|
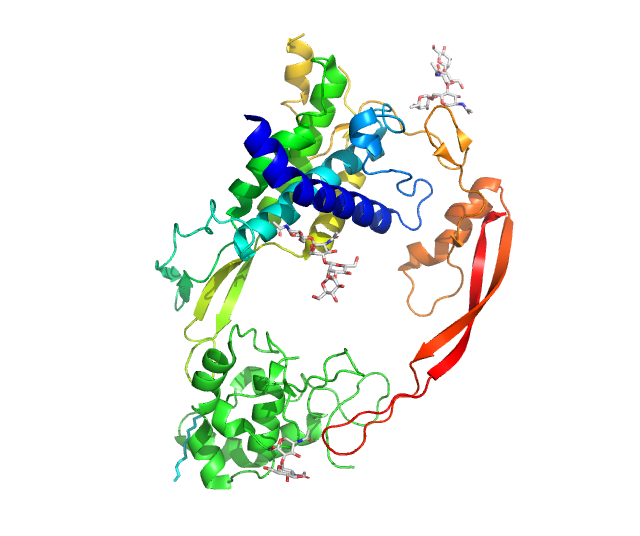
TCF4
Transcription factor 4 (TCF-4) also known as immunoglobulin transcription factor 2 (ITF-2) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TCF4 gene located on chromosome 18q21.2. Function TCF4 proteins act as transcription factors which will bind to the immunoglobulin enhancer mu-E5/kappa-E2 motif. TCF4 activates transcription by binding to the E-box (5’-CANNTG-3’) found usually on SSTR2-INR, or somatostatin receptor 2 initiator element. TCF4 is primarily involved in neurological development of the fetus during pregnancy by initiating neural differentiation by binding to DNA. It is found in the central nervous system, somites, and gonadal ridge during early development. Later in development it will be found in the thyroid, thymus, and kidneys while in adulthood TCF4 it is found in lymphocytes, muscles, mature neurons, and gastrointestinal system. Clinical significance Mutations in TCF4 cause Pitt-Hopkins Syndrome (PTHS). These mutations cause TCF4 proteins to not bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wnt Signaling Pathway
In cellular biology, the Wnt signaling pathways are a group of signal transduction pathways which begin with proteins that pass signals into a cell through cell surface receptors. The name Wnt, pronounced "wint", is a portmanteau created from the names Wingless and Int-1. Wnt signaling pathways use either nearby cell-cell communication (paracrine) or same-cell communication (autocrine). They are highly evolutionarily conserved in animals, which means they are similar across animal species from fruit flies to humans. Three Wnt signaling pathways have been characterized: the canonical Wnt pathway, the noncanonical planar cell polarity pathway, and the noncanonical Wnt/calcium pathway. All three pathways are activated by the binding of a Wnt-protein ligand to a Frizzled family receptor, which passes the biological signal to the Dishevelled protein inside the cell. The canonical Wnt pathway leads to regulation of gene transcription, and is thought to be negatively regulated in part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, Cell signaling, responding to stimuli, providing Cytoskeleton, structure to cells and Fibrous protein, organisms, and Intracellular transport, transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the Nucleic acid sequence, nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific Protein structure, 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called pep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and non-coding genes. During gene expression (the synthesis of Gene product, RNA or protein from a gene), DNA is first transcription (biology), copied into RNA. RNA can be non-coding RNA, directly functional or be the intermediate protein biosynthesis, template for the synthesis of a protein. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring, is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits from one generation to the next. These genes make up different DNA sequences, together called a genotype, that is specific to every given individual, within the gene pool of the population (biology), population of a given species. The genotype, along with environmental and developmental factors, ultimately determines the phenotype ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromosome 18 (human)
Chromosome 18 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 18 spans about 80 million base pairs (the building material of DNA) and represents about 2.5 percent of the total DNA in cells. Genes Number of genes The following are some of the gene count estimates of human chromosome 18. Because researchers use different approaches to genome annotation their predictions of the number of genes on each chromosome varies (for technical details, see gene prediction). Among various projects, the collaborative consensus coding sequence project ( CCDS) takes an extremely conservative strategy. So CCDS's gene number prediction represents a lower bound on the total number of human protein-coding genes. Gene list The following is a partial list of genes on human chromosome 18. For complete list, see the link in the infobox on the right. Diseases and disorders The following diseases are some of those related to genes o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transcription Factor
In molecular biology, a transcription factor (TF) (or sequence-specific DNA-binding factor) is a protein that controls the rate of transcription (genetics), transcription of genetics, genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA, by binding to a specific DNA sequence. The function of TFs is to regulate—turn on and off—genes in order to make sure that they are Gene expression, expressed in the desired Cell (biology), cells at the right time and in the right amount throughout the life of the cell and the organism. Groups of TFs function in a coordinated fashion to direct cell division, cell growth, and cell death throughout life; cell migration and organization (body plan) during embryonic development; and intermittently in response to signals from outside the cell, such as a hormone. There are approximately 1600 TFs in the human genome. Transcription factors are members of the proteome as well as regulome. TFs work alone or with other proteins in a complex, by promoting (a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
E-box
An E-box (enhancer box) is a Response element, DNA response element found in some eukaryotes that acts as a protein-binding site and has been found to regulate gene expression in neurons, muscles, and other tissues. Its specific DNA sequence, CANNTG (where N can be any nucleotide), with a palindromic canonical sequence of CACGTG, is recognized and bound by transcription factors to initiate gene transcription (genetics), transcription. Once the transcription factors bind to the promoters through the E-box, other enzymes can bind to the promoter and facilitate transcription from DNA to mRNA. Discovery The E-box was discovered in a collaboration between Susumu Tonegawa's and Walter Gilbert's laboratories in 1985 as a control element in immunoglobulin heavy-chain enhancer. They found that a region of 140 base pairs in the tissue-specific transcriptional enhancer element was sufficient for different levels of transcription Enhancer (genetics), enhancement in different tissues and sequenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SSTR2
Somatostatin receptor type 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SSTR2'' gene. The SSTR2 gene is located on chromosome 17 on the long arm in position 25.1 in humans. It is also found in most other vertebrates. The somatostatin receptor 2 (SSTR2), which belongs to the G-protein coupled receptor family, is a protein which is most highly expressed in the pancreas (both alpha- and beta-cells), but also in other tissues such as the cerebrum and kidney and in lower amount in the jejunum, colon and liver. In the pancreas, after binding to somatostatin, it inhibits the secretion of peptide hormones from pancreatic islets. During development, it stimulates neuronal migration and axon outgrowth. The somatostatin receptor 2 is expressed in most tumors. Patients with neuroendocrine tumors that over-express the somatostatin receptor 2 have an improved prognosis. The over expression of SSTR2 in tumors can be exploited to selectively deliver radio-peptides to tumors to either de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymphocyte
A lymphocyte is a type of white blood cell (leukocyte) in the immune system of most vertebrates. Lymphocytes include T cells (for cell-mediated and cytotoxic adaptive immunity), B cells (for humoral, antibody-driven adaptive immunity), and innate lymphoid cells (ILCs; "innate T cell-like" cells involved in mucosal immunity and homeostasis), of which natural killer cells are an important subtype (which functions in cell-mediated, cytotoxic innate immunity). They are the main type of cell found in lymph, which prompted the name "lymphocyte" (with ''cyte'' meaning cell). Lymphocytes make up between 18% and 42% of circulating white blood cells. Types The three major types of lymphocyte are T cells, B cells and natural killer (NK) cells. They can also be classified as small lymphocytes and large lymphocytes based on their size and appearance. Lymphocytes can be identified by their large nucleus. T cells and B cells T cells (thymus cells) and B cells ( bone marrow- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transcription Factors
In molecular biology, a transcription factor (TF) (or sequence-specific DNA-binding factor) is a protein that controls the rate of transcription of genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA, by binding to a specific DNA sequence. The function of TFs is to regulate—turn on and off—genes in order to make sure that they are expressed in the desired cells at the right time and in the right amount throughout the life of the cell and the organism. Groups of TFs function in a coordinated fashion to direct cell division, cell growth, and cell death throughout life; cell migration and organization (body plan) during embryonic development; and intermittently in response to signals from outside the cell, such as a hormone. There are approximately 1600 TFs in the human genome. Transcription factors are members of the proteome as well as regulome. TFs work alone or with other proteins in a complex, by promoting (as an activator), or blocking (as a repressor) the recruitment o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |