrand crosslinks or ICLs). This can eventually lead to malig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SLX4
SLX4 (also known as BTBD12 and FANCP) is a protein involved in DNA repair, where it has important roles in the final steps of homologous recombination. Mutations in the gene are associated with the disease Fanconi anemia. The version of SLX4 present in humans and other mammals acts as a sort of scaffold upon which other proteins form several different multiprotein complexes. The SLX1-SLX4 complex acts as a Holliday junction resolvase. As such, the complex cleaves the links between two homologous chromosomes that form during homologous recombination. This allows the two linked chromosomes to resolve into two unconnected double-strand DNA molecules. The SLX4 interacting protein interacts with SLX4 in the DNA repair process, specifically in interstrand crosslink repair. SLX4 also associates with RAD1, RAD10 and SAW1 in the single-strand annealing pathway of homologous recombination. The DNA repair function of SLX4 is involved in sensitivity to proton beam radiation. Model orga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
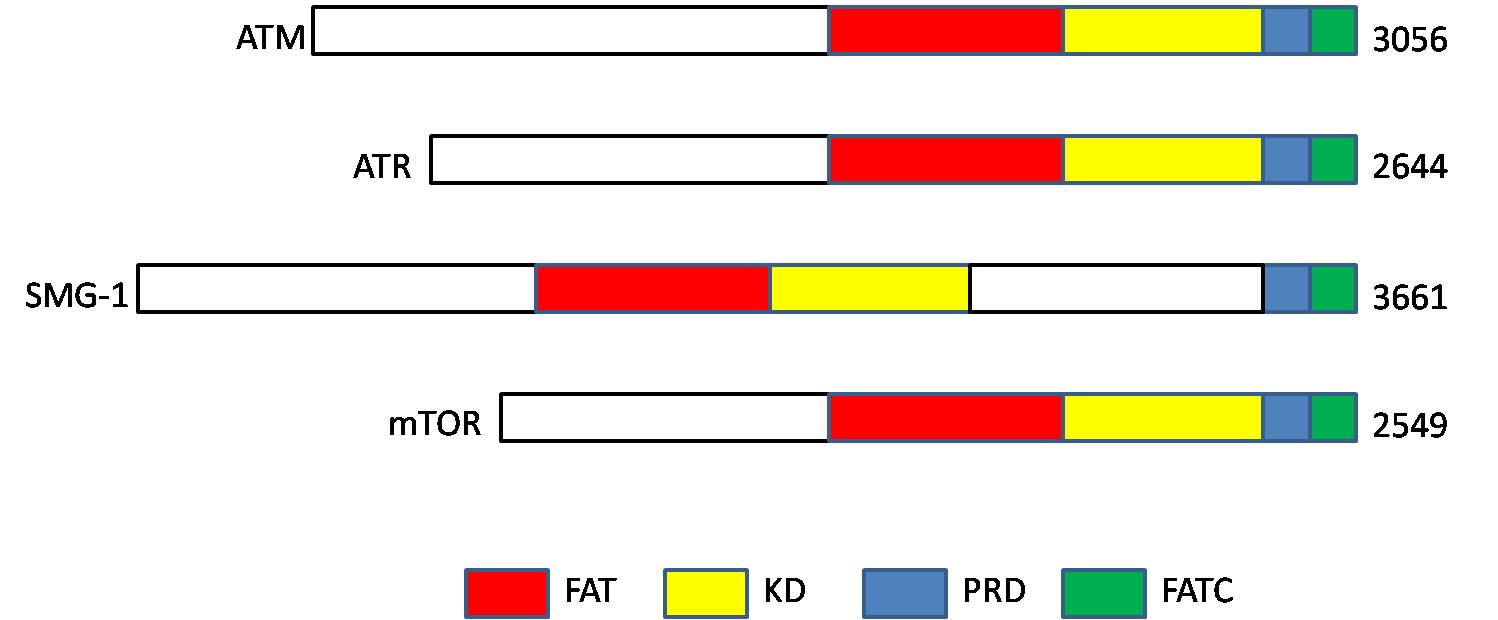
ATM Kinase
ATM serine/threonine kinase or Ataxia-telangiectasia mutated, symbol ATM, is a serine/threonine protein kinase that is recruited and activated by DNA double-strand breaks. It phosphorylates several key proteins that initiate activation of the DNA damage checkpoint, leading to cell cycle arrest, DNA repair or apoptosis. Several of these targets, including p53, CHK2, BRCA1, NBS1 and H2AX are tumor suppressors. In 1995, the gene was discovered by Yosef Shiloh who named its product ATM since he found that its mutations are responsible for the disorder ataxia–telangiectasia. In 1998, the Shiloh and Kastan laboratories independently showed that ATM is a protein kinase whose activity is enhanced by DNA damage. Introduction Throughout the cell cycle DNA is monitored for damage. Damages result from errors during replication, by-products of metabolism, general toxic drugs or ionizing radiation. The cell cycle has different DNA damage checkpoints, which inhibit the next or m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |